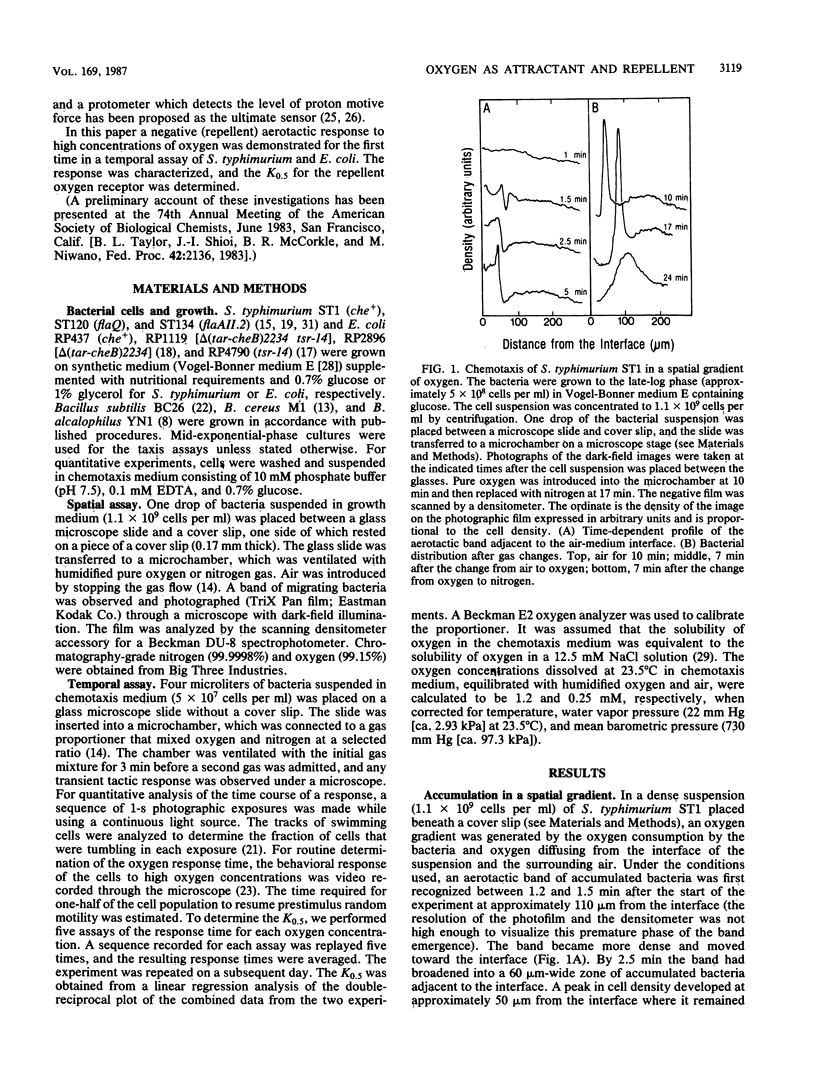
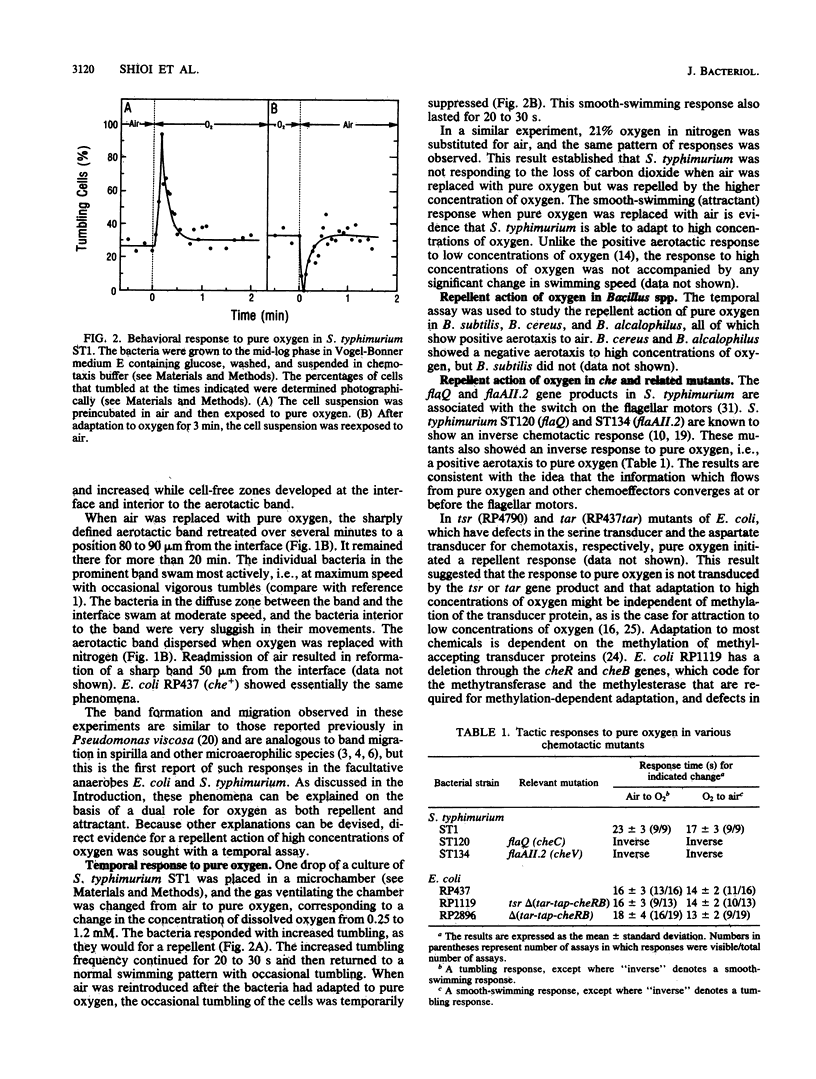
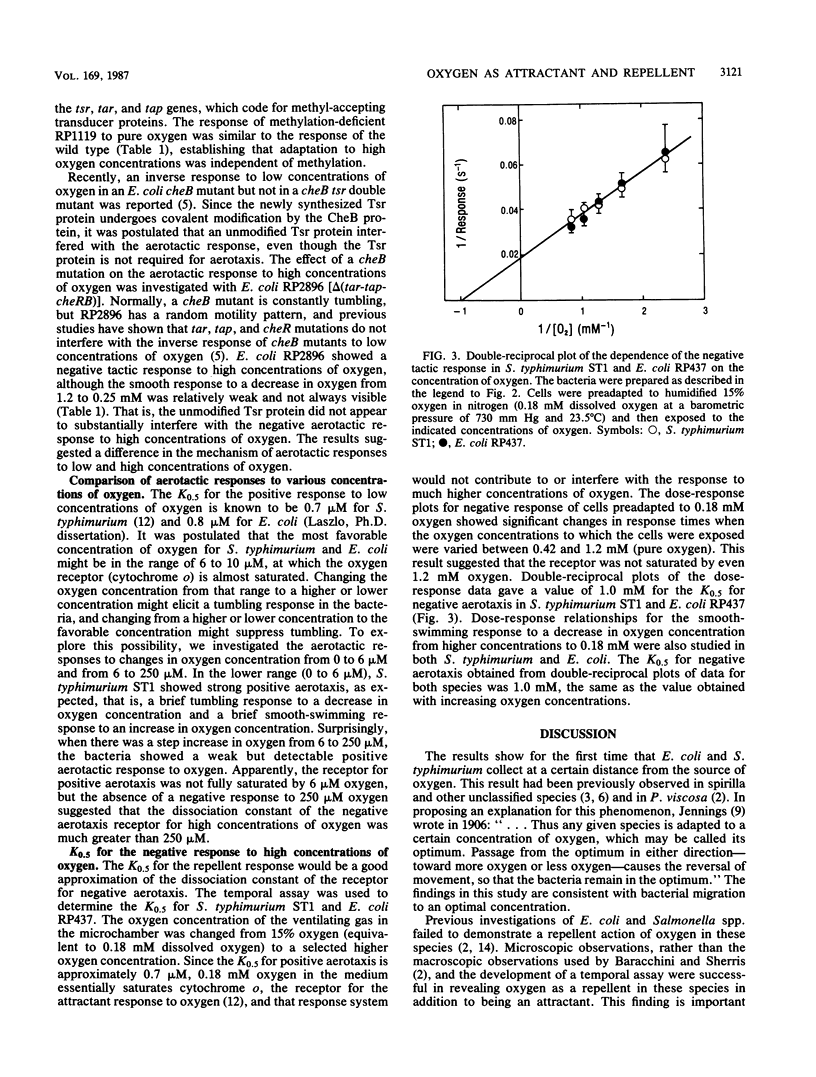
Abstract
Studies of bacterial chemotaxis to oxygen (aerotaxis) over a broad range of oxygen concentrations showed that at high concentrations, oxygen was a repellent of Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli, and some bacilli, whereas it is known that at lower concentrations (less than or equal to 0.25 mM dissolved oxygen), oxygen is an attractant. In a temporal assay of aerotaxis, S. typhimurium in medium equilibrated with air (0.25 mM dissolved oxygen) and then exposed to pure oxygen (1.2 mM) tumbled continuously for approximately 20 s. The oxygen concentration that elicited a half-maximal negative (repellent) response was 1.0 mM for both S. typhimurium and E. coli. The receptor for the negative chemoresponse to high concentrations of oxygen is apparently different from the receptor for the positive chemoresponse to low concentrations of oxygen, since the oxygen concentration that elicits a half-maximal positive (attractant) response in S. typhimurium and E. coli is reported to be 0.7 microM. Adaptation to high concentrations of oxygen, like adaptation to low concentrations of oxygen, was independent of methylation of a transducer protein. Only the response to low oxygen concentrations, however, was altered by interaction with the amidated Tsr transducer in cheB mutants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):708–716. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARACCHINI O., SHERRIS J. C. The chemotactic effect of oxygen on bacteria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(2):565–574. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Niwano M., Ryu J., Taylor B. L. Inversion of aerotactic response in Escherichia coli deficient in cheB protein methylesterase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):275–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.275-280.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M., DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Inversion of a behavioral response in bacterial chemotaxis: explanation at the molecular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4150–4154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo D. J., Fandrich B. L., Sivaram A., Chance B., Taylor B. L. Cytochrome o as a terminal oxidase and receptor for aerotaxis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):663–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.663-667.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo D. J., Niwano M., Goral W. W., Taylor B. L. Bacillus cereus electron transport and proton motive force during aerotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):820–824. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.820-824.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo D. J., Taylor B. L. Aerotaxis in Salmonella typhimurium: role of electron transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):990–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.990-1001.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwano M., Taylor B. L. Novel sensory adaptation mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis to oxygen and phosphotransferase substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Novel mutations affecting a signaling component for chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):953–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.953-961.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubik B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Potentiation, desensitization, and inversion of response in bacterial sensing of chemical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRIS J. C., PRESTON N. W., SHOESMITH J. G. The influence of oxygen and arginine on the motility of a strain of Pseudomonas sp. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):86–96. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J. I., Galloway R. J., Niwano M., Chinnock R. E., Taylor B. L. Requirement of ATP in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7969–7975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J. I., Imae Y., Oosawa F. Protonmotive force and motility of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1083–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1083-1088.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J., Taylor B. L. Oxygen taxis and proton motive force in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10983–10988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L. Role of proton motive force in sensory transduction in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:551–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. S., Krieg N. R. Cultivation of Spirillum volutans in a Bacteria-Free Environment. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):817–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.817-818.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Fujita H., Ishihara A., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):187–193. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.187-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



