Abstract
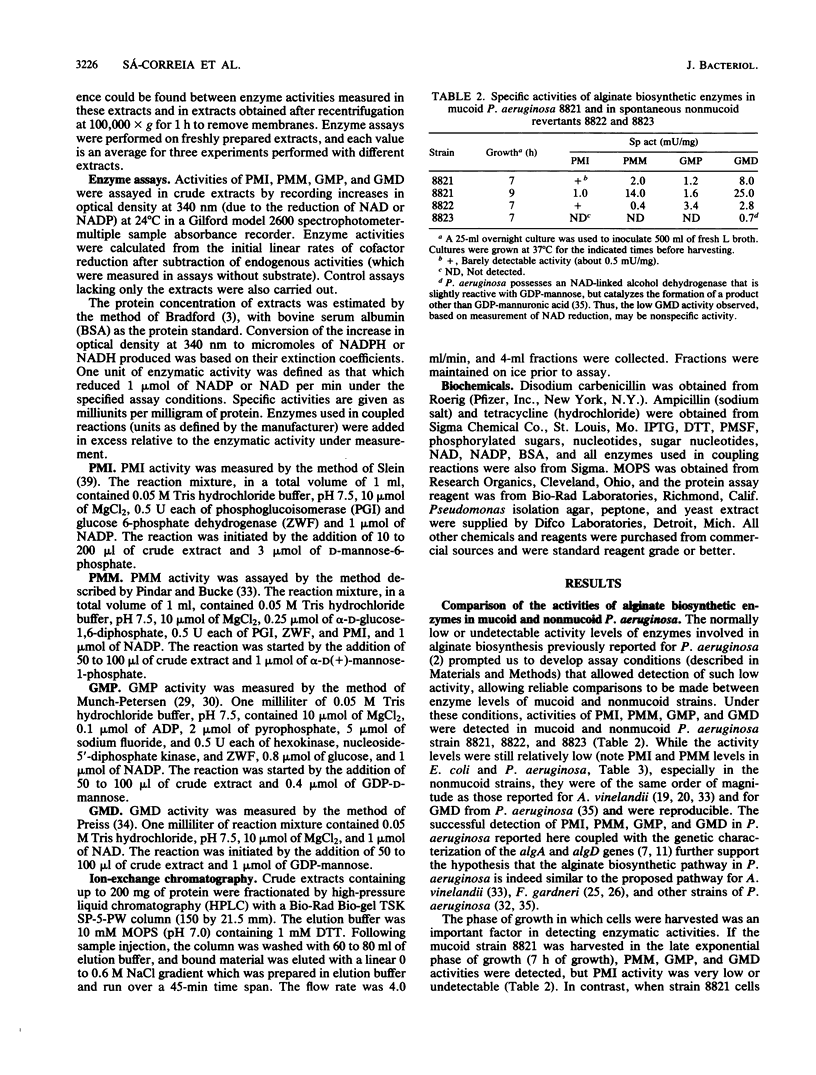
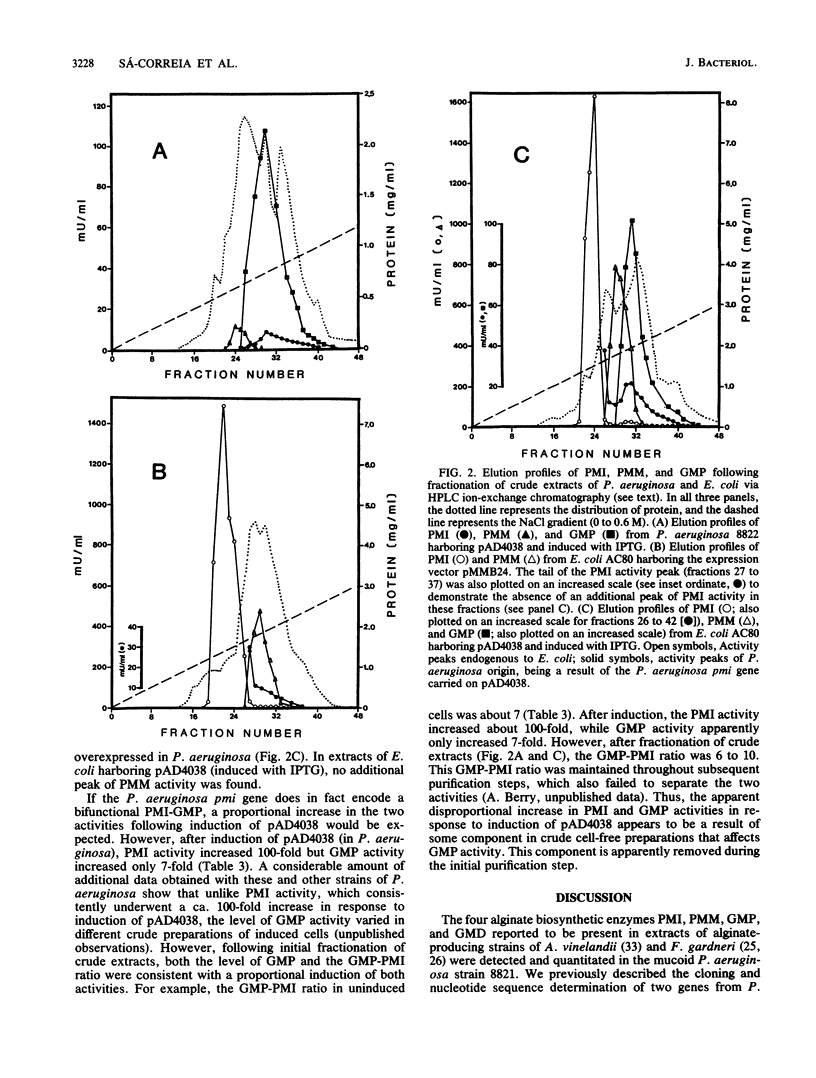
The specific activities of phosphomannose isomerase (PMI), phosphomannomutase (PMM), GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase (GMP), and GDP-mannose dehydrogenase (GMD) were compared in a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and in two spontaneous nonmucoid revertants. In both revertants some or all of the alginate biosynthetic enzymes we examined appeared to be repressed, indicating that the loss of the mucoid phenotype may be a result of decreased formation of sugar-nucleotide precursors. The introduction and overexpression of the cloned P. aeruginosa phosphomannose isomerase (pmi) gene in both mucoid and nonmucoid strains led not only to the appearance of PMI levels in cell extracts several times higher than those present in the wild-type mucoid strain, but also in higher PMM and GMP specific activities. In extracts of both strains, however, the specific activity of GMD did not change as a result of pmi overexpression. In contrast, the introduction of the cloned Escherichia coli manA (pmi) gene in P. aeruginosa caused an increase in only PMI and PMM activities, having no effect on the level of GMP. This suggests that an increase in PMI activity alone does not induce high GMP activity in P. aeruginosa. The heterologous overexpression of the P. aeruginosa pmi gene in the E. coli manA mutant CD1 led to the appearance in cell extracts of not only PMI activity but also GMP activity, both of which are normally undetectable in extracts of CD1. We discuss the implications of these results and propose a mechanism by which overexpression of the P. aeruginosa pmi gene can cause an elevation in both PMM and GMP activities.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee P. C., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M., Maitra P. K. Alginic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants defective in carbohydrate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.238-245.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Frantz B., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the phosphomannose isomerase gene (pmi) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and comparison with the corresponding Escherichia coli gene manA. Gene. 1986;42(3):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Nixon L. L., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa phosphomannose isomerase genes and their expression in alginate-negative mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):249–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.249-257.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Wang S. K., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Clustering of mutations affecting alginic acid biosynthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):516–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.516-524.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene algD coding for GDPmannose dehydrogenase is transcriptionally activated in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.351-358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne W. M., Jr, Buckmire F. L. Partial purification and characterization of a polymannuronic acid depolymerase produced by a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from a patient with cystic fibrosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):562–567. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.562-567.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. F., Deretic V., Chakrabarty A. M. Overproduction and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phosphomannose isomerase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):611–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.611-615.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., McMillan C. The instability of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: fluctuation test and improved stability of the mucoid form in shaken culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jan;110(1):229–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-1-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Nakatsukasa M., Nester E. Regulation of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis 168. Purification, characterization, and subunit structure of the bifunctional enzyme 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate synthetase-chorismate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4467–4472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IACOCCA V. F., SIBINGA M., BARBERO G. J. RESPIRATORY TRACT BACTERIOLOGY IN CYSTIC FIBROSIS. Am J Dis Child. 1963 Sep;106:315–324. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1963.02080050317012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M., Markovitz A. Depression of guanosine diphosphate-mannose pyrophosphorylase by mutations in two different regulator genes involved in capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.965-972.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M., Shaparis A., Markovitz A. Control of uridine diphosphate-glucose dehydrogenase synthesis and uridine diphosphate-glucuronic acid accumulation by a regulator gene mutation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):959–964. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.959-964.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. Y., Hassid W. Z. Isolation of guanosine diphosphate uronic acids from a marine brown alga, Fucus gardneri Silva. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3283–3293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz A., Lieberman M. M., Rosenbaum N. Derepression of phosphomannose isomerase by regulator gene mutations involved in capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1497–1501. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1497-1501.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian F. A., Jarman T. R., Righelato R. C. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norval M., Sutherland I. W. The production of enzymes involved in exopolysaccharide synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes types 1 and 8. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):209–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREISS J. SUGAR NUCLEOTIDE REACTIONS IN ARTHROBACTER. II. BIOSYNTHESIS OF GUANOSINE DIPHOSPHOMANNURONATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3127–3132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindar D. F., Bucke C. The biosynthesis of alginic acid by Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):617–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1520617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugashetti B. K., Vadas L., Prihar H. S., Feingold D. S. GDPmannose dehydrogenase and biosynthesis of alginate-like polysaccharide in a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1107–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1107-1110.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherbrock-Cox V., Russell N. J., Gacesa P. The purification and chemical characterisation of the alginate present in extracellular material produced by mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Carbohydr Res. 1984 Dec 15;135(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Wimpenny J. W. Extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis by Pseudomonas NCIB 11264. Studies on precursor-forming enzymes and factors affecting exopolysaccharide production by washed suspensions. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jan;116(1):133–141. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


