Abstract
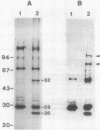
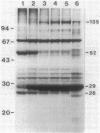
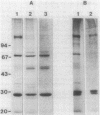
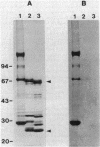
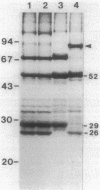
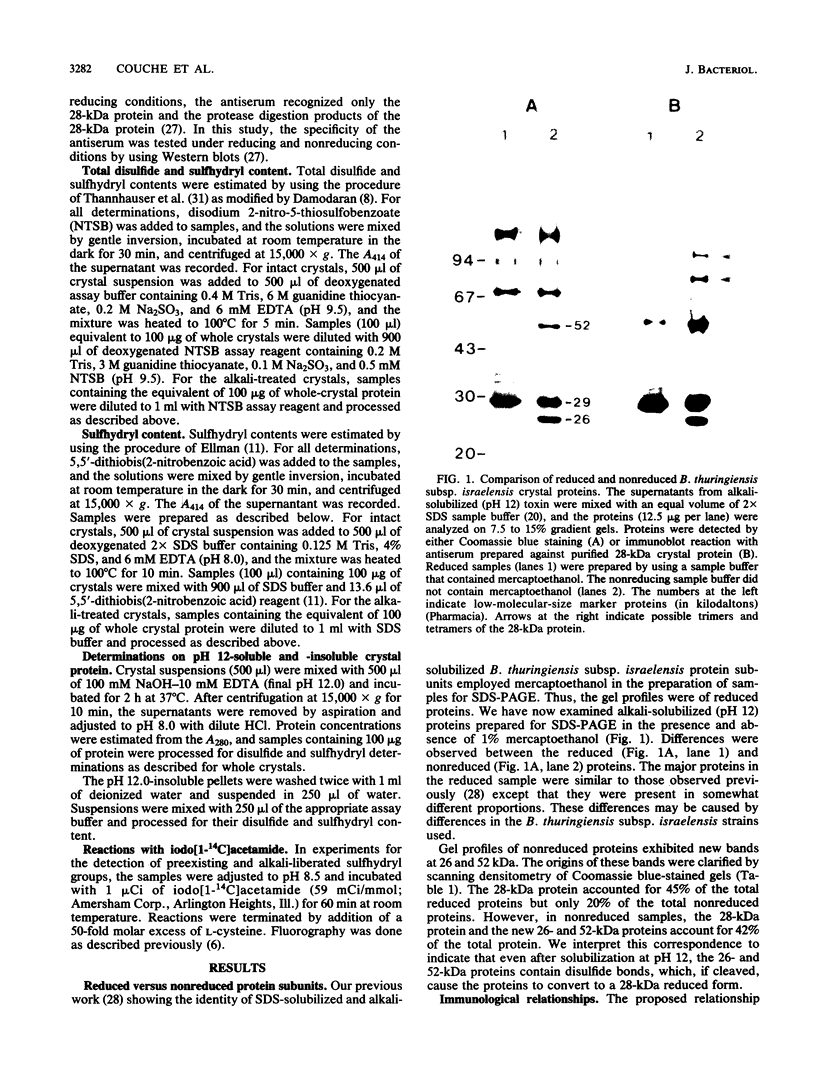
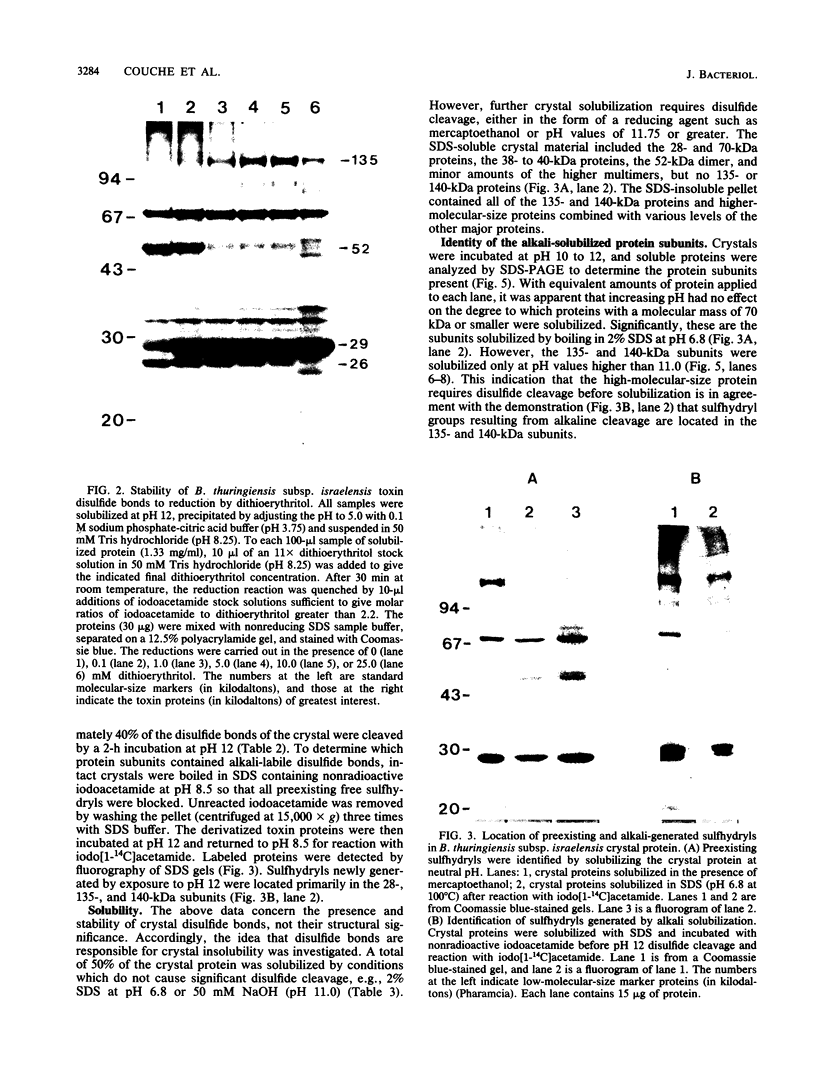
We examined disulfide bonds in mosquito larvicidal crystals produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Intact crystals contained 2.01 X 10(-8) mol of free sulfhydryls and 3.24 X 10(-8) mol of disulfides per mg of protein. Reduced samples of alkali-solubilized crystals resolved into several proteins, the most prominent having apparent molecular sizes of 28, 70, 135, and 140 kilodaltons (kDa). Nonreduced samples contained two new proteins of 52 and 26 kDa. When reduced, both the 52- and 26-kDa proteins were converted to 28-kDa proteins. Furthermore, both bands reacted with antiserum prepared against reduced 28-kDa protein. Approximately 50% of the crystal proteins could be solubilized without disulfide cleavage. These proteins were 70 kDa or smaller. Solubilization of the 135- and 140-kDa proteins required disulfide cleavage. Incubation of crystals at pH 12.0 for 2 h cleaved 40% of the disulfide bonds and solubilized 83% of the crystal protein. Alkali-stable disulfides were present in both the soluble and insoluble portions. The insoluble pellet contained 12 to 14 disulfides per 100 kDa of protein and was devoid of sulfhydryl groups. Alkali-solubilized proteins contained both intrachain and interchain disulfide bonds. Despite their structural significance, it is unlikely that disulfide bonds are involved in the formation or release of the larvicidal toxin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. E., Jr, Bibilos M. M., Bulla L. A., Jr Protease activation of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.737-742.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. L., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. Delta endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.39-46.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Unterman B. M., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Abbene S. J., Bowditch R. D. Purification of the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus and evidence for high-molecular-weight precursors. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):738–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.738-747.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Kramer K. J., Davidson L. I. Characterization of the entomocidal parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):375–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.375-383.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese D. M., Nickerson K. W., Lane L. C. A comparison of protein crystal subunit sizes in Bacillus thuringiensis. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Aug;26(8):1006–1010. doi: 10.1139/m80-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadd R. H. Alkalinity within the midgut of mosquito larvae with alkaline-active digestive enzymes. J Insect Physiol. 1975 Nov;21(11):1847–1853. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(75)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damodaran S. Estimation of disulfide bonds using 2-nitro-5-thiosulfobenzoic acid: limitations. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;145(1):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastidar P. G., Nickerson K. W. Interchain crosslinks in the entomocidal Bacillus thuringiensis protein crystal. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80575-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W., White T. M. Alkaline hydrolysis of the disulfide bonds of ovomucoid and of low molecular weight aliphatic and aromatic disulfides. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 5;10(1):32–38. doi: 10.1021/bi00777a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. M., Lee S. G., Andrews R. E., Jr, Klowden M. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Separation of the cytolytic and mosquitocidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):961–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra J. E., Federici B. A. Isolation of a relatively nontoxic 65-kilodalton protein inclusion from the parasporal body of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.527-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insell J. P., Fitz-James P. C. Composition and Toxicity of the Inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.56-62.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane L. C. A simple method for stabilizing protein-sulfhydryl groups during SDS-gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;86(2):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90792-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. G., Eckblad W., Bulla L. A., Jr Diversity of protein inclusion bodies and identification of mosquitocidal protein in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):953–960. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Muthukumar G., Nickerson K. W. Stability of the larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: amino acid modification and denaturants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1196–1199. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1196-1199.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Ross E. J., Nickerson K. W. Immunological relationships among proteins making up the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis crystalline toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):644–649. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.644-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schesser J. H., Kramer K. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Bioassay for homogeneous parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis using the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):878–880. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.878-880.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Pfannenstiel M. A., Nickerson K. W. Bioassay of solubilized Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis crystals by attachment to latex beads. Science. 1984 Mar 16;223(4641):1191–1193. doi: 10.1126/science.6701520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thannhauser T. W., Konishi Y., Scheraga H. A. Sensitive quantitative analysis of disulfide bonds in polypeptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90786-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1983 Mar;60:181–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.60.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrell D. J., Bulla L. A., Jr, Andrews R. E., Jr, Kramer K. J., Davidson L. I., Nordin P. Comparative biochemistry of entomocidal parasporal crystals of selected Bacillus thuringiensis strains. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1052-1062.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Dullemans A. M., van Workum M. E., Visser B. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of the Mr 28 000 crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8207–8217. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]