Abstract
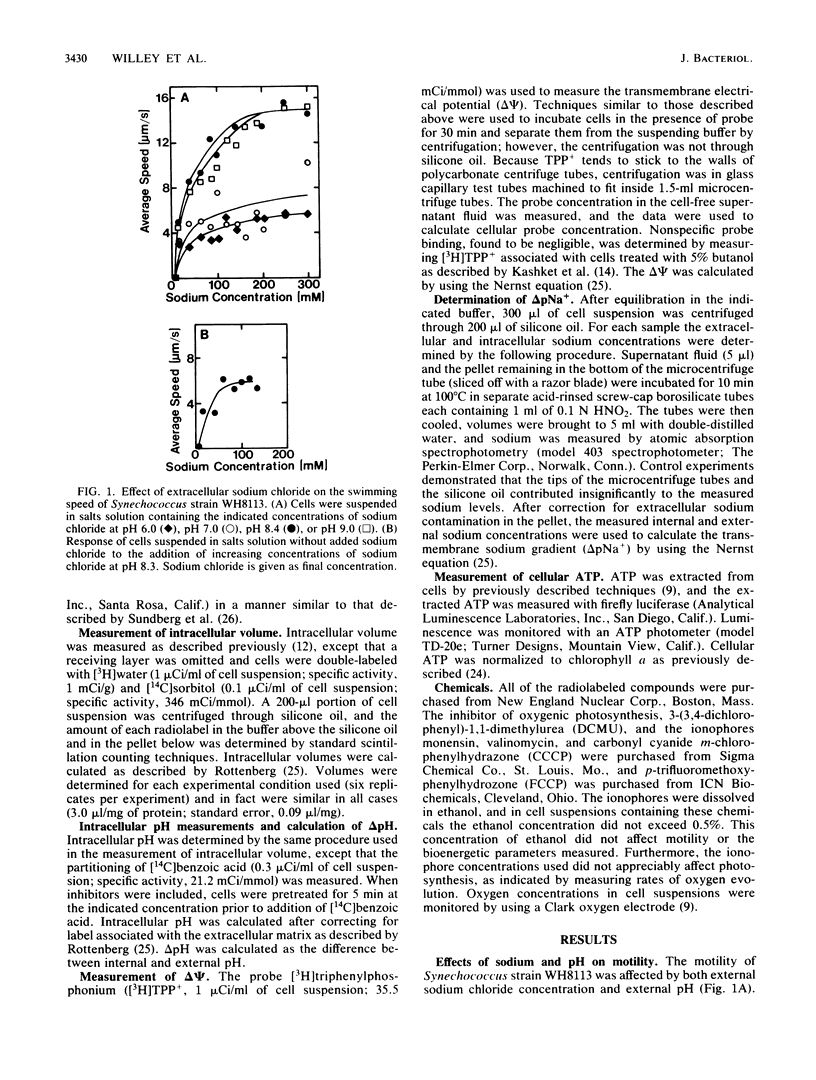
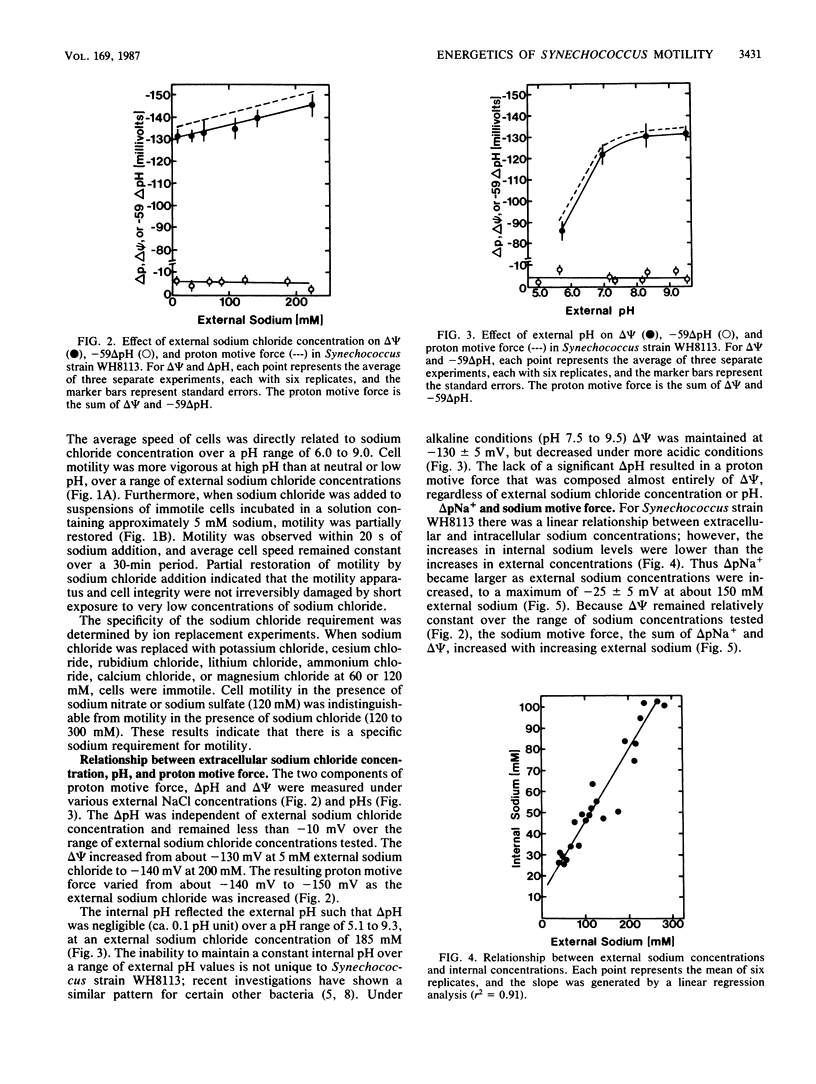
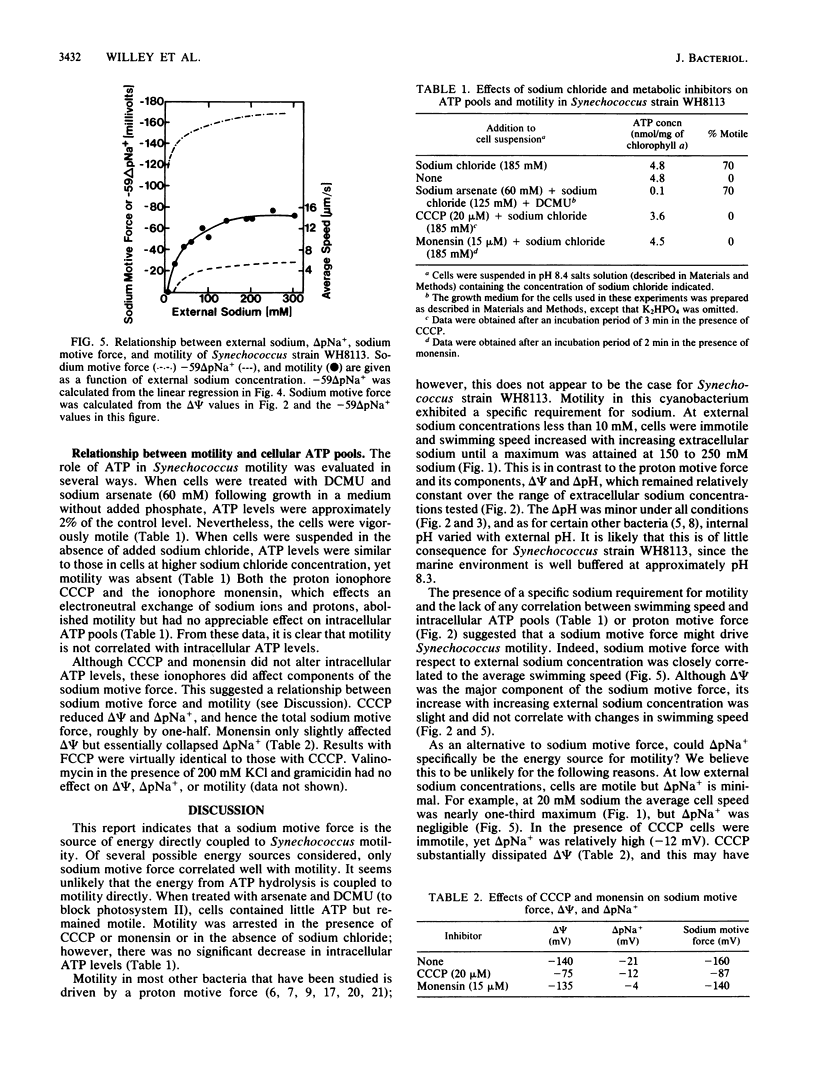
The energetics of motility in Synechococcus strain WH8113 were studied to understand the unique nonflagellar swimming of this cyanobacterium. There was a specific sodium requirement for motility such that cells were immotile below 10 mM external sodium and cell speed increased with increasing sodium levels above 10 mM to a maximum of about 15 microns/s at 150 to 250 mM sodium. The sodium motive force increased similarly with increasing external sodium from -120 to -165 mV, but other energetic parameters including proton motive force, electrical potential, the proton diffusion gradient, and the sodium diffusion gradient did not show such a correlation. Over a range of external sodium concentrations, cell speed was greater in alkaline environments than in neutral or acidic environments. Monensin and carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone inhibited motility and affected components of sodium motive force but did not affect ATP levels. Cells were motile when incubated with 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea and arsenate, which decreased cellular ATP to about 2% of control values. The results of this investigation are consistent with the conclusion that the direct source of energy for Synechococcus motility is a sodium motive force and that below a threshold of about -100 mV, cells are immotile.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block S. M., Berg H. C. Successive incorporation of force-generating units in the bacterial rotary motor. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):470–472. doi: 10.1038/309470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. E., Pate J. L., Betzig R. J. Isolation and characterization of nonspreading mutants of the gliding bacterium Cytophaga johnsonae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):26–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.26-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibrov P. A., Kostryko V. A., Lazarova R. L., Skulachev V. P., Smirnova I. A. The sodium cycle. I. Na+-dependent motility and modes of membrane energization in the marine alkalotolerant vibrio Alginolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 23;850(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibrov P. A., Lazarova R. L., Skulachev V. P., Verkhovskaya M. L. The sodium cycle. II. Na+-coupled oxidative phosphorylation in Vibrio alginolyticus cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 23;850(3):458–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glagolev A. N., Skulachev V. P. The proton pump is a molecular engine of motile bacteria. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):280–282. doi: 10.1038/272280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Kashket E. R. H+/ATP stoichiometry of cowpea Rhizobium sp. strain 32H1 cells grown under nitrogen-fixing and nitrogen-nonfixing conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.216-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne E. A., Jr, Greenberg E. P. Relationship between proton motive force and motility in Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1450–1457. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1450-1457.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Imae Y. Na+-driven flagellar motors of an alkalophilic Bacillus strain YN-1. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10577–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1210-1214.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Blanchard A. G., Metzger W. C. Proton motive force during growth of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.128-134.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller K. H., Grady M., Dworkin M. Surface tension gradients: feasible model for gliding motility of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1358–1366. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1358-1366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus I. R., Berg H. C. Gliding motility of Cytophaga sp. strain U67. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):384–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.384-398.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: the molecular biology of a behavioral system. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978;5(4):291–341. doi: 10.3109/10409237809177145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P. M., Berg H. C. Energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):541–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Sensory electrophysiology of bacteria: relationship of the membrane potential to motility and chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4752–4756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong L. J., Glazer A. N., Waterbury J. B. An unusual phycoerythrin from a marine cyanobacterium. Science. 1984 Apr 6;224(4644):80–83. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4644.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Selection and properties of phototaxis-deficient mutants of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):282–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.282-287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterbury J. B., Willey J. M., Franks D. G., Valois F. W., Watson S. W. A cyanobacterium capable of swimming motility. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):74–76. doi: 10.1126/science.230.4721.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



