Abstract
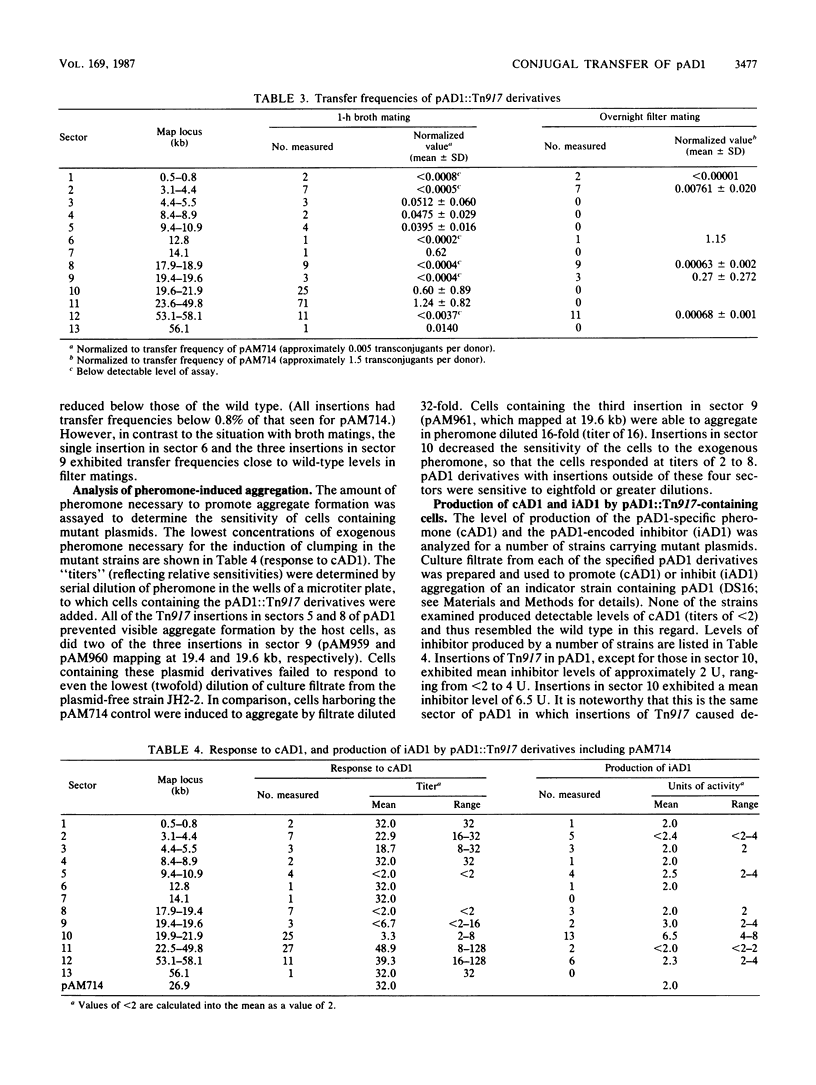
The conjugative plasmid pAD1 (59.6 kilobases) of Streptococcus faecalis shows a 10,000-fold increase in transfer frequency following induction by the sex pheromone cAD1. Mutagenesis of the plasmid with transposon Tn917 was undertaken to determine the region(s) of pAD1 required for the mating response. The relevant genetic material was found to be distributed over a 31.2-kilobase contiguous region of the plasmid. Although insertions in two previously identified regions (traA and traB) exhibited increased transfer frequencies, insertions in five new regions (D, E, F, G, and H) decreased the ability of pAD1 to transfer. Insertions in region H allowed the cells to form visible mating aggregates, but the plasmid transfer frequency was decreased to levels below detection during a 1-h broth mating. Mutants with mutations in region G were able to form aggregates; however, insertions in regions D, E, and F prevented aggregate formation. Insertions in region C decreased the sensitivity of the cell to exogenous cAD1 and exhibited increased activity of the pheromone inhibitor iAD1. Surface protein profiles produced by a number of these mutants were examined, and in some cases were found to be different from those of the wild type. A map showing the various regions is presented, and related aspects of the regulation of the pAD1 mating response are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christie P. J., Dunny G. M. Identification of regions of the Streptococcus faecalis plasmid pCF-10 that encode antibiotic resistance and pheromone response functions. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):230–241. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Brown B. L. Sex pheromone cAD1 in Streptococcus faecalis: induction of a function related to plasmid transfer. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1063–1065. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1063-1065.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Tomich P. K., Gawron-Burke M. C., Franke A. E., Yagi Y., An F. Y. Mapping of Streptococcus faecalis plasmids pAD1 and pAD2 and studies relating to transposition of Tn917. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1220–1230. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1220-1230.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Brown B. L., Clewell D. B. Induced cell aggregation and mating in Streptococcus faecalis: evidence for a bacterial sex pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Craig R. A., Carron R. L., Clewell D. B. Plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis: production of multiple sex pheromones by recipients. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Zimmerman D. L., Tortorello M. L. Induction of surface exclusion (entry exclusion) by Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromones: use of monoclonal antibodies to identify an inducible surface antigen involved in the exclusion process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8582–8586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. E., Kessler R. E., Clewell D. B. Identification of pheromone-induced surface proteins in Streptococcus faecalis and evidence of a role for lipoteichoic acid in formation of mating aggregates. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.6-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ike Y., Clewell D. B. Genetic analysis of the pAD1 pheromone response in Streptococcus faecalis, using transposon Tn917 as an insertional mutagen. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):777–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.777-783.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ike Y., Craig R. A., White B. A., Yagi Y., Clewell D. B. Modification of Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromones after acquisition of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5369–5373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ike Y., Hashimoto H., Clewell D. B. Hemolysin of Streptococcus faecalis subspecies zymogenes contributes to virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):528–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.528-530.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. E., Hobbs S. J. Conjugal transfer of plasmid-borne multiple antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):360–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.360-372.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Yagi Y. Identification and partial characterization of a pheromone-induced adhesive surface antigen of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.714-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSAN B., WILLIAMS N. B. HYALURONIDASE PRODUCTION BY ORAL ENTEROCOCCI. Arch Oral Biol. 1964 May-Jun;9:291–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(64)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. H., Clewell D. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B-resistance transposon Tn917 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):782–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.782-796.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Mori M., Sakagami Y., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Craig R. A., Clewell D. B. Isolation and structure of bacterial sex pheromone, cPD1. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.6436978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Properties of erythromycin-inducible transposon Tn917 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1366-1374.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Damle S. P., Clewell D. B. Plasmid-related transmissibility and multiple drug resistance in Streptococcus faecalis subsp. zymogenes strain DS16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):828–830. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortorello M. L., Dunny G. M. Identification of multiple cell surface antigens associated with the sex pheromone response of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):131–137. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.131-137.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Skurray R. The conjugation system of F-like plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:41–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth R., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Highly efficient protoplast transformation system for Streptococcus faecalis and a new Escherichia coli-S. faecalis shuttle vector. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.831-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., Kessler R. E., Shaw J. H., Lopatin D. E., An F., Clewell D. B. Plasmid content of Streptococcus faecalis strain 39-5 and identification of a pheromone (cPD1)-induced surface antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):1207–1215. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]