Abstract
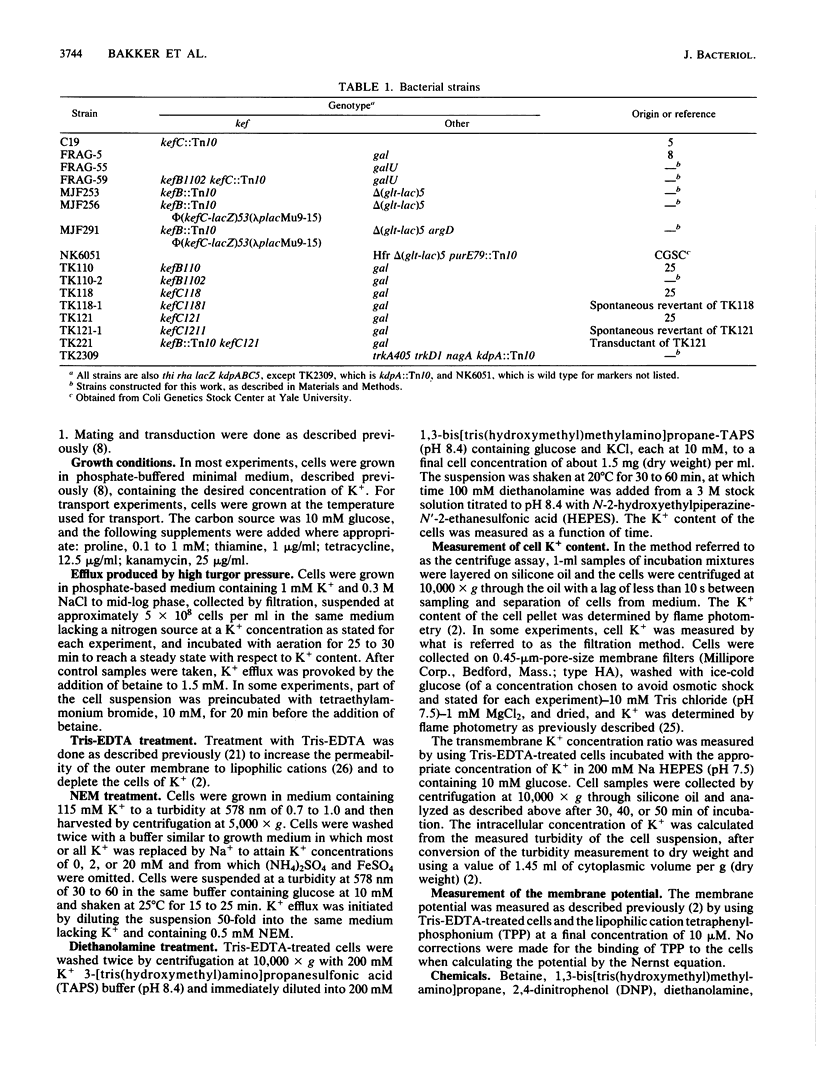
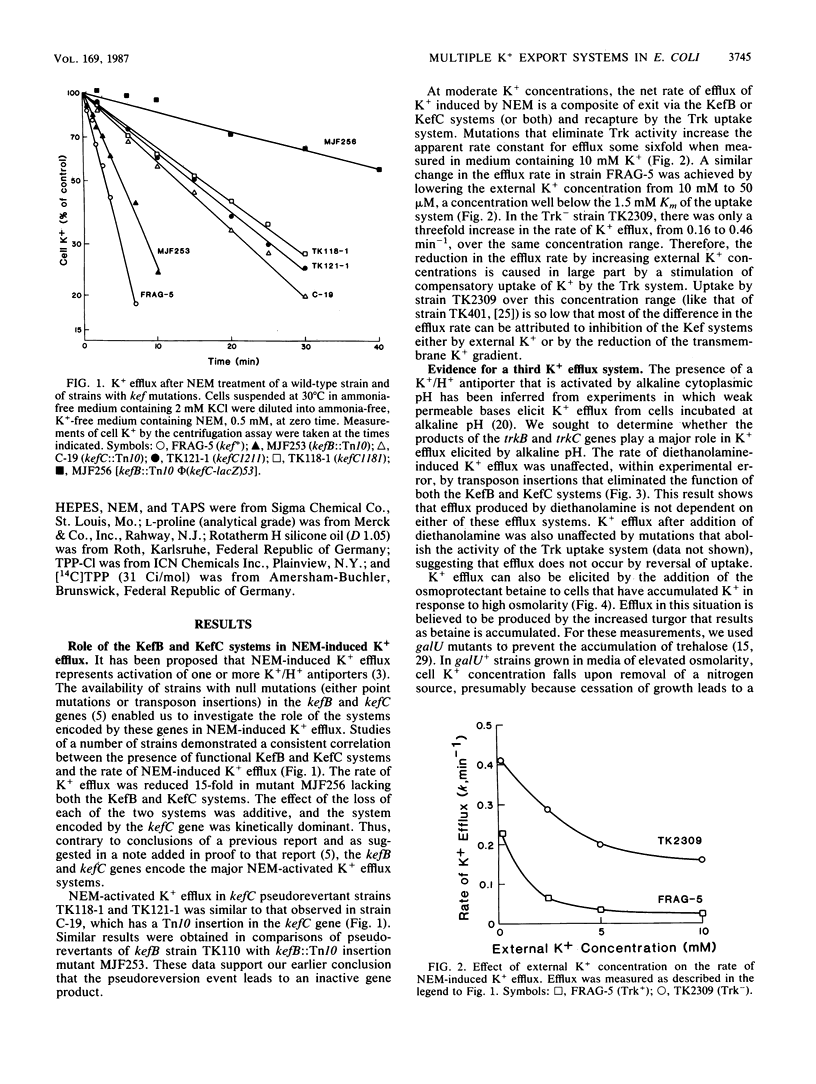
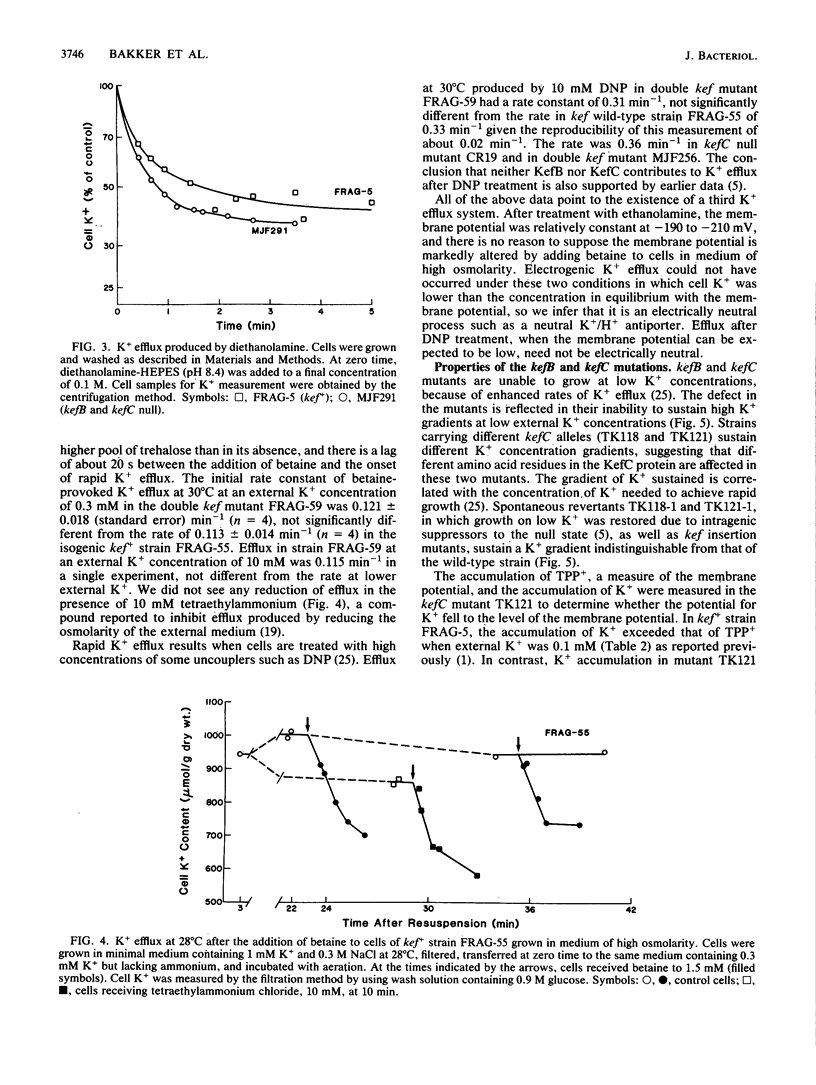
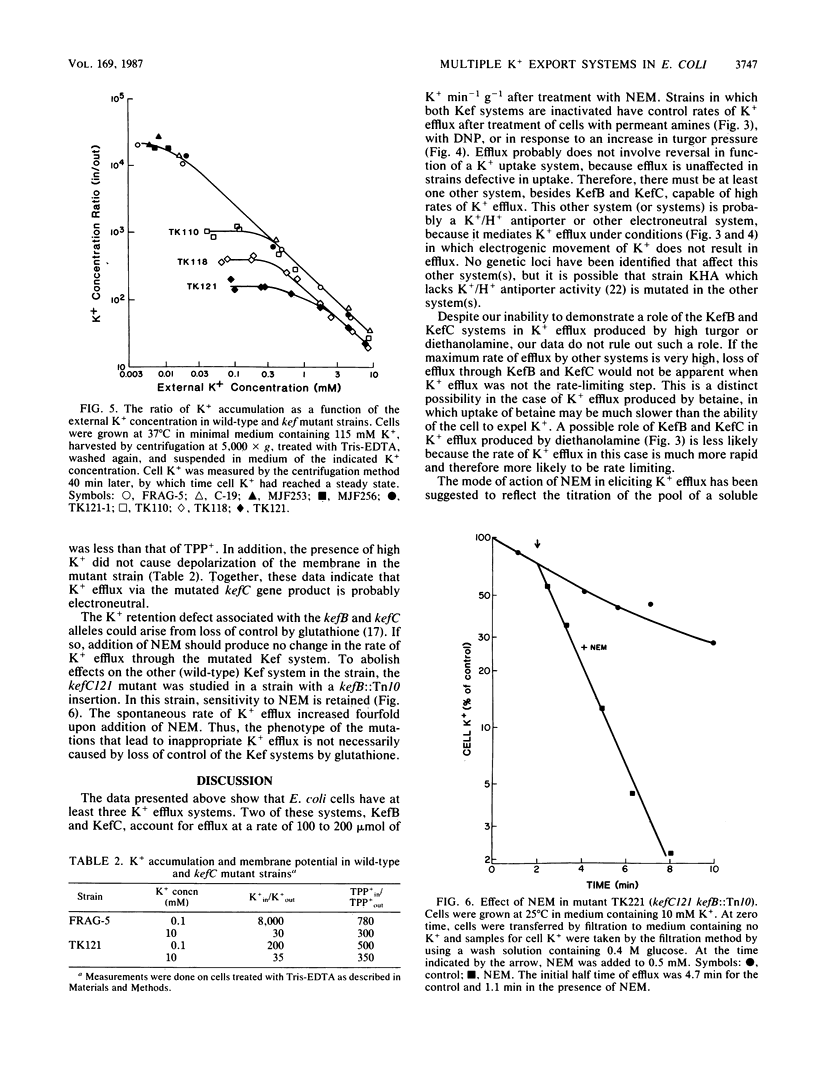
The role of the K+ transport systems encoded by the kefB (formerly trkB) and kefC (formerly trkC) genes of Escherichia coli in K+ efflux has been investigated. The rate of efflux produced by N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), increased turgor pressure, alkalinization of the cytoplasm, or 2,4-dinitrophenol in a mutant with null mutations in both kef genes was compared with the rate of efflux in a wild-type strain for kef. The results show that these two genes encode the major paths for NEM-stimulated efflux. However, neither efflux system appears to be a significant path of K+ efflux produced by high turgor pressure, by alkalinization of the cytoplasm, or by addition of high concentrations of 2,4-dinitrophenol. Therefore, this species must have at least one other system, besides those encoded by kefB and kefC, capable of mediating a high rate of K+ efflux. The high, spontaneous rate of K+ efflux characteristic of the kefC121 mutation increases further when the strain is treated with NEM. Therefore, the mutational defect that leads to spontaneous efflux in this strain does not abolish the site(s) responsible for the action of NEM.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. N-ethylmaleimide induces K+ -H+ antiport activity in Escherichia coli K-12. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80888-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Epstein W., Giffard P. M., Rowland G. C. Roles of the trkB and trkC gene products of Escherichia coli in K+ transport. Biochimie. 1985 Jan;67(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer E., Silhavy T. J., Weinstock G. M. Transposable lambda placMu bacteriophages for creating lacZ operon fusions and kanamycin resistance insertions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1092–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1092-1099.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Schultz S. G. Cation Transport in Escherichia coli: V. Regulation of cation content. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Nov 1;49(2):221–234. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itikawa H., Baumberg S., Vogel H. J. Enzymic basis for a genetic suppression: accumulation and deacylation of N-acetylglutamic gamma-semialdehyde in enterobacterial mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 9;159(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Osmotic control of kdp operon expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):464–468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. I., Sydnes L. K., Landfald B., Strøm A. R. Osmoregulation in Escherichia coli by accumulation of organic osmolytes: betaines, glutamic acid, and trehalose. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Feb;147(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00492896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Kepes A. Glutathione and the gated potassium channels of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):339–343. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Kepes A. The regulation of potassium fluxes for the adjustment and maintenance of potassium levels in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):165–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Lebail S., Kepes A. Opening of potassium channels in Escherichia coli membranes by thiol reagents and recovery of potassium tightness. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;113(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Robin A., Monnier-Champeix P. Turgor-controlled K+ fluxes and their pathways in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):613–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plack R. H., Jr, Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Absence of potassium/proton antiporter activity in a pH-sensitive mutant. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3824–3825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. IX. Regulation of K transport. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):283–295. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Wilson T. H. Galactoside transport dissociated from proton movement in mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90875-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



