Abstract
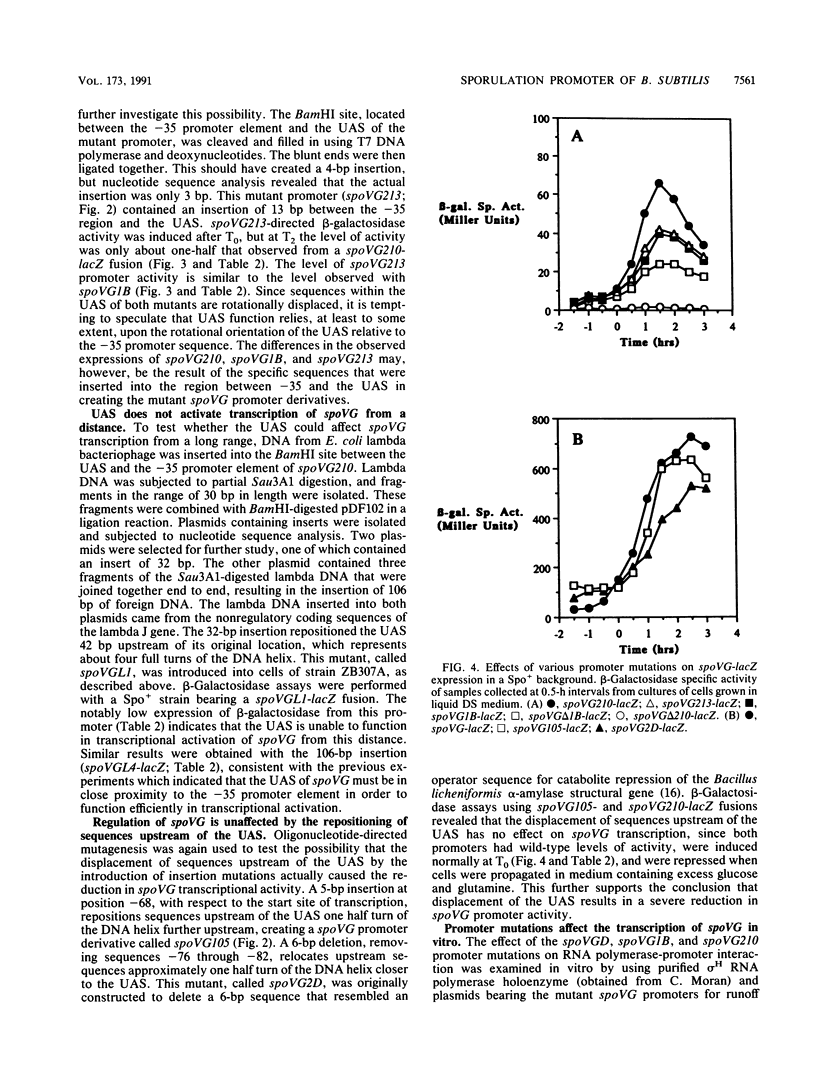
The transcription from the spoVG promoter of Bacillus subtilis is induced at the start of the stationary phase of growth and is dependent on the expression of the spoOA, spoOB, and spoOH genes. It is repressed in cells grown in the presence of excess glucose and glutamine and is under the negative control of the abrB gene. The spoOA and spoOB gene products function to suppress the negative control exerted by abrB. Transcription initiation requires the form of RNA polymerase holoenzyme that contains the spoOH gene product, sigma H. Optimal transcription also requires an upstream A-T-rich region termed the upstream activating sequence (UAS). The mechanism of UAS function was examined through mutational analysis of the spoVG promoter region. Deletion of the UAS or positioning the UAS one half turn or one full turn of the DNA helix upstream of its location in wild-type spoVG resulted in a severe reduction in promoter activity. Deletion of most of the UAS abolished the abrB-dependent repression of spoVG transcription. Higher activity was observed when the UAS was inserted 10 bp (one turn of the helix) upstream than when the sequence was repositioned either 5 or 13 bp upstream. Sequences upstream of the UAS were found not to be involved with the position-dependent function of the UAS. Positioning the UAS 42 or 116 bp upstream eliminated the stimulatory effect of the sequence on spoVG transcription. These data indicate that the UAS functions effectively when it is in close proximity to the -35 region. In vitro transcription analysis indicated that the deletion and insertion mutation affecting the UAS impair RNA polymerase-spoVG promoter interaction. Deletion of the UAS showed that the negative effect of exogenous glucose and glutamine is not dependent on the UAS but is exerted at a site within or near the -35 and -10 regions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S. Multipartite genetic control elements: communication by DNA loop. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:227–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai U., Lewandoski M., Dubnau E., Smith I. Temporal regulation of the Bacillus subtilis early sporulation gene spo0F. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5432–5439. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5432-5439.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner C. D., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Deletion analysis of a complex promoter for a developmentally regulated gene from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. L., 3rd, Moran C. P., Jr New RNA polymerase sigma factor under spo0 control in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9438–9442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D., Zuber P., Losick R. Two amino acids in an RNA polymerase sigma factor involved in the recognition of adjacent base pairs in the -10 region of a cognate promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Weir J., Nair G., Carter L., 3rd, Moran C., Jr, Smith I. Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for sigma 30 (sigma H). J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1054-1062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Sonenshein A. L. A target for carbon source-dependent negative regulation of the citB promoter of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):835–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.835-844.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürbass R., Gocht M., Zuber P., Marahiel M. A. Interaction of AbrB, a transcriptional regulator from Bacillus subtilis with the promoters of the transition state-activated genes tycA and spoVG. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Mar;225(3):347–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00261673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Henkin T. M. The rpsD gene, encoding ribosomal protein S4, is autogenously regulated in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4595–4602. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4595-4602.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J., Weir J., Smith I., Losick R. Post-transcriptional control of a sporulation regulatory gene encoding transcription factor sigma H in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):477–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laoide B. M., Chambliss G. H., McConnell D. J. Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase gene, amyL, is subject to promoter-independent catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2435–2442. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2435-2442.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirmo S., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. I. Kinetic analysis of the roles of the upstream activator region and supercoiling on transcription of the rrnB P1 promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):555–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Kleckner N. Mismatch repair mutations of Escherichia coli K12 enhance transposon excision. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):3–19. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. F., Achberger E. C. Rotational orientation of upstream curved DNA affects promoter function in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10451–10456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachaliel N., Melnick J., Gafny R., Glaser G. Ribosome associated protein(s) specifically bind(s) to the upstream activator sequence of the E. coli rrnA P1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9811–9822. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Marahiel M. A., Zuber P. Identification of a genetic locus required for biosynthesis of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5662–5668. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5662-5668.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands J. T., Ross W., Gosink K. K., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. II. characterization of complexes of rrnB P1 promoters containing or lacking the upstream activator region with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):569–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90101-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollington J. F., Haldenwang W. G., Huynh T. V., Losick R. Developmentally regulated transcription in a cloned segment of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):432–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.432-442.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price V. A., Feavers I. M., Moir A. Role of sigma H in expression of the fumarase gene (citG) in vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5933–5939. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5933-5939.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. B., Gocht M., Marahiel M. A., Zuber P. AbrB, a regulator of gene expression in Bacillus, interacts with the transcription initiation regions of a sporulation gene and an antibiotic biosynthesis gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8457–8461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Spiegelman G. B., Perego M., Johnson W. C., Burbulys D., Hoch J. A. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1615–1621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Carter H. L., 3rd, Moir A., Moran C. P., Jr Sigma H-directed transcription of citG in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5928–5932. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5928-5932.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Nilsson L., Bosch L. The elongation factor EF-Tu from E. coli binds to the upstream activator region of the tRNA-tufB operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10183–10197. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Healy J., Carter H. L., 3rd, Cutting S., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Mutation changing the specificity of an RNA polymerase sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Role of AbrB in Spo0A- and Spo0B-dependent utilization of a sporulation promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2223–2230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2223-2230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Use of a lacZ fusion to study the role of the spoO genes of Bacillus subtilis in developmental regulation. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




