Abstract
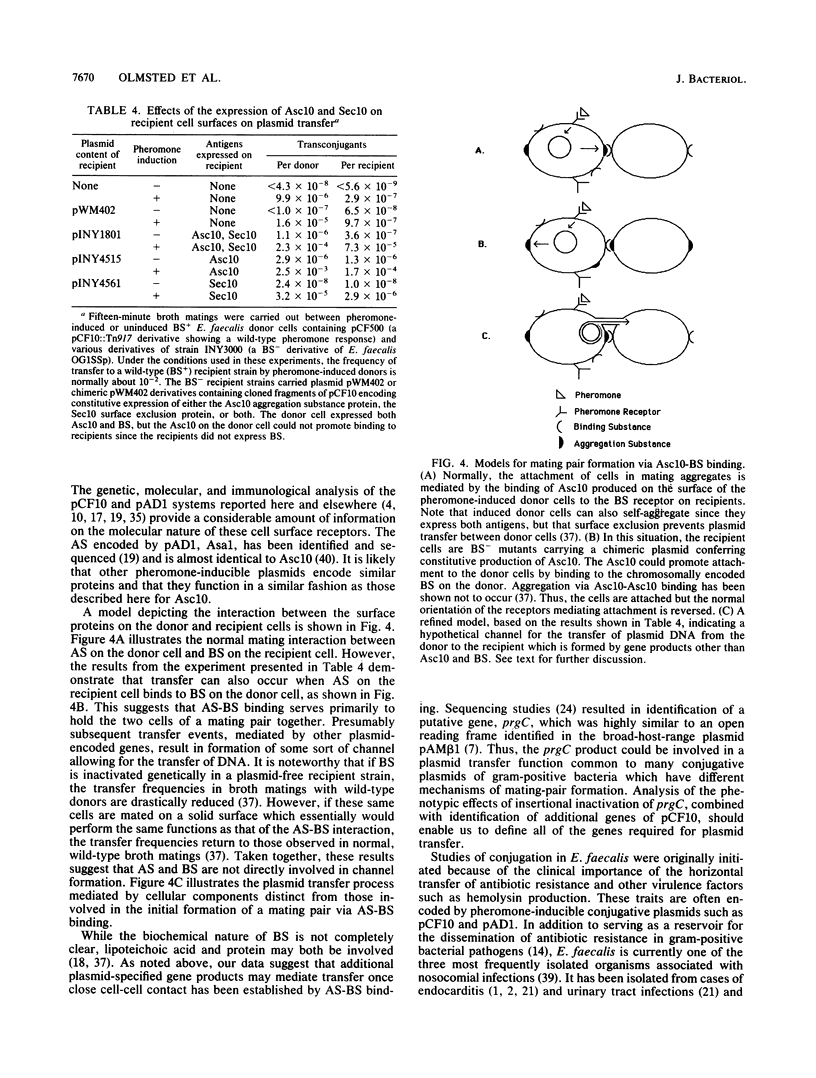
The high transfer frequency of pheromone-inducible conjugative plasmids of Enterococcus faecalis in liquid culture is due in part to the formation of mating aggregates. These aggregates result from the interaction of two surface components, aggregation substance (AS), which is plasmid encoded, and the chromosomally encoded binding substance (BS). In the accompanying paper (S.-M. Kao, S. B. Olmsted, A. S. Viksnins, J.C. Gallo, G. M. Dunny, J. Bacteriol, 173:7650-7664, 1991), the sequence of the prgB gene encoding the AS molecule (Asc10) produced by pheromone-induced cells carrying plasmid pCF10 is presented. Here we report the results of genetic and immunological experiments which define the role of Asc10 in aggregation and plasmid transfer. These data indicate expression of AS on the surface of an E. faecalis cell and its binding to BS expressed on a second cell are required for the formation of a mating pair and the efficient transfer of pCF10 in liquid matings. However, the orientation of the receptors was not critical for transfer; ie., AS expressed on recipient cells could facilitate plasmid transfer via binding to BS on the donor. Our results suggest that additional (as yet unidentified) products are involved in forming the channel that ultimately serves to transfer the DNA, with AS-BS binding serving primarily to generate the initial attachment between cells. The putative prgC gene product, identified by DNA sequencing (data presented in the accompanying paper), could be involved in transfer events occurring subsequent to aggregation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitchison E. J., Lambert P. A., Farrell I. D. Antigenic composition of an endocarditis-associated isolate of Streptococcus faecalis and identification of its glycoprotein antigens by ligand blotting with lectins. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):161–167. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison E. J., Lambert P. A., Smith E. G., Farrell I. D. Serodiagnosis of Streptococcus faecalis endocarditis by immunoblotting of surface protein antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):211–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.211-215.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Kao S. M., Adsit J. C., Dunny G. M. Cloning and expression of genes encoding pheromone-inducible antigens of Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5161–5168. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5161-5168.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Brown B. L. Sex pheromone cAD1 in Streptococcus faecalis: induction of a function related to plasmid transfer. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1063–1065. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1063-1065.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Weaver K. E. Sex pheromones and plasmid transfer in Enterococcus faecalis. Plasmid. 1989 May;21(3):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D. Effects of the modification of transfer buffer composition and the renaturation of proteins in gels on the recognition of proteins on Western blots by monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):144–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Brown B. L., Clewell D. B. Induced cell aggregation and mating in Streptococcus faecalis: evidence for a bacterial sex pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Craig R. A., Carron R. L., Clewell D. B. Plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis: production of multiple sex pheromones by recipients. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M. Genetic functions and cell-cell interactions in the pheromone-inducible plasmid transfer system of Enterococcus faecalis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):689–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Lee L. N., LeBlanc D. J. Improved electroporation and cloning vector system for gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1194–1201. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1194-1201.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Zimmerman D. L., Tortorello M. L. Induction of surface exclusion (entry exclusion) by Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromones: use of monoclonal antibodies to identify an inducible surface antigen involved in the exclusion process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8582–8586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G., Funk C., Adsit J. Direct stimulation of the transfer of antibiotic resistance by sex pheromones in Streptococcus faecalis. Plasmid. 1981 Nov;6(3):270–278. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. E., Clewell D. B. Transfer functions of the Streptococcus faecalis plasmid pAD1: organization of plasmid DNA encoding response to sex pheromone. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3473–3481. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3473-3481.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. E., Kessler R. E., Clewell D. B. Identification of pheromone-induced surface proteins in Streptococcus faecalis and evidence of a role for lipoteichoic acid in formation of mating aggregates. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.6-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli D., Lottspeich F., Wirth R. Sequence analysis of Enterococcus faecalis aggregation substance encoded by the sex pheromone plasmid pAD1. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):895–904. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli D., Wirth R., Wanner G. Identification of aggregation substances of Enterococcus faecalis cells after induction by sex pheromones. An immunological and ultrastructural investigation. Arch Microbiol. 1989;151(6):486–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00454863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmàn C. A., Pruzzo C., LiPira G., Calegari L. Role of adherence in pathogenesis of Enterococcus faecalis urinary tract infection and endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1834–1838. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1834-1838.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. M., Olmsted S. B., Viksnins A. S., Gallo J. C., Dunny G. M. Molecular and genetic analysis of a region of plasmid pCF10 containing positive control genes and structural genes encoding surface proteins involved in pheromone-inducible conjugation in Enterococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7650–7664. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7650-7664.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Yagi Y. Identification and partial characterization of a pheromone-induced adhesive surface antigen of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.714-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Shorrock P. J., Aitchison E. J., Domingue P. A., Power M. E., Costerton J. W. Effect of in vivo growth conditions upon expression of surface protein antigens in Enterococcus faecalis. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1990 May;2(1):51–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. Forty years of genetic recombination in bacteria. A fortieth anniversary reminiscence. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):627–628. doi: 10.1038/324627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Sakagami Y., Ishii Y., Isogai A., Kitada C., Fujino M., Adsit J. C., Dunny G. M., Suzuki A. Structure of cCF10, a peptide sex pheromone which induces conjugative transfer of the Streptococcus faecalis tetracycline resistance plasmid, pCF10. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14574–14578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Sakagami Y., Narita M., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Craig R. A., Clewell D. B., Suzuki A. Isolation and structure of the bacterial sex pheromone, cAD1, that induces plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Dec 3;178(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D., Tuomanen E., Falkow S., Golenbock D. T., Saukkonen K., Wright S. D. Recognition of a bacterial adhesion by an integrin: macrophage CR3 (alpha M beta 2, CD11b/CD18) binds filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1375–1382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90701-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Mori M., Sakagami Y., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Craig R. A., Clewell D. B. Isolation and structure of bacterial sex pheromone, cPD1. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.6436978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortorello M. L., Dunny G. M. Identification of multiple cell surface antigens associated with the sex pheromone response of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):131–137. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.131-137.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortorello M., Adsit J., Krug D., Antczak D., Dunny G. Monoclonal antibodies to cell surface antigens involved in sex pheromone induced mating in Streptococcus faecalis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Apr;132(4):857–864. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-4-857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter K. M., Dunny G. M. Mutants of Enterococcus faecalis deficient as recipients in mating with donors carrying pheromone-inducible plasmids. Plasmid. 1990 Jul;24(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner G., Formanek H., Galli D., Wirth R. Localization of aggregation substances of Enterococcus faecalis after induction by sex pheromones. An ultrastructural comparison using immuno labelling, transmission and high resolution scanning electron microscopic techniques. Arch Microbiol. 1989;151(6):491–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00454864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Jechorek R. P., Erlandsen S. L. Evidence for the translocation of Enterococcus faecalis across the mouse intestinal tract. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):82–90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., Kessler R. E., Shaw J. H., Lopatin D. E., An F., Clewell D. B. Plasmid content of Streptococcus faecalis strain 39-5 and identification of a pheromone (cPD1)-induced surface antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):1207–1215. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]