Abstract
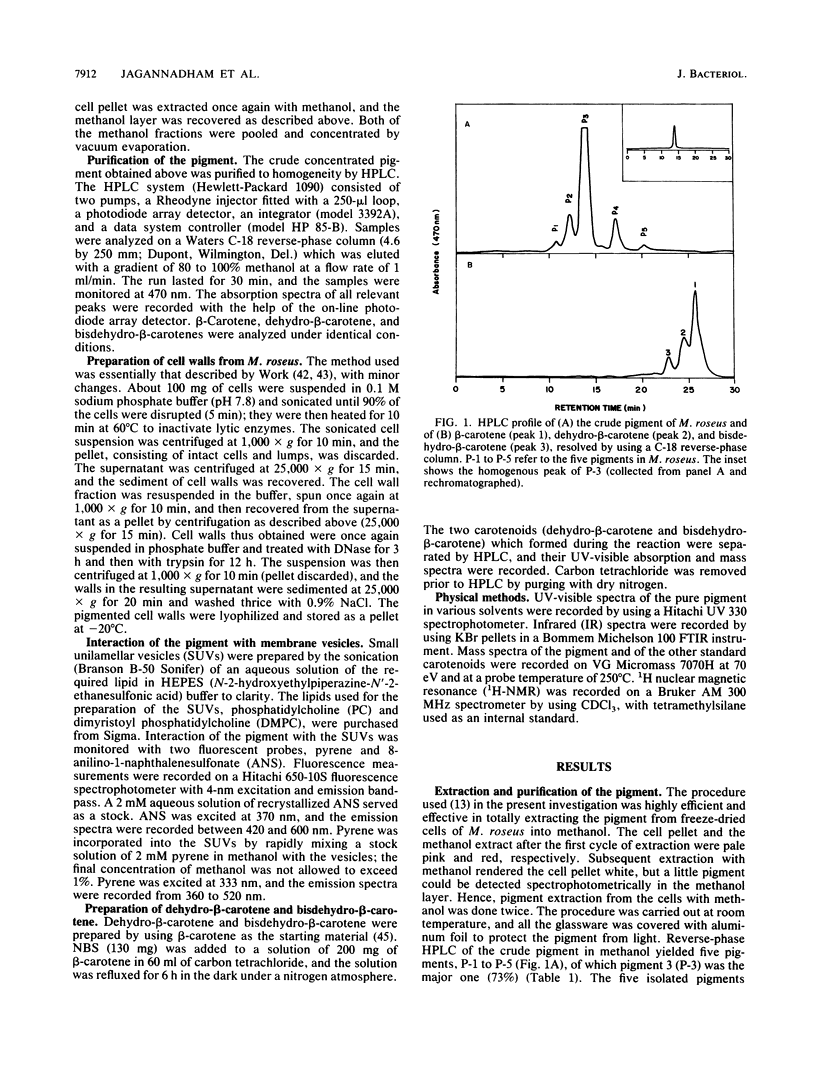
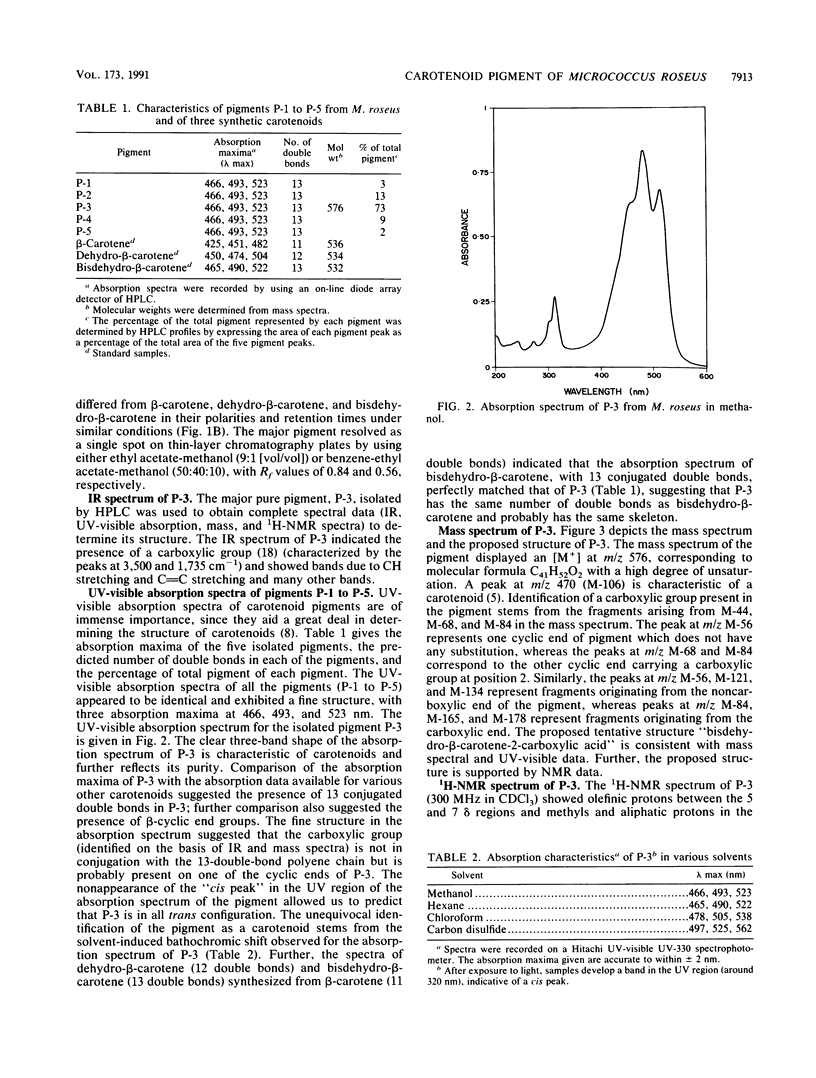
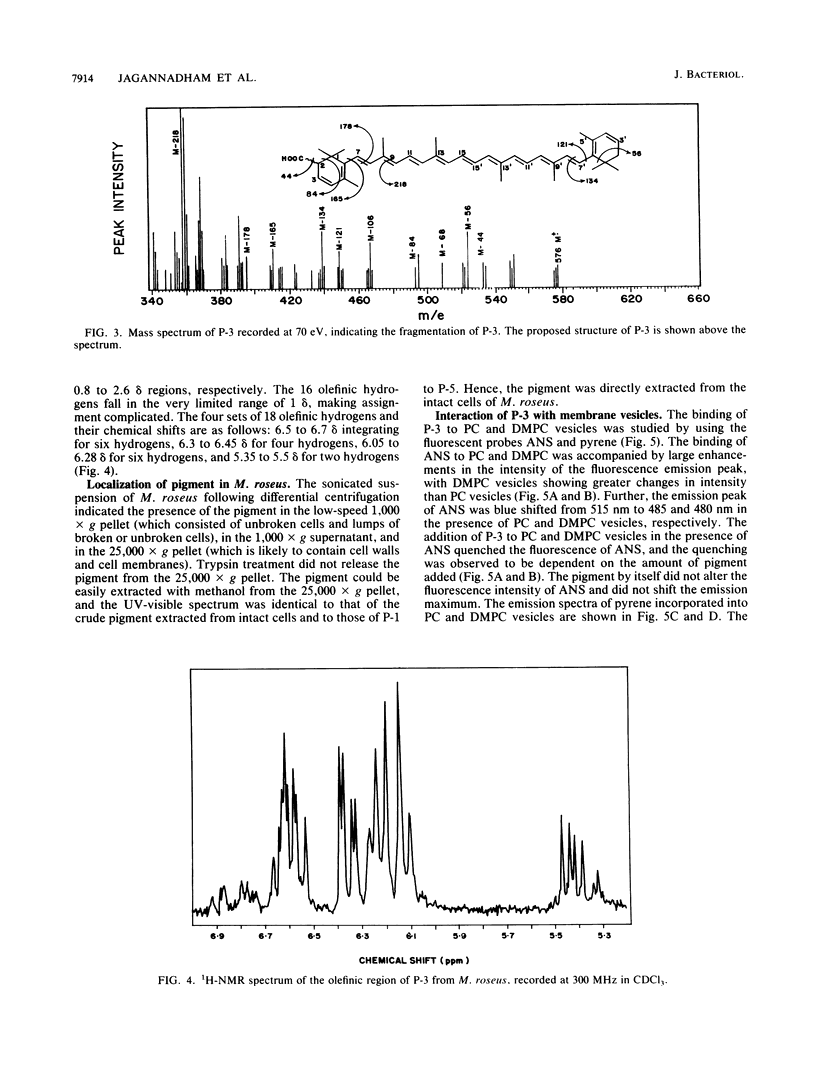
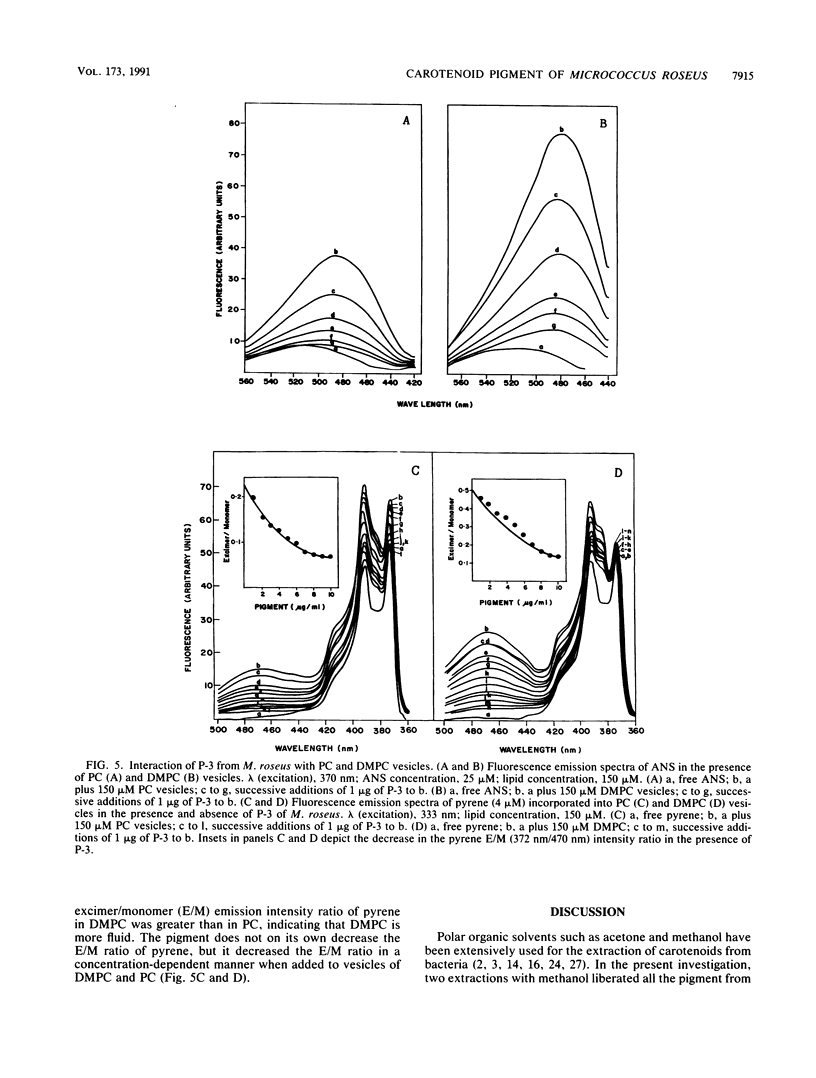
The major carotenoid pigment of a psychrotrophic Micrococcus roseus strain was purified to homogeneity from methanol extracts of dried cells by reverse-phase liquid chromatography and was designated P-3. On the basis of the UV-visible, infrared, mass, and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of P-3, it was identified as bisdehydro-beta-carotene-2-carboxylic acid. The pigment interacted with synthetic membranes of phosphatidylcholine and dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine and stabilized the membranes. These results also indicate that P-3 is different from canthaxanthin, the major carotenoid pigment from a mesophilic M. roseus strain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bramley P. M., Mackenzie A. Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1988;29:291–343. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152829-4.50009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney J. J., Marks H. W., Smith A. M. Isolation and Identification of Canthaxanthin from Micrococcus roseus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):342–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.342-345.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt U. The cell wall as the site of carotenoid in the "Knallgas" bacterium, 12-60-x. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;80(1):32–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00410576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzell C. R., Francis G. W., Liaaen-Jensen S. Mass spectrometric studies of carotenoids. 2. A survey of fragmentation reactions. Acta Chem Scand. 1969;23(3):727–750. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.23-0727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes: use of pyrene excimers as optical probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan F. T., Johns R. B. Normal-phase HPLC analysis of microbial carotenoids and neutral lipids. J Chromatogr Sci. 1983 Jan;21(1):34–38. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/21.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison A. P., Jr Survival of bacteria. Harmful effects of light, with some comparisons with other adverse physical agents. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:143–156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Haug A. Regulation of membrane lipid fluidity in Acholeplasma laidlawii: effect of carotenoid pigment content. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 29;352(3):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Paul R., Balaram P. Fluorescent probe studies of mixed micelles of phospholipids and bile salts. Effect of cholesterol incorporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 27;597(1):70–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelis H. J., De Leenheer A. P. Profiling and quantitation of bacterial carotenoids by liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3065–3071. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3065-3071.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmisano A. C., Cronin S. E., Des Marais D. J. Analysis of lipophilic pigments from a phototrophic microbial mat community by high performance liquid chromatography. J Microbiol Methods. 1988;8:209–217. doi: 10.1016/0167-7012(88)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R., EHTISHAM-UD-DIN A. F. THE LOCALIZATION OF CYTOCHROMES AND CAROTENOIDS IN ISOLATED BACTERIAL MEMBRANES AND ENVELOPES. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Jun;43:255–264. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmann G., Woods W. S., Tuveson R. W. Identification of carotenoids in Erwinia herbicola and in a transformed Escherichia coli strain. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Sep 1;59(1-2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90035-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzel E. H., Cooney J. J. Action of light on Micrococcus roseus. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Jul;20(7):1015–1021. doi: 10.1139/m74-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzel E. H., Cooney J. J. Isolation and identification of echinenone from Micrococcus roseus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):272–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.272-274.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivaji S. Binding of seminalplasmin to the plasma and acrosomal membranes of bovine spermatozoa. Fluorescence studies on the changes in the lipid-phase fluidity. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 17;196(2):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivaji S., Rao N. S., Saisree L., Sheth V., Reddy G. S., Bhargava P. M. Isolation and identification of Pseudomonas spp. from Schirmacher Oasis, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):767–770. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.767-770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkell D., Hunter M. I. Carotenoid-glycoprotein of sarcina flava membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;58(3):289–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-3-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkell D., Hunter M. I. The polar carotenoid fraction from sarcina flava. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;58(3):293–299. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkell D., Strang R. H. Analysis and comparison of the carotenoids of Sarcina flava and S. lutea. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):53–57. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungers G. E., Cooney J. J. Isolation and characterization of carotenoid pigments of Micrococcus roseus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.234-241.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano S., Yano K., Matsuo M. Membrane-stabilizing effect of vitamin E: effect of alpha-tocopherol and its model compounds on fluidity of lecithin liposomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90544-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Callis J. B. Pyrene. A probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4000–4006. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayasarathy S., Shivaji S., Balaram P. Bull sperm plasma and acrosomal membranes: fluorescence studies of lipid phase fluidity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90868-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E. AMINO ACIDS OF WALLS OF MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1107–1109. doi: 10.1038/2011107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Work E., Griffiths H. Morphology and chemistry of cell walls of Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):641–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.641-657.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


