Abstract
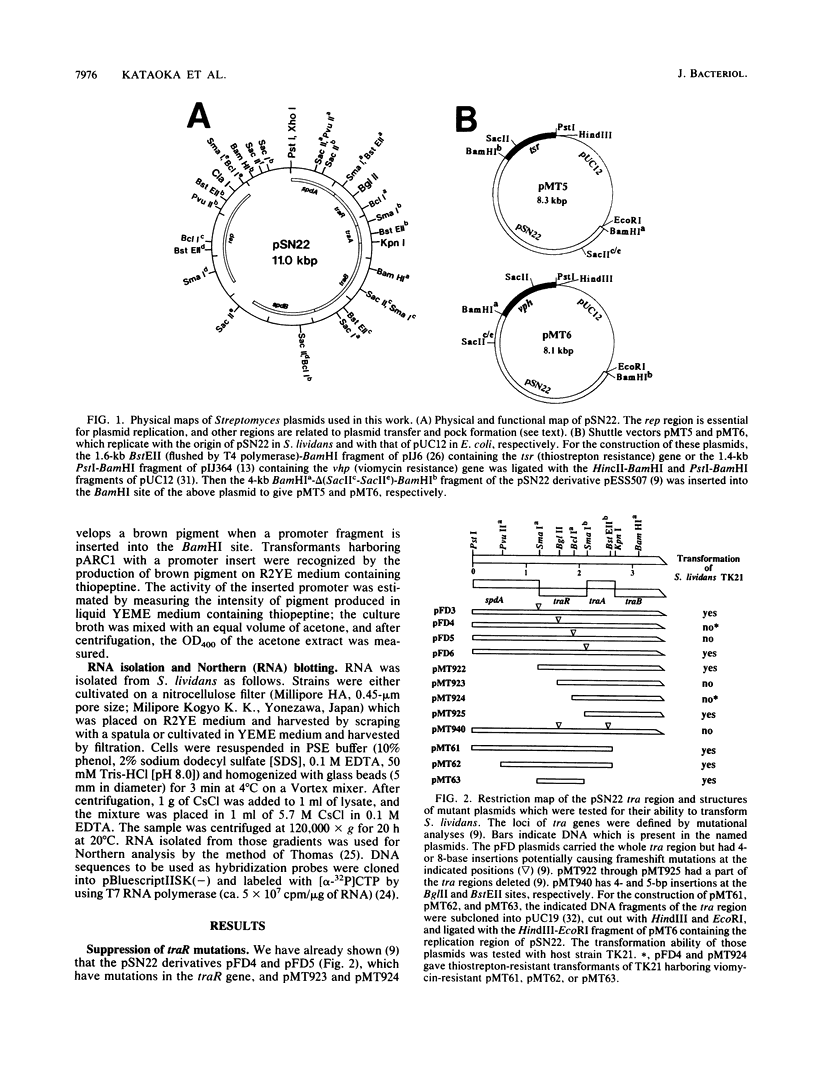
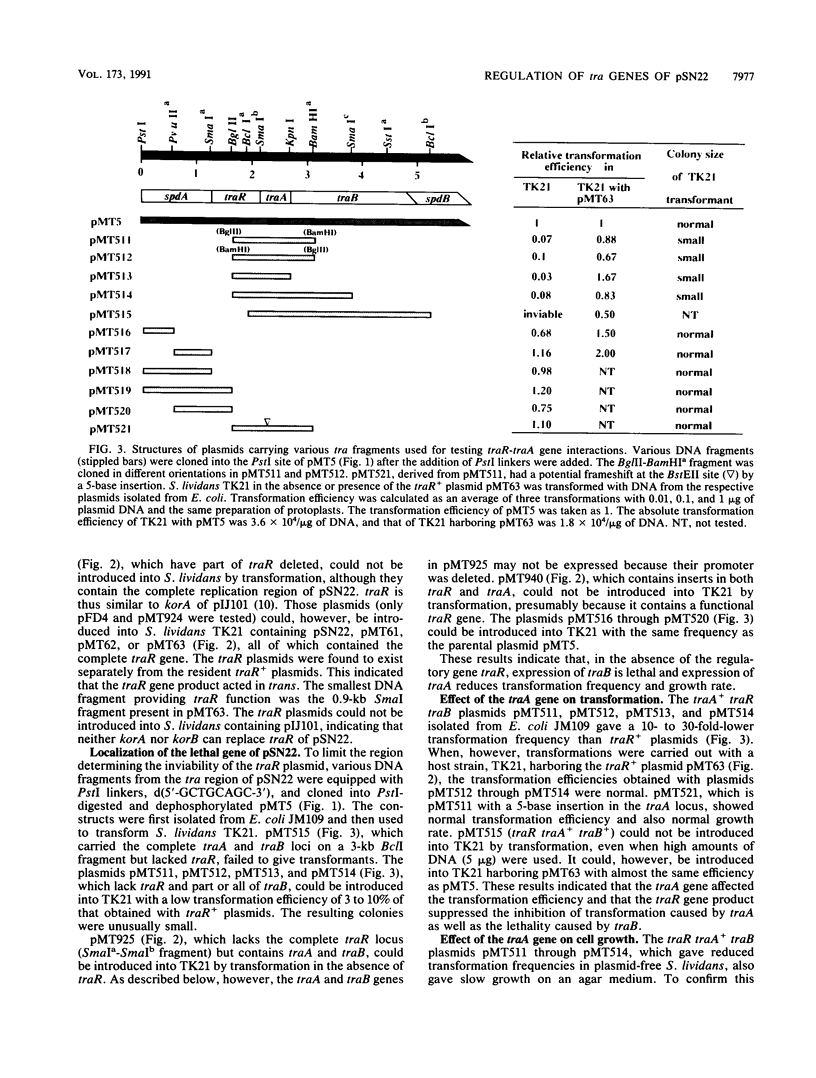
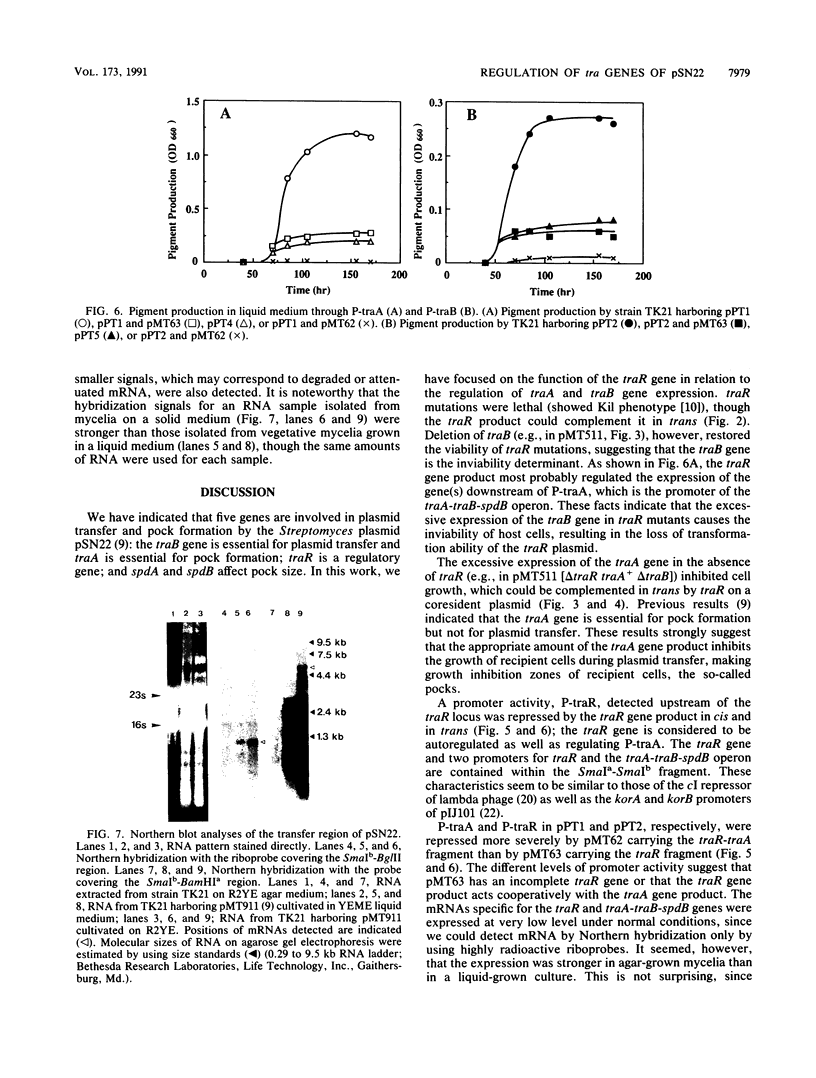
pSN22 is an 11-kb multicopy plasmid from Streptomyces nigrifaciens which is being studied in Streptomyces lividans. A segment of about 7 kb of pSN22 contains five genes involved in conjugation. Three of them, traA, traB, and traR, are essential for plasmid transfer and for the mobilization of chromosomal markers (fertility), while the remaining two genes, spdA and spdB, merely enhance the efficiency of plasmid transfer, resulting in the formation of larger pocks. In vitro promoter-probing experiments identified a 550-bp BglII-SmaI DNA fragment with promoter activity in both orientations; Northern (RNA blot) hybridization identified corresponding divergent transcripts of 1 and 5.2 kb for traR and the traA-traB-spdB operon, respectively. The traR gene product repressed its own transcription and also the transcription of the traA-traB-spdB operon. Plasmids containing a functional traB gene could not "survive" without traR being present in the same cell either in cis or in trans, presumably because unregulated expression of traB is lethal to the host. Plasmids with a functional traA gene but without traR had a low transformation efficiency and inhibited the growth of host cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boccard F., Smokvina T., Pernodet J. L., Friedmann A., Guérineau M. The integrated conjugative plasmid pSAM2 of Streptomyces ambofaciens is related to temperate bacteriophages. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):973–980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J. Resistance, regulatory and production genes for the antibiotic methylenomycin are clustered. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1893–1897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03866.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. K., Chater K. F. Spore colour in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) involves the developmentally regulated synthesis of a compound biosynthetically related to polyketide antibiotics. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1679–1691. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z. X., Kieser T., Hopwood D. A. "Strong incompatibility" between derivatives of the Streptomyces multi-copy plasmid pIJ101. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):286–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00337723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. R., Lee S. C., Kendall K., Cohen S. N. Identification and characterization of a locus inhibiting extrachromosomal maintenance of the Streptomyces plasmid SLP1. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):324–331. doi: 10.1007/BF02464900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Beppu T. Construction and application of a promoter-probe plasmid that allows chromogenic identification in Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):406–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.406-412.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka M., Seki T., Yoshida T. Five genes involved in self-transmission of pSN22, a Streptomyces plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4220–4228. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4220-4228.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 and correlation of the sequence with genetic properties. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4634–4651. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4634-4651.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Plasmid transfer in Streptomyces lividans: identification of a kil-kor system associated with the transfer region of pIJ101. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4177–4183. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4177-4183.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T. Factors affecting the isolation of CCC DNA from Streptomyces lividans and Escherichia coli. Plasmid. 1984 Jul;12(1):19–36. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T., Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M., Thompson C. J. pIJ101, a multi-copy broad host-range Streptomyces plasmid: functional analysis and development of DNA cloning vectors. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(2):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00330791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G. Location of DNA methylation genes on the Escherichia coli K-12 genetic map. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 14;127(1):47–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00267782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Cohen S. N. Plasmid formation in Streptomyces: excision and integration of the SLP1 replicon at a specific chromosomal site. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):429–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00436190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernodet J. L., Simonet J. M., Guérineau M. Plasmids in different strains of Streptomyces ambofaciens: free and integrated form of plasmid pSAM2. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00328697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigac J., Vujaklija D., Toman Z., Gamulin V., Schrempf H. Structural instability of a bifunctional plasmid pZG1 and single-stranded DNA formation in Streptomyces. Plasmid. 1988 May;19(3):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. S., Cohen S. N. Mutational and functional analysis of the korA and korB gene products of Streptomyces plasmid pIJ101. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00633838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Kieser T., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. Physical analysis of antibiotic-resistance genes from Streptomyces and their use in vector construction. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urabe H., Shindoh Y., Nakano M. M., Ogawara H. Characterization of the incompatibility region of Streptomyces plasmid pSL1. Plasmid. 1987 Mar;17(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright L. F., Hopwood D. A. Identification of the antibiotic determined by the SCP1 plasmid of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jul;95(1):96–106. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-1-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]