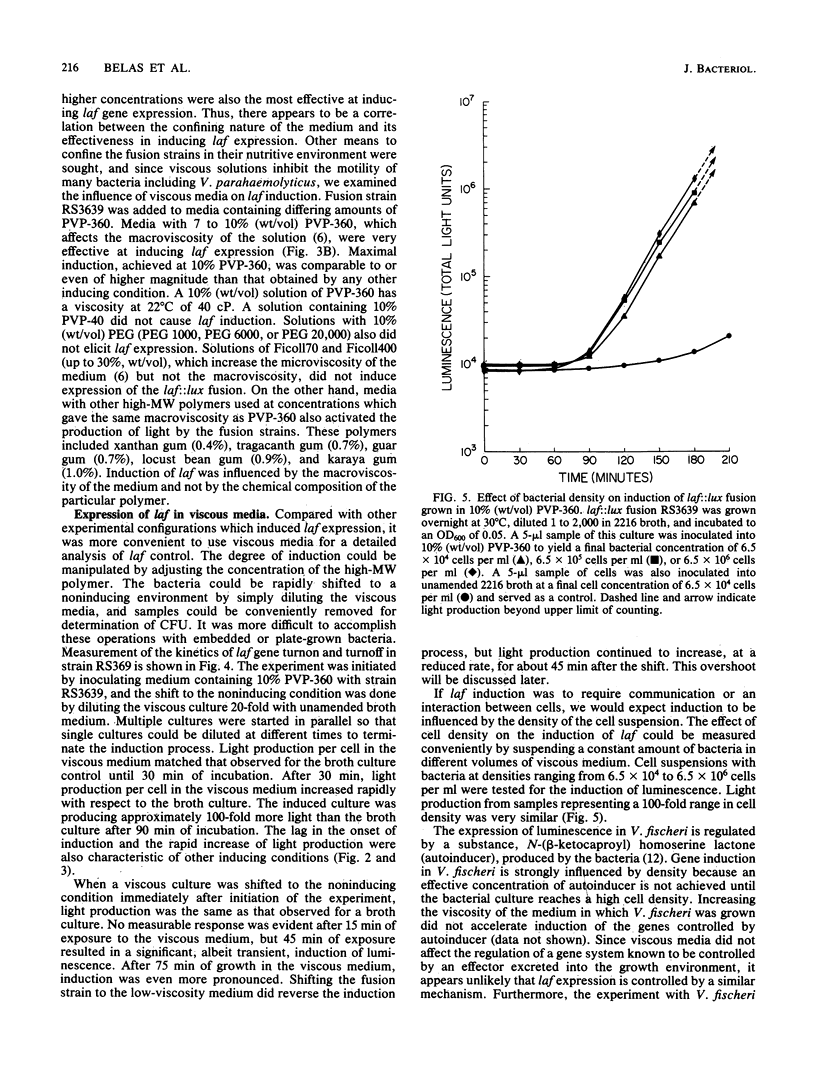
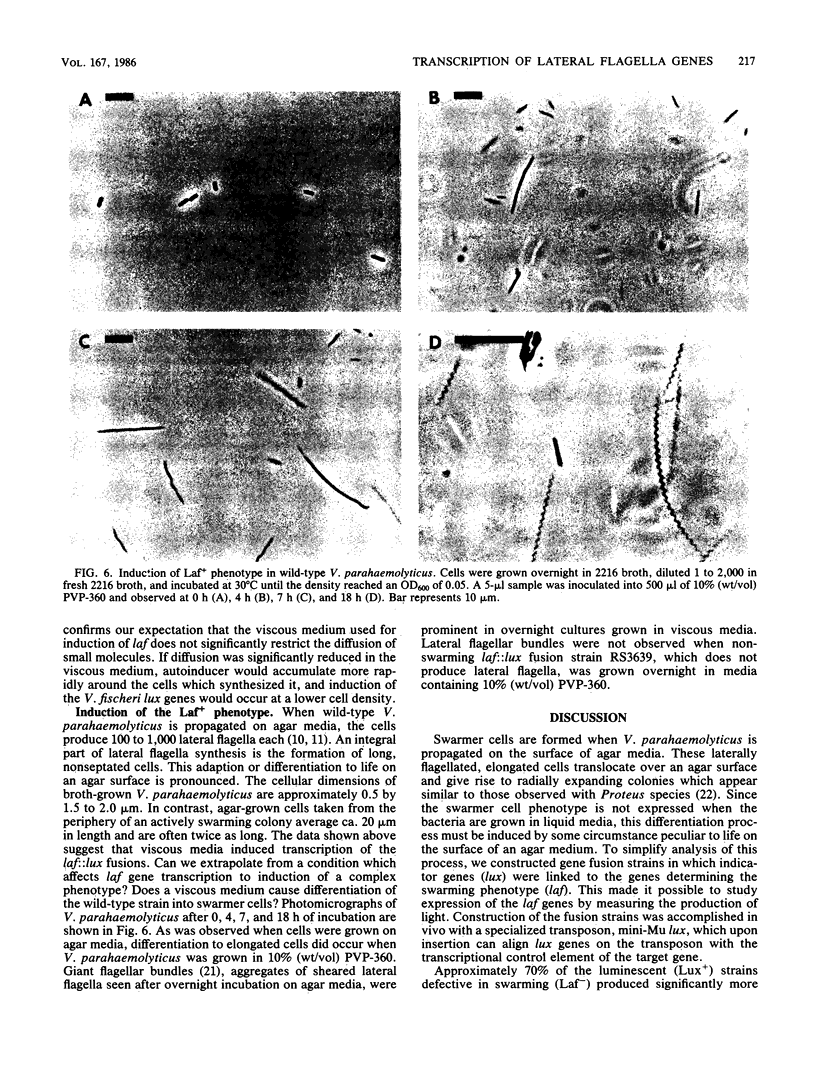
Abstract
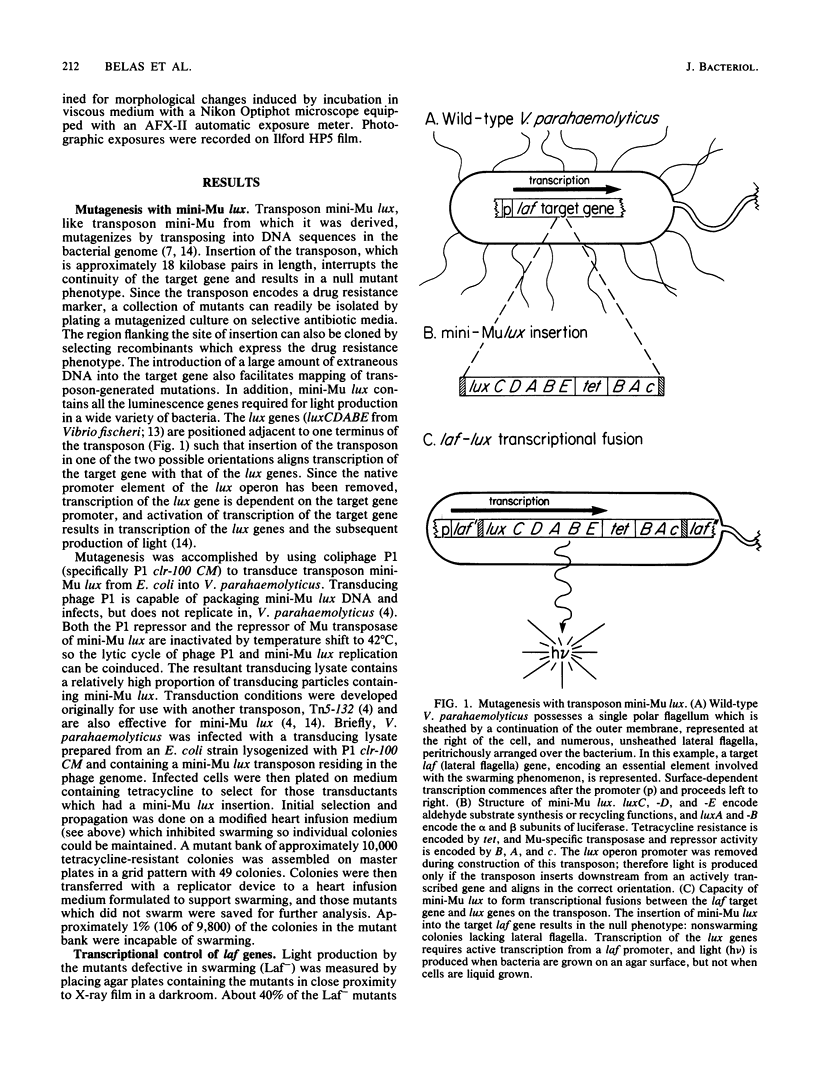
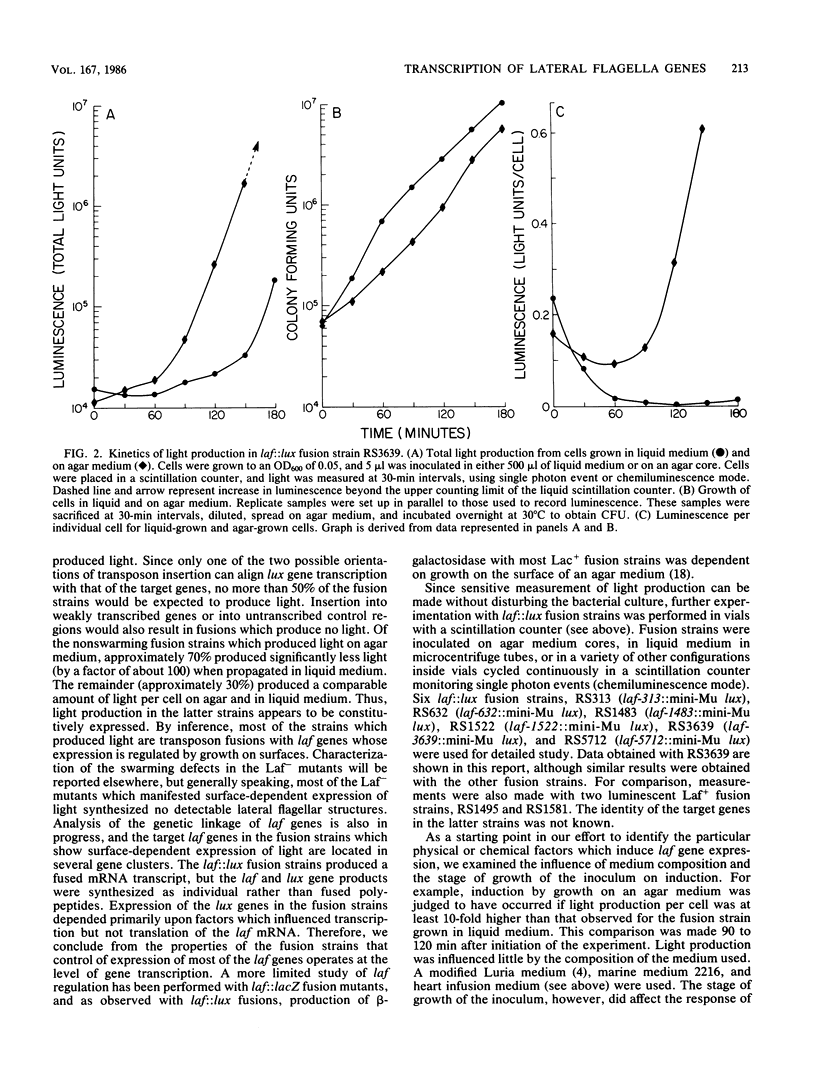
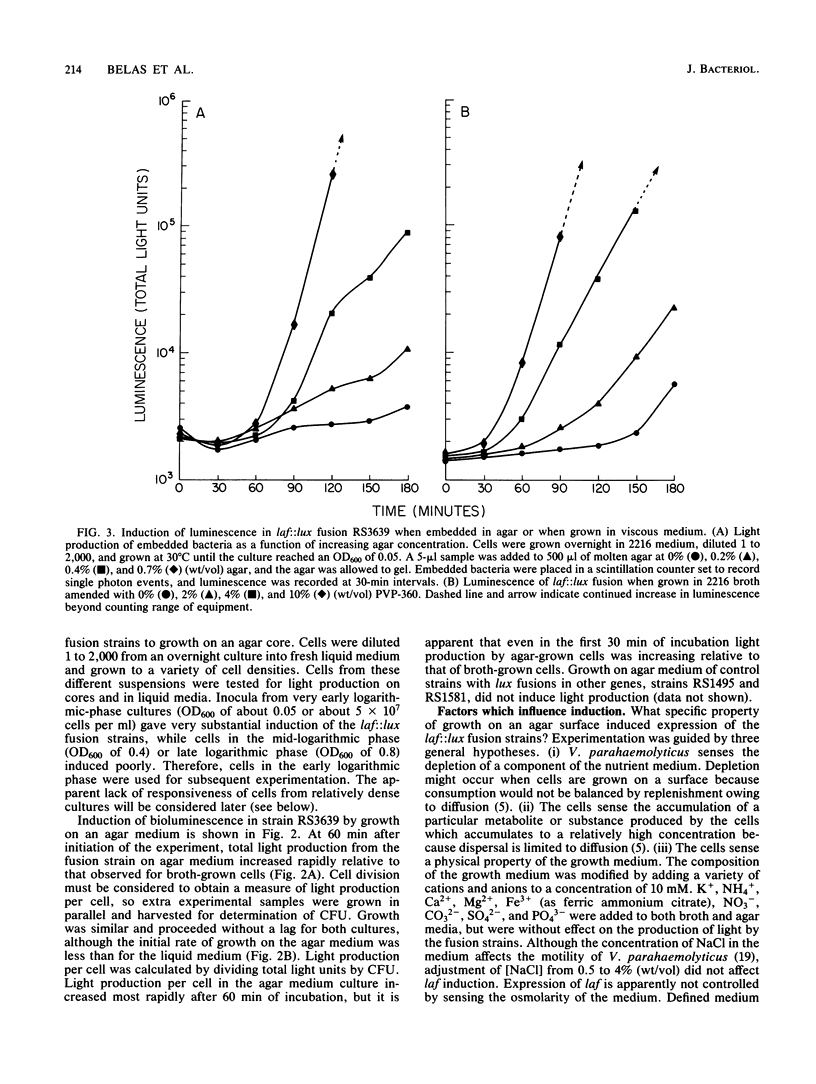
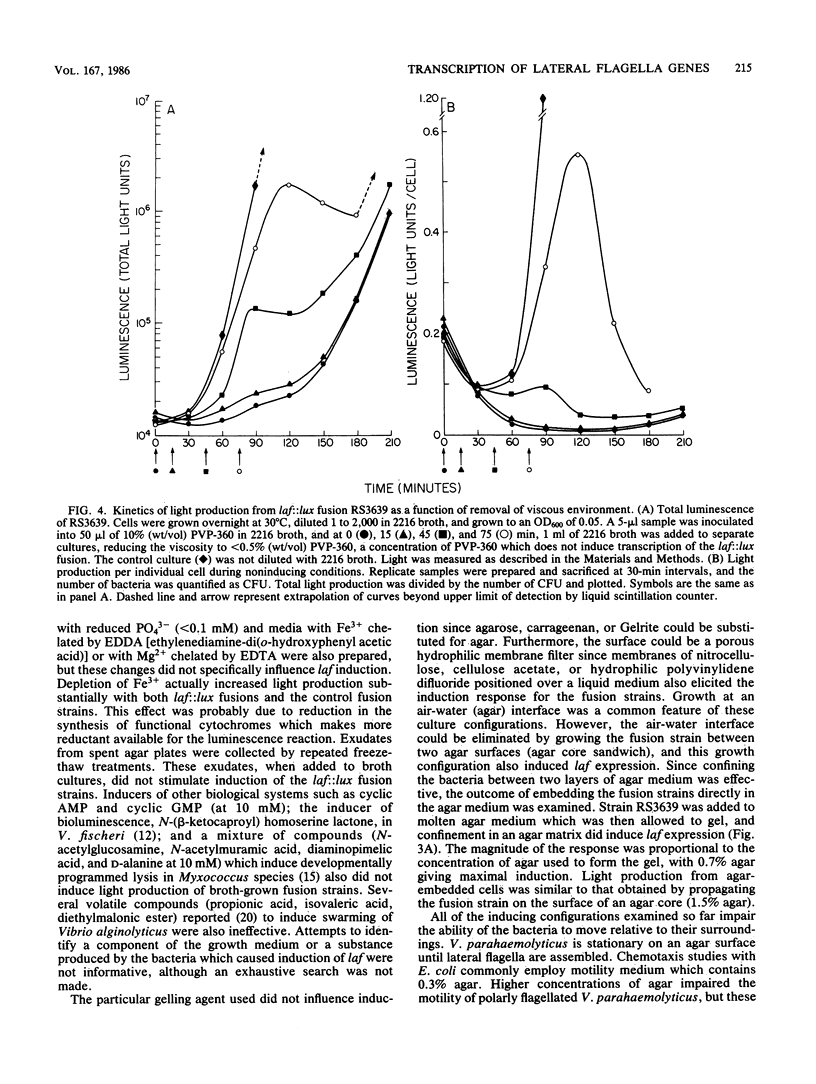
Two distinctly different organelles of locomotion are produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The polar flagellum is responsible for motility in a liquid environment (swimming), and the lateral flagella enable the bacteria to move over surfaces (swarming). Synthesis of lateral flagella occurs when V. parahaemolyticus is grown on agar media but not when it is grown in liquid media. We used lux (luminescence gene) fusions to conveniently and sensitively analyze the factors which influence transcription of lateral flagella genes (laf). Transposon mini-Mu lux was used to mutagenize V. parahaemolyticus and to generate laf::lux transcriptional fusions. Mutants with insertions of mini-Mu lux in laf genes were defective in the swarming phenotype and produced light when the bacteria were propagated on agar media, but not when cells were grown in liquid media. Thus, surface-dependent expression of lateral flagella synthesis is controlled by regulation of transcription. Such fusion strains were also used to further define the environmental conditions which induce laf gene expression. Cultivation on media solidified by gelling agents other than agar also induced light production in fusion strains, as did growth on a variety of hydrophilic membrane filters suspended over liquid media. Growth at an air-surface interface was not necessary for expression since embedding the fusion strains in agar was also effective. Furthermore, induction of laf gene transcription could also be accomplished by increasing the viscosity of the liquid medium by the addition of a high-molecular-weight polymer such as polyvinylpyrrolidone. Increase in luminescence of the fusion strains was detected within 30 min of initiation of the inducing circumstance, and reversal of induction, e.g., by dilution of the viscous medium, resulted in a rapid decline in the rate of increase in luminescence. Conditions that induced luminescence in the fusion strains also induced the synthesis of lateral flagella in wild-type V. parahaemolyticus. The growth environment of the genes, and it appears that the signal that triggers laf expression is physical rather than chemical in nature. Possibilities for a sensing mechanism are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann P., Baumann L. Biology of the marine enterobacteria: genera Beneckea and Photobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:39–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas M. R., Colwell R. R. Adsorption kinetics of laterally and polarly flagellated Vibrio. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1568–1580. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1568-1580.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas M. R., Colwell R. R. Scanning electron microscope observation of the swarming phenomenon of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):956–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.956-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Mileham A., Simon M., Silverman M. Transposon mutagenesis of marine Vibrio spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):890–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.890-896.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Purcell E. M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):193–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85544-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Turner L. Movement of microorganisms in viscous environments. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):349–351. doi: 10.1038/278349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer S. E., Golten C., Scheffers W. A. Effects of some chemical factors on flagellation and swarming of Vibrio alginolyticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(4):385–403. doi: 10.1007/BF02565083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A., Burlingame A. L., Eberhard C., Kenyon G. L., Nealson K. H., Oppenheimer N. J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2444–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Simon M., Silverman M. Measuring gene expression with light. Science. 1985 Mar 15;227(4692):1345–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.2983423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Ecology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.24-32.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Okamoto K. Formation and function of Vibrio parahaemolyticus lateral flagella. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1266–1271. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1266-1271.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzer S. The mechanism of swarming of Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 20;104(1):67–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00447301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S. Effect of temperature, salts, pH, and other factors on the development of peritrichous flagella in Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Aug 28;104(3):285–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00447338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S., Kessel M. Giant flagellar bundles of Vibrio alginolyticus (NCMB 1803). Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 31;94(4):331–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00769028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Schwarzhoff R. H. Nature of the swarming phenomenon in Proteus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:101–122. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




