Abstract
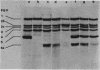
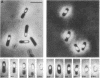
Part of the gene encoding penicillin-binding protein 5 from Bacillus subtilis 168 was cloned in Escherichia coli with a synthetic oligonucleotide as a hybridization probe. The gene was designated dacA by analogy with E. coli. The nucleotide sequence was determined, and the predicted molecular mass was 45,594 daltons (412 amino acids). A comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence with that of the E. coli penicillin-binding protein 5 indicated that these enzymes showed about 25% identity. The B. subtilis dacA gene was mutated by integration of a plasmid into the structural gene by homologous recombination. A comparison of the mutant and control strains revealed that (i) the mutant lacked detectable penicillin-binding protein 5, (ii) the D-alanine carboxypeptidase activity of membranes isolated from the mutant was only 5% of that measured in membranes from the control strain, (iii) the mutant cells showed apparently normal morphology only during exponential growth, and after the end of exponential phase the cells became progressively shorter, (iv) the mutant sporulated normally except that the forespore occupied about two-thirds of the mother cell cytoplasm and, during its development, migrated towards the center of the mother cell, and (v) purified mutant spores were 10-fold less heat resistant but possessed normal refractility and morphology. Preliminary chemical analysis indicated that the structure of the cortex of the mutant was different.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band L., Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis trpE and trpD genes. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Inactivation of D-alanine carboxypeptidase by penicillins and cephalosporins is not lethal in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2814–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E., Strominger J. L. Altered penicillin-binding components in penicillin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. J., Winter G., Wilkinson A. J., Fersht A. R. The use of double mutants to detect structural changes in the active site of the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (Bacillus stearothermophilus). Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):835–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Thompson C. J. Gene cloning in Streptomyces. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:69–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Nguyen A., Lang D., Hoch J. A. Construction and properties of an integrable plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1513-1515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Banner C. D., Ollington J. F., Losick R., Hoch J. A., O'Connor M. B., Sonenshein A. L. Mapping a cloned gene under sporulation control by inserttion of a drug resistance marker into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.90-98.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins A. D. Polarity and topology of DNA segregation and septation in cells and sporangia of the bacilli. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Oct;24(10):1104–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imae Y., Strominger J. L. Relationship between cortex content and properties of Bacillus sphaericus spores. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):907–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.907-913.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Glycopeptide transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):656–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. E., Strominger J. L. Synthesis of peptidoglycan by high molecular weight penicillin-binding proteins of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1483–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Brenner S. A new selective phage cloning vector, lambda 2001, with sites for XbaI, BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SstI and XhoI. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Bott K. F. Cloning the gyrA gene of Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6307–6323. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. XVI. The reversible fixation of radioactive penicillin G to the D-alanine carboxypeptidase of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3660–3666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton T. J., Doi R. H. The stability of messenger ribonucleic acid during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3189–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz Z., Broome-Smith J. K., Schwarz U., Spratt B. G. Spherical E. coli due to elevated levels of D-alanine carboxypeptidase. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):702–704. doi: 10.1038/297702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Takagaki Y., Maruyama I. N., Tamaki S., Nishimura Y., Suzuki H., Ogino U., Hirota Y. Mutants of Escherichia coli lacking in highly penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2976–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet B., Goze A., Ehrlich S. D. Insertional mutagenesis in Bacillus subtilis: mechanism and use in gene cloning. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Curtis C. A., de Lencastre H. Use of integrational plasmid vectors to demonstrate the polycistronic nature of a transcriptional unit (spoIIA) required for sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2123–2136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E., Shepherd S. T., Chase H. A. Identification of the binding protein which may be the target of penicillin action in Bacillus megaterium. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):568–570. doi: 10.1038/271568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A., Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. D-alanine carboxypeptidase and cell wall cross-linking in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):926–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.926-927.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Kawamura F., Kobayashi Y., Saito H. Early sporulation gene spo0F: nucleotide sequence and analysis of gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowell M. O., Buchanan C. E. Changes in penicillin-binding proteins during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1331–1337. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1331-1337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Deletion of the penicillin-binding protein 5 gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1190–1192. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1190-1192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A computer program to enter DNA gel reading data into a computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):499–503. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Computer methods to locate signals in nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):505–519. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Graphic methods to determine the function of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):521–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bone E. J., Ellar D. J. The sporulation-specific penicillin-binding protein 5a from Bacillus subtilis is a DD-carboxypeptidase in vitro. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):825–828. doi: 10.1042/bj2300825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Ellar D. J. Alteration in the penicillin-binding profile of Bacillus megaterium during sporulation. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):640–643. doi: 10.1038/300640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit J. N., Strominger J. L. D-alanine carboxypeptidase from Bacillus subtilis membranes. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6759–6766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warth A. D., Strominger J. L. Structure of the peptidoglycan from spores of Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1389–1396. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Primary structure of the COOH-terminal membranous segment of a penicillin-sensitive enzyme purified from two Bacilli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):2067–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Sequence of active site peptides from the penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase of Bacillus subtilis. Mechanism of penicillin action and sequence homology to beta-lactamases. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3964–3976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Gene amplification in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1613–1621. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Perkins J. B., Losick R. A novel method for the rapid cloning in Escherichia coli of Bacillus subtilis chromosomal DNA adjacent to Tn917 insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):424–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00341443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]