Abstract
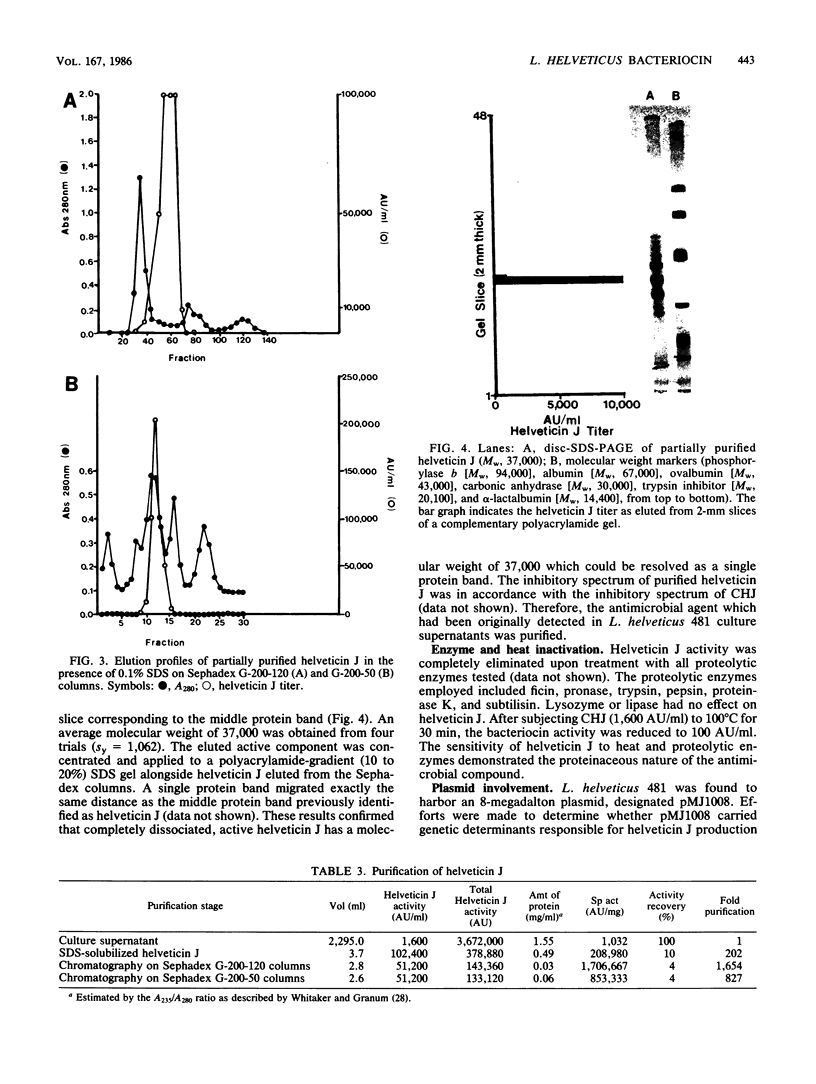
Lactobacillus helveticus 481 produced an antimicrobial agent active against five closely related species. The sensitive indicators included L. helveticus 1846 and 1244, L. bulgaricus 1373 and 1489, and L. lactis 970. The antimicrobial compound was active at neutral pH under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, was sensitive to proteolytic enzymes and heat (30 min at 100 degrees C), and demonstrated a bactericidal mode of action against sensitive indicators. These data confirmed that antimicrobial activity of L. helveticus 481 was mediated by a bacteriocin, designated helveticin J. Production of helveticin J was maximized in an anaerobic fermentor held at a constant pH of 5.5. Ultrafiltration experiments on culture supernatants containing the bacteriocin revealed that helveticin J was present as an aggregate with a molecular weight in excess of 300,000. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of helveticin J purified through Sephadex chromatography resolved a 37,000-dalton protein band with bacteriocin activity. L. helveticus 481 was shown to harbor a single 8-megadalton plasmid (pMJ1008). Isolates cured of pMJ1008 were phenotypically identical to plasmid-bearing cells in fermentation patterns, helveticin J activity, and immunity spectra. The data provided evidence for a chromosomal location of helveticin J and host immunity determinants.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin-Prather S. L., Booth S. J. Evidence for a membrane-bound form of a bacteriocin of Bacteroides uniformis Tl-1. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Feb;30(2):268–272. doi: 10.1139/m84-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barefoot S. F., Klaenhammer T. R. Detection and activity of lactacin B, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1808–1815. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1808-1815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barefoot S. F., Klaenhammer T. R. Purification and characterization of the Lactobacillus acidophilus bacteriocin lactacin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):328–334. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. J., Cundy K. R., Fernandes P. B., Hoober J. K. Purification and characterization of a bacteriocin from Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1171–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1171-1177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W. Differentiation of lactic streptococcal phages into phage species by DNA-DNA homology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):343–349. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.343-349.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Improved lysis of group N streptococci for isolation and rapid characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):592–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.592-600.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kékessy D. A., Piguet J. D. New method for detecting bacteriocin production. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):282–283. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.282-283.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J. The ecology and taxonomic status of the lactobacilli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:279–301. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihelc V. A., Duncan C. L., Chambliss G. H. Characterization of a bacteriocinogenic plasmid in Clostridium perfringens CW55. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):771–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L. Bacteriocins of Diplococcus pneumoniae. I. Antagonistic relationships and genetic transformations. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1090–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1090-1098.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherwitz K. M., Baldwin K. A., McKay L. L. Plasmid linkage of a bacteriocin-like substance in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis strain WM4: transferability to Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1506–1512. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1506-1512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenson L. R., Klaenhammer T. R. Streptococcus cremoris M12R transconjugants carrying the conjugal plasmid pTR2030 are insensitive to attack by lytic bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):851–858. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.851-858.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., McGiven A. R. Assay system for bacteriocins. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):943–943. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.943-943.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upreti G. C., Hinsdill R. D. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriocin from a homofermentative Lactobacillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):487–494. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upreti G. C., Hinsdill R. D. Production and mode of action of lactocin 27: bacteriocin from a homofermentative Lactobacillus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Tersch M. A., Carlton B. C. Megacinogenic plasmids of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.872-877.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. R., Granum P. E. An absolute method for protein determination based on difference in absorbance at 235 and 280 nm. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):156–159. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk H. C., Smit J. A. Properties of a Lactobacillus fermenti bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]