Abstract
Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus picocyanobacteria are dominant contributors to marine primary production over large areas of the ocean. Phytoplankton cells are entrained in the water column and are thus often exposed to rapid changes in irradiance within the upper mixed layer of the ocean. An upward fluctuation in irradiance can result in photosystem II photoinactivation exceeding counteracting repair rates through protein turnover, thereby leading to net photoinhibition of primary productivity, and potentially cell death. Here we show that the effective cross-section for photosystem II photoinactivation is conserved across the picocyanobacteria, but that their photosystem II repair capacity and protein-specific photosystem II light capture are negatively correlated and vary widely across the strains. The differences in repair rate correspond to the light and nutrient conditions that characterize the site of origin of the Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus isolates, and determine the upward fluctuation in irradiance they can tolerate, indicating that photoinhibition due to transient high-light exposure influences their distribution in the ocean.
Introduction
The smallest category of free living photosynthetic cells is picophytoplankton, defined as less than 3 µm diameter. Picophytoplankton cells, although individually minute, dominate carbon assimilation and primary productivity over large areas of the ocean. Among the taxonomically diverse groups composing the picophytoplankton the cyanobacteria Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus are major contributors to primary production and carbon export over large areas of the open ocean [1]. Prochlorococcus, the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth [2], is restricted to the warm rather oligotrophic waters of the latitudinal band extending from 40°N to 40°S [3]–[5] and laboratory experiments show it does not grow well at low temperatures [6]. Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus co-occur in many oceanographic regions, but Synechococcus tolerates a broader temperature range [6], [7] and thrives in more meso- and eutrophic waters, even though Prochlorococcus can also grow at these higher nutrient levels [2]. Synechococcus are often less abundant in warmer, oligotrophic ecosystems where Prochlorococcus is the major primary producer [2], [5].
Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus have cell types (often referred to as ecotypes) which have identifiable geographic ranges that correspond to particular temperature, nutrient concentration, as well as light regimes [2]. Synechococcus cell types differ in their pigment content, allowing these organisms to exploit specific spectral niches [8]–[10], which tend to vary along a horizontal offshore-onshore axis within the upper mixed layer [11]–[15]. In contrast, Prochlorococcus ecotypes are found at different depths in the water column, and are adapted to different average irradiance [2], . The surface ecotypes of Prochlorococcus have optimal growth irradiances similar to Synechococcus strains [6], [19], [20]. Average irradiance contributes to niche partitioning with depth among Prochlorococcus ecotypes, but even in combination with temperature and nutrient regime, does not fully account for the differential distribution of the Prochlorococcus and the Synechococcus strains. In particular, the absence of Prochlorococcus in temperate, permanently mixed shallow seas such as the English Channel where Synechococcus is very abundant, remains poorly understood [2].
The ocean is a dynamic environment in which phytoplankton must cope with rapid changes in resources, particularly irradiance [21], [22]. For a phytoplankton cell, irradiance changes rapidly if light attenuation and mixing in the water column are large, as the cell moves vertically through a large depth/irradiance gradient. Downward mixing of a phytoplankton cell leads to lower irradiance and therefore a decrease in growth, but with no immediate risk of cellular death. In contrast, when a cell is taken upwards in the water column, it must often withstand both rapid and large increases in irradiance. To maintain photosynthesis and viability, phytoplankton must counter the photoinactivation of photosystem II (PSII) [23], [24] with repair [25] through proteolytic removal of photodamaged D1 protein [26] and the coordinated insertion of newly synthesized D1 into the thylakoid membrane [27]. If an increase in irradiance causes photoinactivation to outrun repair, the cell suffers net photoinhibitory loss of photosynthetic capacity, leading potentially to cell death. The risk of exposure to upward fluctuations in irradiance may therefore constitute a potent selective pressure contributing to niche partitioning among cyanobacterial cell types.
To determine if upward fluctuations in irradiance are an important selective factor in niche partitioning among marine picocyanobacteria, we quantitatively analyzed the relative capacities to tolerate a sudden increase in irradiance across five ecologically significant types of Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus isolated from habitats with contrasting dynamic irradiance regimes.
Results and Discussion
The Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus cell types exhibited a gradient in their photophysiological tolerance of upward fluctuations in irradiance (Fig. 1), resulting from different capacities to induce repair (RPSII, functional PSII gained s−1) to counter the PSII photoinactivation rate (PSII lost s−1). To tolerate and therefore exploit upward fluctuations in irradiance, PSII repair must equal the magnitude of the rate of PSII photoinactivation, which we parameterized as:
| (1) |
where E is the scalar irradiance in photons nm−2 s−1 and σi is the effective target size for photons driving PSII photoinactivation [28], with nominal units of nm2. If RPSII<E•|σi|, the cells suffer a net loss of photosynthetic capacity termed photoinhibition [27], and eventually cell death. Quantifying the parameters in Eq. (1) allowed us to determine the basis for different capacities among the Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus cell types to cope with upward fluctuations in irradiance, thereby illuminating their distributions in the ocean.
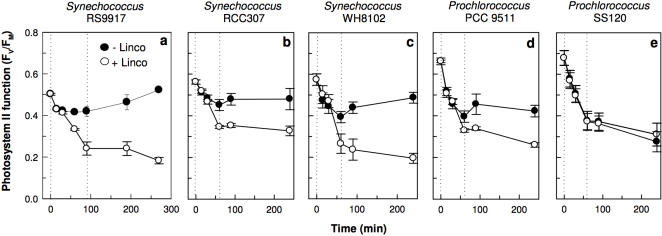
Figure 1. Five marine cyanobacteria from a range of ecological niches show distinct responses of photosystem II quantum yield (FV/FM), reflecting photosystem II activity, to a 10 fold irradiance increase episode followed by recovery under growth light.
The high light episode is delineated by the dotted lines. Cultures were treated (closed) or not (open) with the protein synthesis inhibitor lincomycin to block photosystem II repair (n = 4, ±1 s.e.). Note the strong recovery of photosystem II function in Synechococcus sp. RSS9917, and the lack of recovery in Prochlorococcus sp. SS120.
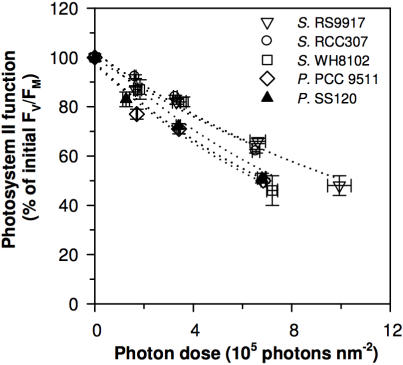
We estimated σi, the effective target size for photons driving PSII photoinactivation under blue light (see Supplementary Data S1 and Figure S1 for the choice of parameterization through target theory), as the exponential decay of PSII function plotted versus cumulative photon dose nm−2 (Fig. 2). We separated the primary photoinactivation of PSII from the counteracting repair using lincomycin, an inhibitor of 16S ribosomal function, to block the synthesis of the D1 protein, thus preventing any PSII repair (Fig. 1). We then monitored the PSII activity by fluorimetry. When RPSII was blocked, σi fell in a narrow range across the five strains (Table 1; Fig. 2), with an average magnitude of 9.1×10−7±0.7×10−7 nm2, comparable to earlier estimates for the photoinactivation target size for higher plants [28]. For a given irradiance wavelength range, σi is likely a fundamental parameter of PSII across oxygenic photosynthetic organisms and growth conditions. In contrast the functional antenna size driving PSII photochemistry (σPSII) varied widely among the strains (Table 1). In blue light, σPSII is ∼2–3×106 times larger than the magnitude of σi and the ratio σPSII/|σi| estimates the relative probability of PSII photochemistry versus PSII photoinactivation. Our results are consistent with PSII photoinactivation depending upon a rare, rate-limiting initial photon capture by a target separate from the main photosynthetic antenna, probably within the oxygen evolving subcomplex of PSII [27], [29], [30]; (see Supplementary Data S1, Figure S1).
Figure 2. Five marine cyanobacteria show comparable inhibition of Photosystem II plotted versus cumulative photon dose (µmol photons nm−2 s−1×s), when photosystem II repair is blocked (lincomycin treated cultures; n = 4, ±1 s.e.).
Open triangle: Synechococcus RS9917; open circle: Synechococcus RCC307; open square: Synechococcus WH8102; open diamond: Prochlorococcus PCC 9511; closed triangle: Prochlorococcus SS120.
Table 1. Origins and photophysiological features of the five marine cyanobacteria used in this study.
| Synechococcus RS9917 | Synechococcus RCC307 | Synechococcus WH8102 | Prochlorococcus PCC 9511 | Prochlorococcus SS120 | |
| Origin | Gulf of Aqaba, surface | Mediterranean, surface | Caribbean Sea, surface | Sargasso Sea, surface | Sargasso Sea, 120 m depth |
| Water regime | Eutrophic | Mesotrophic | Oligotrophic | Oligotrophic | Oligotrophic |
| Antenna type | Small PBS, Amax∼620 nm | Large PBS, Amax∼550 nm | Large PBS, Amax∼495 nm | Pcb ring, Amax∼465 nm | Pcb ring, Amax∼465 nm |
| NPQ | 0.07±0.02 | 0.43±0.16 | 0.22±0.01 | 0.07±0.02 | 0.04±0.01 |
| σPSII (nm2 PSII−1) | 0.2±0.02 | 1.7±0.3 | 2.8±0.1 | 2.1±0.1 | 2.9±0.5 |
| D1 content (fmol µg protein−1) | 34±5 | 21±2 | 26±6 | 78±7 | 102±15 |
| Protein specific σPSII (nm2 µg protein−1) | 0.5±0.01×1010 | 2.1±0.04×1010 | 4.3±0.04×1010 | 9.8±0.04×1010 | 18±0.5×1010 |
| |σi| (nm2) | 7.6±0.7×10−7 | 7.4±0.3×10−7 | 11±0.02×10−7 | 9.7±0.4×10−7 | 9.5±0.7×10−7 |
| RPSII (s−1) | 1.3±0.2×10−4 | 1.1±0.1×10−4 | 1.6±0.4×10−4 | 0.9±0.3×10−4 | 0.1±0.05×10−4 |
| E TOLl, (µmol m−2 s−1) | 283±26 | 255±5 | 223±31 | 152±45 | 20±9 |
PBS, phycobilisome; Pcb, Prochlorophyte chlorophyll binding protein; NPQ, non photochemical quenching of fluorescence induced at 300 µmol photons m−2 s−1; σPSII, PSII effective absorbance cross section for blue light; |σI|, magnitude of the effective target size for PSII photoinactivation by blue light; RPSII, PSII repair rate; E TOL, maximal variable irradiance (n = 4±s.e.).
In spite of their comparable σi, these picocyanobacteria showed different tolerances to a sudden onset of high irradiance, which were largely explicable through differences in their inducible RPSII (Table 1). The Synechococcus strains all rapidly induced a strong RPSII in response to increased irradiance, thereby countering the increased photoinactivation rate and limiting any net decrease in PSII capacity. The same induction of RPSII under high irradiance supported rapid subsequent recovery of PSII capacity upon a return to low irradiance, particularly in the coastal Synechococcus RS9917 and the mesotroph Synechococcus RCC307 (Fig. 1A, B). The Prochlorococcus strains are functionally differentiated from the Synechococcus by their weaker inducible RPSII, especially in the low light adapted Prochlorococcus SS120, which showed negligible induction of RPSII in response to transient high light exposure (Table 1), and no ability to recover within 3 h of a return to low light (Fig. 1E). Only two of the Synechococcus strains induced a modest non-photochemical quenching to divert excitation from reaction centre II [31], [32] (Table 1), and in all strains the recovery from high irradiance was thus dependent upon protein synthesis (Fig. 1, Fig. S2), and not upon relaxation of non-photochemical quenching of fluorescence.
We compared the tolerance of the strains of a short-term increase in irradiance by estimating the maximum irradiance, E TOL, at which rapidly inducible repair can counter photoinactivation for each strain through a rearrangement of Eq. (1): E TOL = RPSII/|σi|. The coastal Synechococcus RS9917 could withstand a remarkable 14-fold short-term increase above its acclimated low growth irradiance through rapid induction of RPSII to counter the increased rate of photoinactivation (Table 1). This ability to exploit upward fluctuations in irradiances decreases among the strains from onshore to deep offshore waters (Table 1). The deep-sea ecotype Prochlorococcus SS120 showed little capacity to withstand a short-term exposure to an upward fluctuation in irradiance (Table 1), and no capacity for subsequent recovery within 3 h (Fig. 1), in keeping with selection for a deep ecological niche characterized by low and stable irradiance. Both Prochlorococcus strains contain significantly more of the PSII D1 protein (Table 1, Figure S2) than do the Synechococcus strains. Maintaining this heavy investment may be untenable for Prochlorococcus in the face of faster PSII photoinactivation under increased light. Moreover, Prochlorococcus possess large light harvesting antennae composed of membrane-intrinsic Prochlorophyte chlorophyll binding (Pcb) proteins [17], which form an annular ring around PSII [16]. We hypothesize that this Pcb antenna may hinder the turnover of photoinactivated D1 proteins (Figure S2), thereby limiting Prochlorococcus modulation of RPSII in comparison to the Synechococcus strains with extrinsic phycobilisome antennae.
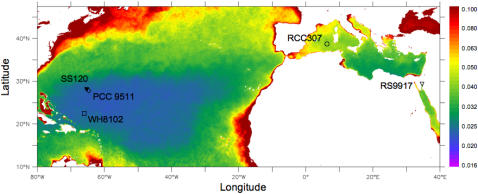
The abilities of these picocyanobacteria to withstand and exploit short-term exposure to high irradiance correlate with the origins of the strains along an onshore to offshore axis (Fig. 3). Coastal phytoplankton experience more variability in irradiance compared to open ocean organisms, notably due to an increase in the vertical attenuation of irradiance (kd) and water mixing in the water column towards shore (Fig. 3; [21], [22]. Vertical irradiance profiles near-shore change more rapidly with depth than in offshore waters. As a result, phytoplankton circulating in the near-shore water column experiences more rapid changes in irradiance under otherwise comparable conditions [21], [22]. The capacity for tolerance and exploitation of sudden irradiance changes thus appears less important in offshore, clear, stratified waters.
Figure 3. The ability of five marine cyanobacteria strains to tolerate short-term increases in irradiance (E TOL) relates to the vertical light attenuation coefficient (k490) at their location of origin.
Color bar indicates the 2006 annual average vertical attenuation coefficient at 490 nm, k490. Symbols indicate the origin of the strains sampled near the surface (open symbols) except for SS120 strain sampled at 120 meters (closed triangle).
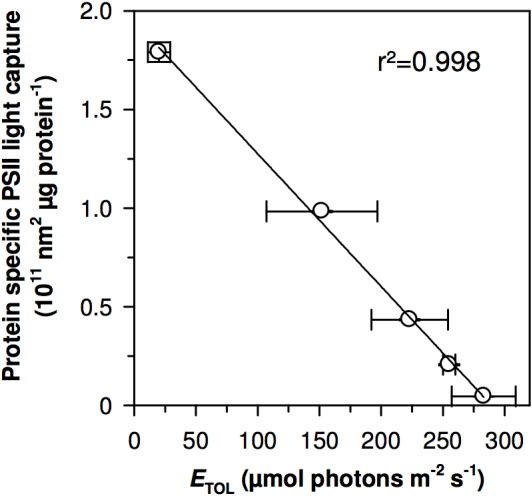
Prochlorococcus cells dominate over Synechococcus of the WH8102 type in oligotrophic marine ecosystems [2], [5], even though Synechococcus WH8102 shows comparable functional photosynthetic antenna size per PSII (Table 1) and a higher capacity to tolerate and exploit upward fluctuations in irradiance. The large phycobilisome of Synechococcus WH8102 is, however, more expensive in nitrogen than the Pcb antenna of Prochlorococcus [33]. Despite the superior ability of Synechococcus WH8102 to exploit and recover from irradiance fluctuations the high nitrogen cost for its antenna may relegate this cell type to minority status in oligotrophic cyanobacterial communities. We find that the Prochlorococcus strains do achieve much higher capacity for PSII light capture per cellular protein investment, when compared to Synechococcus (Table 1; Fig. 4). Across the strains, protein-specific blue light capture capacity varied 40-fold, and showed a strong negative correlation with E TOL, the capacity to tolerate upward irradiance fluctuations (Fig. 4). The evolution from a Synechococcus-like ancestor to Prochlorococcus with a lower nitrogen cost Pcb photosynthetic antenna may have led to limitations on the induction of PSII repair, and a consequent susceptibility to irradiance fluctuations through specialization for stable, oligotrophic environments [33]. A constrained nitrogen budget may thus force a cellular allocation of resources between PSII repair capacity, altering E TOL, and the ability of cells to harvest light. Prochlorococcus may thus dominate these oligotrophic, stratified environments not only because of the relatively low nitrogen cost of their photosynthetic antennae but also because their limited modulation of PSII repair is feasible where there is little fluctuation in light.
Figure 4. A trade-off between protein specific light capture capacity (protein specific σPSII) and tolerance of irradiance variations (E TOL) across five marine cyanobacteria.
Prochlorococcus strains show a high protein specific σPSII, which varied 40-fold across the strains and shows a strong negative correlation with E TOL (µmol photons m−2 s−1), the capacity to tolerate upward irradiance fluctuations, which was highest in the coastal Synechococcus RSS9917 (n = 4, ±1 s.e.; r2 = 0.98).
Our measurements of the effective target cross-section for photosystem II photoinactivation show that this parameter is conserved across marine picocyanobacteria, likely as a fundamental property of photosystem II [28]. This σi can now be combined with active fluorimetry to efficiently estimate photosystem II repair rates and the maximum short-term increase in irradiance (E TOL) that can be tolerated and exploited by phytoplankton species or communities in the field. These parameters are therefore valuable components for future biogeochemical and ecosystem models of the distribution and abundance of picocyanobacteria, definitions of phytoplankton functional groups, and their responses to environmental change. Current models of picophotoautotroph community responses to environmental change have heretofore considered steady state parameters determined on fully acclimated cultures, including the optimal irradiance for growth (see e.g. [34]). We show here that surface Prochlorococcus have less capacity to induce PSII repair than marine Synechococcus, despite a similar optimal irradiance for growth [6], [19], [20] consistent with their geographic distribution. A high optimal irradiance for acclimated growth may not necessarily correlate with tolerance and exploitation of sudden irradiance increases, a dynamic factor contributing to niche-partitioning among marine picocyanobacteria.
Materials and Methods
Culturing and time course experiment
The marine cyanobacteria Synechococcus strains RS9917, WH8102, RCC307 [35] and Prochlorococcus strains PCC 9511 and SS120 [6], [18] were grown in PCR-S11 medium [36] in polystyrene culture flasks at 22°C and 25 µmol photons m−2 s−1 white light. These picocyanobacteria were selected because of their importance as representatives of the major ecological functional groups of marine picophytoplankton, because their genomes are sequenced and they are thus emerging model organisms, and because their small cell size and simple, consistent optical properties [37] facilitated the fluorescence measurements and estimates of effective absorbance cross sections.
Exponential cultures were split into two flasks. One was supplemented with 500 µg mL−1 lincomycin and both flasks were incubated in the dark for 10 min, to allow the antibiotic to penetrate the cells and inhibit ribosome function. The two flasks were then shifted for 60–90 min to ca. 280 µmol photons m−2 s−1 blue light (LEE Filter #183, Panavision; 455–479 nm peak transmission, 406–529 nm half-height width). Samples were collected at 15, 30 and 60 (and 90) min to measure biophysical properties and for later protein immunodetection. The sub-cultures were then shifted back to their initial growth light and sampled after 30 and 180 min of recovery.
Fluorescence measurements
Culture aliquots were dark-adapted and a blue-green modulated measuring light (4 Hz; Xenon-PAM, Walz, Effetrich, Germany) was activated to measure F0. Actinic irradiance was then activated at 280 µmol photons m−2 s−1; after signal stabilisation (Ft level), a saturating light pulse (4,000 µmol photons m−2 s−1, 500 ms) was triggered to determine the light acclimated maximal fluorescence (FM′). The PSII inhibitor 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea was then added and after signal stabilisation, a light pulse was triggered again to determine the maximal fluorescence FM to estimate the photochemical yield of PSII, FV/FM = (FM−F0)/FM and NPQ = (FM−FM′)/FM′ under the treatment light level.
The light-acclimated effective absorption cross-section serving PSII photochemistry (σPSII, nm2 PSII−1), reflecting the functional antenna size, was determined on a culture aliquot illuminated for 2 min under the treatment light level (blue LED, 455±20 nm), followed by a saturating single turn-over flash (blue LED, 455±20 nm; FIRe fluorimeter, Satlantic, Halifax, NS Canada) to determine the σPSII of the open PSII reaction center [38], [39]. We estimated the capacity for PSII light capture per cellular protein investment as the product of σPSII (nm2 PSII−1) and D1 per µg protein (see below), assuming that under acclimation to low growth light, D1 protein content closely approximates functional PSII content [40].
For comparison with σPSII, and to facilitate future modelling efforts, we chose to estimate an effective target cross section for PSII photoinactivation (σi, nm2) by plotting the exponential decay of the PSII quantum yield FV/FM in the absence of repair versus the cumulative photon dose nm−2 (see Supplementary Data S1 and Figure S1 for justification). Note that the σi and σPSII estimates are for blue irradiance, approximating the spectral light quality in marine environments. Under other wavelength ranges σi would differ because the absorbance cross section for photoinactivation is dependent upon wavelength [29], [41].
Immunodetections
Cells were harvested on glass fibre filters (25 mm, Whatman) and the proteins were extracted by 3 thawing/sonicating rounds in extraction buffer. The total protein concentration was determined (Lowry protein assay kit, Biorad). Two µg of total protein were loaded on a 4–12% acrylamide precast NuPAGE gel (Invitrogen). Along with the samples, D1 protein standards (Agrisera) were loaded to establish a standard curve. Electrophoresis was run for 40 min at 200 V and the proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane. Following the transfer, the membrane was immersed in blocking solution (Amersham Biosciences) for at least 2 hours. The PVDF membranes were successively incubated with primary antibodies directed against D1 (Agrisera, 1/50,000) in Tween-TBS in the presence of 2% blocking agent and anti-chicken secondary antibodies coupled with horseradish peroxidase (Biorad, 1/50,000). The membranes were developed by chemoluminescence using ECL Advance (Amersham biosciences) and a CCD imager (FluorSMax, Biorad). Target protein concentrations were determined by fitting the sample signal values on these curves to protein standard curves.
Remote Sensing data
The 2006 annual average vertical attenuation coefficients at 490 nm (k490) were obtained from the MODIS project [42].
Supporting Information
Parameterisation of photosystem II photoinactivation
(0.04 MB DOC)
Exponential decays of PSII capacity in lincomycin treated cultures of the five picocyanobacteria. In contrast to Figure 2, the photoinhibitory photon dose was calculated as coming through the photosynthetic antenna, by multiplying E×time×σPSII for the X-axis. Note the greater scatter among species in this plot compared to Figure 2.
(0.19 MB TIF)
The initial level and subsequent variations in the core subunit D1 of Photosystem II among the five marine cyanobacteria during exposure to a high light episode and recovery. D1 protein was determined by quantitative immunoblotting in cultures treated (closed) or not (open) with the protein synthesis inhibitor lincomycin to block photosystem II repair (n = 4, ±1 s.e.). The high irradiance episode is delineated by dotted lines. Note that in the absence of repair, Synechococcus RSS9917 was able to degrade and clear D1 proteins from photoinactivated photosystems II (A) as seen by the rapid 70% decrease in D1 content in cultures treated with lincomycin. In contrast, Prochlorococcus SS120 appeared to have limited 30% clearance of D1 protein during the high light episode (E), in spite of suffering significant photoinactivation of PSII (Figure 1E).
(0.30 MB TIF)
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Barnett & J. Cullen (Dalhousie University) for guidance in the application of their Fireworx software for analyses of σPSII. A. Cockshutt and C. Brown (Environmental Proteomics, New Brunswick, Canada) provided characterized D1 protein standards, antibodies and protocols.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: Douglas A. Campbell is a minority share-holder in Environmental Proteomics, a company which provided an anti-PsbA antibody and associated protein quantitation standard used to generate data for Table 1 and Figure S2 for this study. We do not believe this connection constitutes a competing interest.
Funding: The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada provided Discovery grant (DAC, ZVF, AJI), University Faculty Award (ZVF) and Canada Research Chair (DAC) funding, while the Canada and New Brunswick Innovation Foundations (DAC, ZVF) provided equipment funding.
References
- 1.Richardson TL, Jackson GA. Small phytoplankton and carbon export from the surface ocean. Science. 2007;315:838–840. doi: 10.1126/science.1133471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Partensky F, Hess WR, Vaulot D. Prochlorococcus, a marine photosynthetic prokaryote of global significance. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 1999;63:106–127. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.63.1.106-127.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bouman HA, Ulloa O, Scanlan DJ, Zwirglmaier K, Li WK, et al. Oceanographic basis of the global surface distribution of Prochlorococcus ecotypes. Science. 2006;312:918–921. doi: 10.1126/science.1122692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson ZI, Zinser ER, Coe A, McNulty NP, Woodward EM, et al. Niche partitioning among Prochlorococcus ecotypes along ocean-scale environmental gradients. Science. 2006;311:1737–1740. doi: 10.1126/science.1118052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zwirglmaier K, Heywood JL, Chamberlain K, Woodward EM, Zubkov MV, et al. Basin-scale distribution patterns of picocyanobacterial lineages in the Atlantic Ocean. Environ Microbiol. 2007;9:1278–1290. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moore LR, Goericke R, Chisholm SW. Comparative physiology of Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus: influence of light and temperature on growth, pigments, fluorescence and absorptive properties. Marine Ecology-Progress Series. 1995;116:259–275. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Not F, Massana R, Latasa M, Marie D, Colson C, et al. Late summer community composition and abundance of photosynthetic picoeukaryotes in Norwegian and Barents Seas. Limnology and Oceanography. 2005;50:1677–1686. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Palenik B. Chromatic adaptation in marine Synechococcus strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2001;67:991–994. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.2.991-994.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Everroad C, Six C, Partensky F, Thomas JC, Holtzendorff J, et al. Biochemical bases of type IV chromatic adaptation in marine Synechococcus spp. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:3345–3356. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.9.3345-3356.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stomp M, Huisman J, de Jongh F, Veraart AJ, Gerla D, et al. Adaptive divergence in pigment composition promotes phytoplankton biodiversity. Nature. 2004;432:104–107. doi: 10.1038/nature03044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lantoine F, Neveux J. Spatial and seasonal variations in abundance and spectral characteristics of phycoerythrins in the tropical northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Deep - Sea Research I. 1997;44:223–246. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Olson RJ, Zettler ER, Armbrust EV, Chisholm SW. Pigment, size and distribution of Synechococcus in the North Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Limnology and Oceanography. 1990;35:45–58. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sherry ND, Wood AM. Phycoerythrin-containing picocyanobacteria in the Arabian Sea in February 1995: diel patterns, spatial variability, and growth rates. Deep Sea Research Part Ii Topical Studies in Oceanography. 2001;48:1263–1283. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wood AM, Phinney DA, Yentsch CS. Water column transparency and the distribution of spectrally distinct forms of phycoerythrin-containing organisms. Marine Ecology - Progress Series. 1998;162:25–31. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wood AM, Lipsen M, Coble P. Fluorescence-based characterization of phycoerythrin-containing cyanobacterial communities in the Arabian Sea during the Northeast and early Southwest Monsoon (1994–1995). Deep Sea Research II. 1999;46:1769–1790. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bibby TS, Mary I, Nield J, Partensky F, Barber J. Low-light-adapted Prochlorococcus species possess specific antennae for each photosystem. Nature. 2003;424:1051–1054. doi: 10.1038/nature01933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Partensky F, Garczarek L. The photosynthetic apparatus of chlorophyll b- and d-containing Oxychlorobacteria. In: Larkum AWD, editor. Photosynthesis in Algae. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moore LR, Rocap G, Chisholm SW. Physiology and molecular phylogeny of coexisting Prochlorococcus ecotypes. Nature. 1998;393:464–467. doi: 10.1038/30965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Six C, Thomas JC, Brahamsha B, Lemoine Y, Partensky F. Photophysiology of the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH8102, a new model organism. Aquatic Microbial Ecology. 2004;35:17–29. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kana TM, Glibert PM. Effect of irradiances up to 2000 µE m−2 s−1 on marine Synechococcus WH7803 - I. Growth, pigmentation, and cell composition. Deep-Sea Research. 1987;34:479–485. [Google Scholar]
- 21.MacIntyre HL, Kana TM, Geider RJ. The effect of water motion on short-term rates of photosynthesis by marine phytoplankton. Trends Plant Sci. 2000;5:12–17. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(99)01504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schubert H, Sagert S, Forster RM. Evaluation of the different levels of variability in the underwater light field of a shallow estuary. Helgoland Marine Research. 2001;55:12–22. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Park YI, Chow WS, Anderson JM. Light inactivation of functional photosystem II in leaves of peas grown in moderate light depends on photon exposure. Planta. 1995;196:401–411. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tyystjarvi E, Aro EM. The rate constant of photoinhibition, measured in lincomycin-treated leaves, is directly proportional to light intensity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:2213–2218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.5.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shelly K, Heraud P, Beardall J. Nitrogen limitation in Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) leads to increased susceptibility to damage by ultraviolet-B radiation but also increased repair capacity. Journal of Phycology. 2002;38:713–720. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nixon PJ, Barker M, Boehm M, de Vries R, Komenda J. FtsH-mediated repair of the photosystem II complex in response to light stress. J Exp Bot. 2005;56:357–363. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev SI, Murata N. A new paradigm for the action of reactive oxygen species in the photoinhibition of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1757:742–749. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sinclair J, Park YI, Chow WS, Anderson JM. Target theory and the photoinactivation of Photosystem II. Photosynthesis Research. 1996;50:33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00018219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sarvikas P, Hakala M, Patsikka E, Tyystjarvi T, Tyystjarvi E. Action spectrum of photoinhibition in leaves of wild type and npq1-2 and npq4-1 mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006;47:391–400. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcj006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hakala M, Tuominen I, Keranen M, Tyystjarvi T, Tyystjarvi E. Evidence for the role of the oxygen-evolving manganese complex in photoinhibition of Photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1706:68–80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2004.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wilson A, Ajlani G, Verbavatz JM, Vass I, Kerfeld CA, et al. A soluble carotenoid protein involved in phycobilisome-related energy dissipation in cyanobacteria. Plant Cell. 2006;18:992–1007. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.040121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bailey S, Mann NH, Robinson C, Scanlan DJ. The occurrence of rapidly reversible non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll a fluorescence in cyanobacteria. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:275–280. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ting CS, Rocap G, King J, Chisholm SW. Cyanobacterial photosynthesis in the oceans: the origins and significance of divergent light-harvesting strategies. Trends Microbiol. 2002;10:134–142. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(02)02319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Follows MJ, Dutkiewicz S, Grant S, Chisholm SW. Emergent biogeography of microbial communities in a model ocean. Science. 2007;315:1843–1846. doi: 10.1126/science.1138544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fuller NJ, Marie D, Partensky F, Vaulot D, Post AF, et al. Clade-specific 16S ribosomal DNA oligonucleotides reveal the predominance of a single marine Synechococcus clade throughout a stratified water column in the Red Sea. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2003;69:2430–2443. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.5.2430-2443.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rippka R, Coursin T, Hess W, Lichtlé C, Scanlan DJ, et al. Prochlorococcus marinus Chisholm et al. 1992 subsp. pastoris subsp. nov. strain PCC 9511, the first axenic chlorophyll a 2/b 2-containing cyanobacterium (Oxyphotobacteria). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 2000;50:1833–1847. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-5-1833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Morel A, Ahn YH, Partensky F, Vaulot D, Claustre H. Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus: A comparative study of their optical properties in relation to their size and pigmentation. Journal of Marine Research. 1993;51:617–649. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gorbunov MY, Kolber ZS, Falkowski PG. Measuring photosynthetic parameters in individual algal cells by Fast Repetition Rate fluorometry. Photosynth Res. 1999;62:141–153. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Barnett AB. 2007 Fireworx ( http://sourceforge.net/projects/fireworx), Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Burns RA, MacKenzie TDB, Campbell DA. Inorganic carbon repletion constrains steady-state light acclimation in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus. Journal of Phycology. 2006;42:610–621. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cullen JJ, Neale PJ, Lesser MP. Biological weighting function for the inhibition of phytoplankton photosynthesis by ultraviolet radiation. Science. 1992;258:646–650. doi: 10.1126/science.258.5082.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Feldman GC, McClain CR. Ocean Color Web, Aqua-MODIS Reprocessing 1.1, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. 2007 Eds. Kuring, N., Bailey, S. W. 10 July 2007 ( http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/) [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sicora C, Mate Z, Vass I. The interaction of visible and UV-B light during photodamage and repair of Photosystem II. Photosynth Res. 2003;75:127–137. doi: 10.1023/A:1022852631339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Neale PJ. Modeling the effects of ultraviolet radiation on estuarine phytoplankton production: impact of variations in exposure and sensitivity to inhibition. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;62:1–8. doi: 10.1016/s1011-1344(01)00159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Heraud P, Roberts S, Shelly K, Beardall J. Interactions between UV-B exposure and phosphorus nutrition. II. Effects on rates of damage and repair. Journal of Phycology. 2005;41:1212–1218. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Boucher NP, Prezelin BB. An in situ biological weighting function for UV inhibition of phytoplankton carbon fixation in the Southern Ocean. Marine Ecology - Progress Series. 1996;144:223–236. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Parameterisation of photosystem II photoinactivation
(0.04 MB DOC)
Exponential decays of PSII capacity in lincomycin treated cultures of the five picocyanobacteria. In contrast to Figure 2, the photoinhibitory photon dose was calculated as coming through the photosynthetic antenna, by multiplying E×time×σPSII for the X-axis. Note the greater scatter among species in this plot compared to Figure 2.
(0.19 MB TIF)
The initial level and subsequent variations in the core subunit D1 of Photosystem II among the five marine cyanobacteria during exposure to a high light episode and recovery. D1 protein was determined by quantitative immunoblotting in cultures treated (closed) or not (open) with the protein synthesis inhibitor lincomycin to block photosystem II repair (n = 4, ±1 s.e.). The high irradiance episode is delineated by dotted lines. Note that in the absence of repair, Synechococcus RSS9917 was able to degrade and clear D1 proteins from photoinactivated photosystems II (A) as seen by the rapid 70% decrease in D1 content in cultures treated with lincomycin. In contrast, Prochlorococcus SS120 appeared to have limited 30% clearance of D1 protein during the high light episode (E), in spite of suffering significant photoinactivation of PSII (Figure 1E).
(0.30 MB TIF)