Abstract
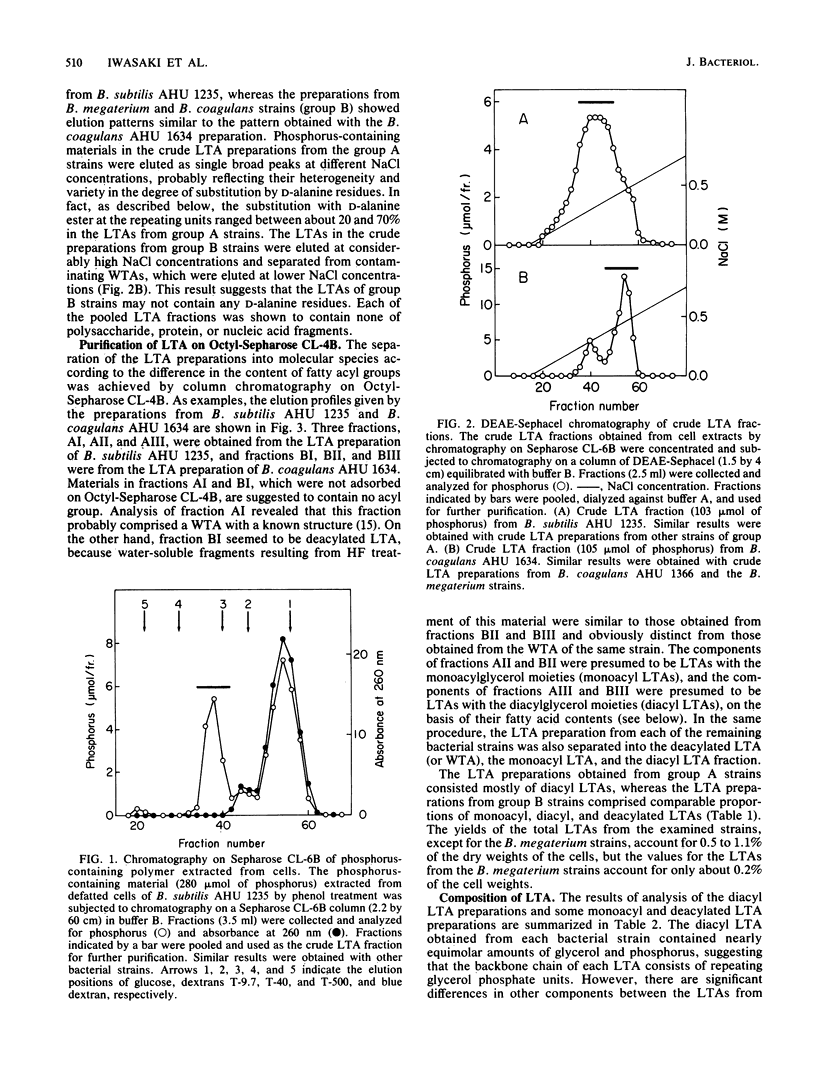
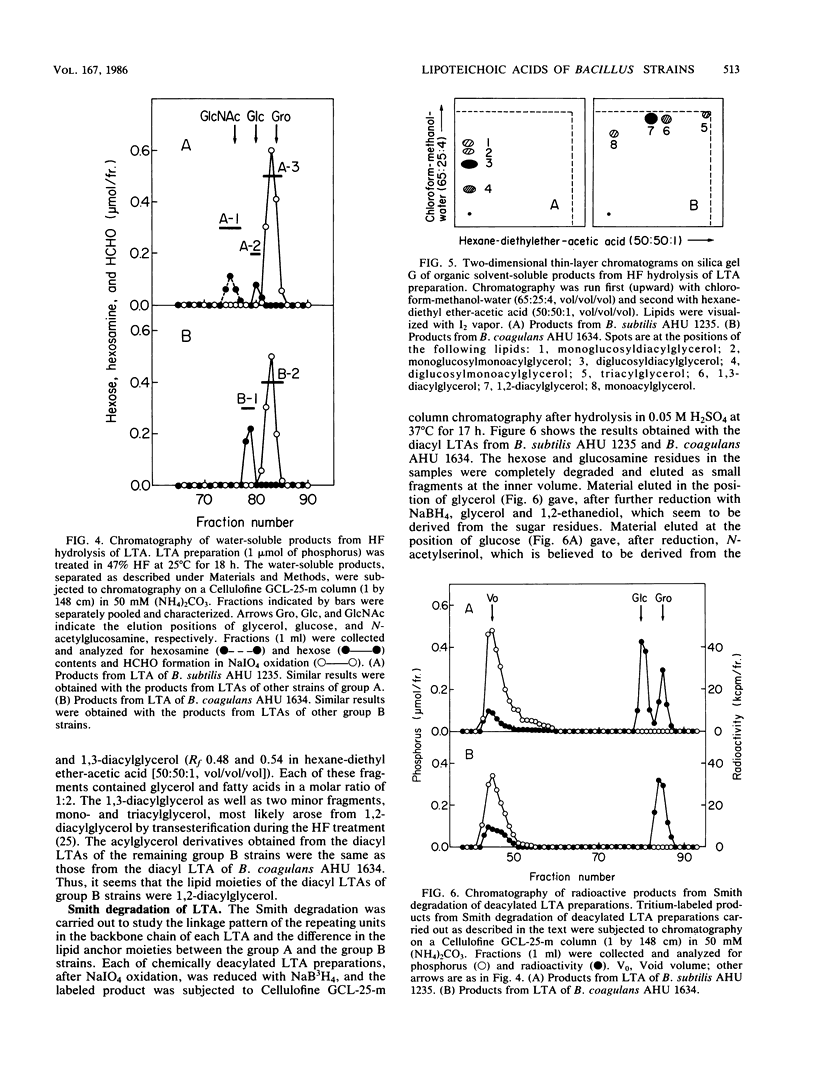
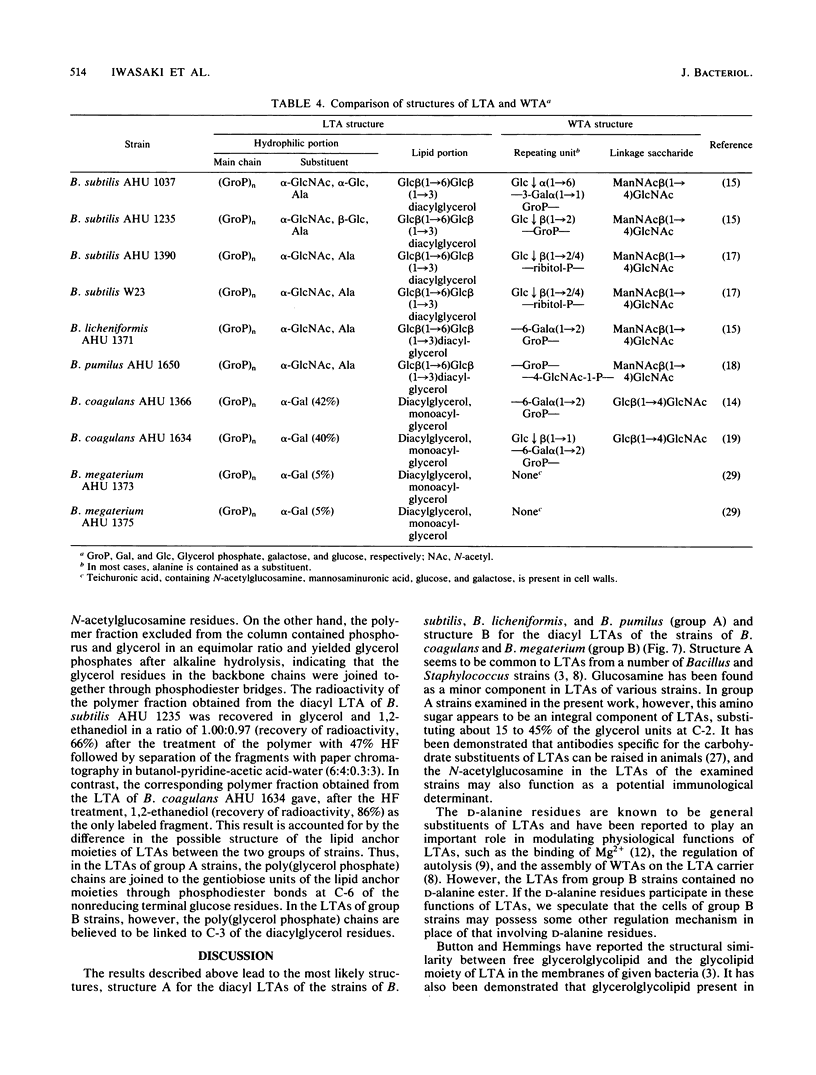
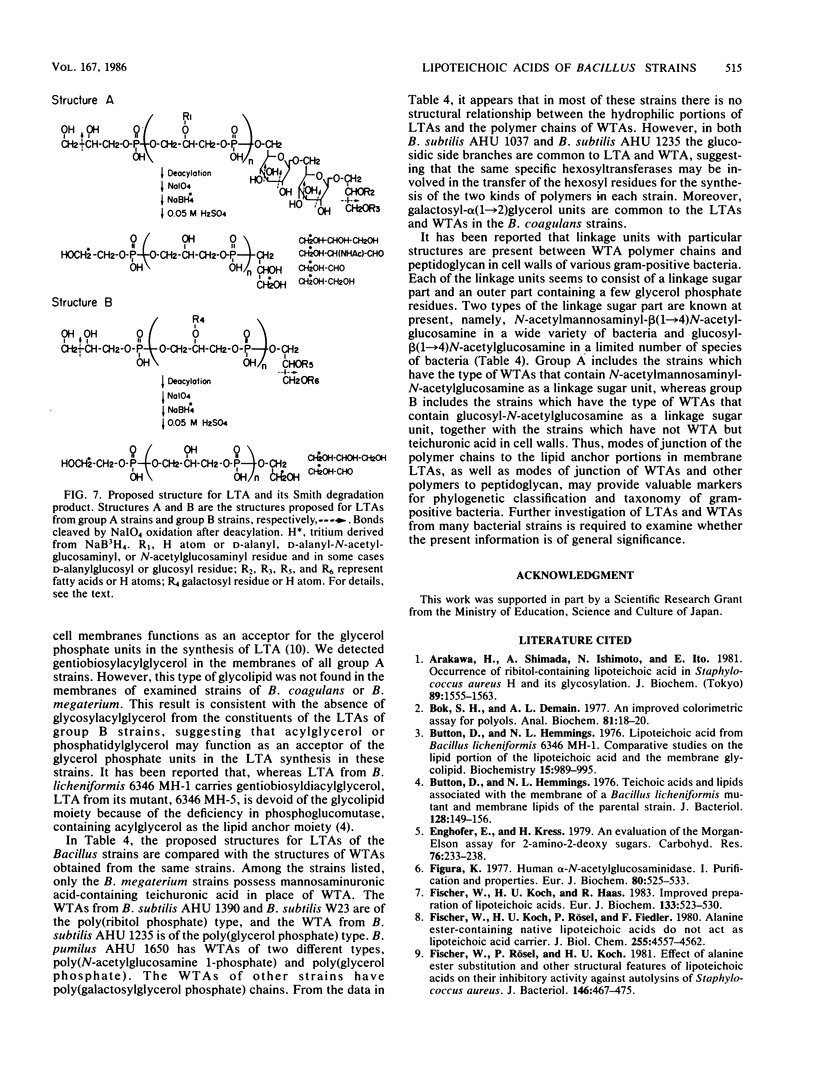
Structural studies were carried out on lipoteichoic acids obtained from defatted cells of 10 Bacillus strains by phenol-water partition followed by chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel and Octyl-Sepharose columns. A group of the tested bacteria (group A), Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus pumilus, was shown to have a diacyl form of lipoteichoic acids which contained D-alanine, D-glucose, D-glucosamine, fatty acids, and glycerol in molar ratios to phosphorus of 0.35 to 0.69, 0.07 to 0.15 to 0.43, 0.06 to 0.11, and 0.95 to 1.18, respectively, whereas the other group (group B), Bacillus coagulans and Bacillus megaterium, had diacyl lipoteichoic acids which contained D-galactose, fatty acids, and glycerol in molar ratios to phosphorus of 0.05 to 0.42, 0.06 to 0.12, and 0.96 to 1.07, respectively. After treatment with 47% hydrogen fluoride, the lipoteichoic acids obtained from group A strains commonly gave a hydrophobic fragment, gentiobiosyl-beta (1----1 or 3)diacylglycerol, in addition to dephosphorylated repeating units, glycerol, 2-D-alanylglycerol, N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl-alpha (1----2)glycerol, and D-alanyl-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl-alpha (1----2)glycerol, whereas the lipoteichoic acids from group B strains yielded diacylglycerol in addition to glycerol and D-galactosyl-alpha (1----2)glycerol. The results together with data from Smith degradations indicate that in the lipoteichoic acids of group A strains the polymer chains, made up of partially alanylated glycerol phosphate and glycosylglycerol phosphate units, are joined to the acylglycerol anchors through gentiobiose. However, in the lipoteichoic acids of group B strains, the partially galactosylated poly(glycerolphosphate) chains are believed to be directly linked to the acylglycerol anchors.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa H., Shimada A., Ishimoto N., Ito E. Occurrence of ribitol-containing lipoteichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus H and its glycosylation. J Biochem. 1981 May;89(5):1555–1563. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bok S. H., Demain A. L. An improved colorimetric assay for polyols. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jul;81(1):18–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Button D., Hemmings N. L. Lipoteichoic acid from Bacillus licheniformis 6346 MH-1. Comparative studies on the lipid portion of the lipoteichoic acid and the membrane glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):989–995. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Button D., Hemmings N. L. Teichoic acids and lipids associated with the membrane of a Bacillus licheniformis mutant and the membrane lipids of the parental strain. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.149-156.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enghofer E., Kress H. An evaluation of the Morgan--Elson assay for 2-amino-2-deoxy sugars. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Nov;76:233–238. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(79)80022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Koch H. U., Haas R. Improved preparation of lipoteichoic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):523–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Koch H. U., Rösel P., Fiedler F. Alanine ester-containing native lipoteichoic acids do not act as lipoteichoic acid carrier. Isolation, structural and functional characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4557–4562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Rösel P., Koch H. U. Effect of alanine ester substitution and other structural features of lipoteichoic acids on their inhibitory activity against autolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):467–475. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.467-475.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganfield M. C., Pieringer R. A. The biosynthesis of nascent membrane lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus faecium (S. faecalis ATCC 9790) from phosphatidylkojibiosyl diacylglycerol and phosphatidylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5164–5169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabasakalian P., Kalliney S., Westcott A. Enzymatic blood glucose determination by colorimetry of N,N-diethylaniline-4-aminoantipyrine. Clin Chem. 1974 May;20(5):606–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya S., Araki Y., Ito E. Structural studies on the linkage unit between poly(galactosylglycerol phosphate) and peptidoglycan in cell walls of Bacillus coagulans. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):41–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya S., Yokoyama K., Araki Y., Ito E. N-acetylmannosaminyl(1----4)N-acetylglucosamine, a linkage unit between glycerol teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in cell walls of several Bacillus strains. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):990–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.990-996.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch H. U., Fischer W. Acyldiglucosyldiacylglycerol-containing lipoteichoic acid with a poly(3-O-galabiosyl-2-O-galactosyl-sn-glycero-1-phosphate) chain from Streptococcus lactis Kiel 42172. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5275–5281. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima N., Araki Y., Ito E. Structure of the linkage units between ribitol teichoic acids and peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):299–306. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.299-306.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima N., Iida J., Araki Y., Ito E. Structural studies on the linkage unit between poly(N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate) and peptidoglycan in cell walls of Bacillus pumilus AHU 1650. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):331–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima N., Uchikawa K., Araki Y., Ito E. A common linkage saccharide unit between teichoic acids and peptidoglycan in cell walls of Bacillus coagulans. J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1085–1092. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Occurrence and function of membrane teichoic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 31;472(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVAK M. COLORIMETRIC ULTRAMICRO METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:431–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Fischer W. Trihexosyldiacylglycerol and acyltrihexosyldiacylglycerol as lipid anchors of the lipoteichoic acid of Lactobacillus casei DSM 20021. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Jan;359(1):1–11. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Araki Y., Ito E. Structure of teichoic-acid--glycopeptide complexes from cell walls of Bacillus cereus AHU 1030. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Stead A. The reaction of phosphoglycolipids and other lipids with hydrofluoric acid. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):461–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1430461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengenmayer F., Ueberschär K. H., Kurz G., Sund H. D-galactose dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas saccharophila. Purification, properties and structure. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 3;40(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Araki Y., Ito E. The primary structure of teichuronic acid in Bacillus subtilis AHU 1031. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):83–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Koike Y., Arakawa H., Yokoyama K., Sasaki Y., Kawamura T., Araki Y., Ito E., Takao S. Distribution of mannosamine and mannosaminuronic acid among cell walls of Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.15-21.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K. Human alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase. 1. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):523–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


