Abstract
The virulence of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolated from various water sources was compared with that of clinical strains by in vitro assays of adhesion, invasion and cytotoxicity to HeLa cells. Variation in degree of attachment was observed, but this did not appear to be related to strain source, However, water strains were less invasive and less cytotoxic to HeLa cells than clinical strains as shown by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. These differences were particularly evident between clinical and water isolates of the same serotype and biotype implicated in an outbreak of campylobacter enteritis in a school. The enhanced virulence of the clinical isolates, possibly induced by passage, was confirmed by colonization tests on infant mice.
Full text
PDF


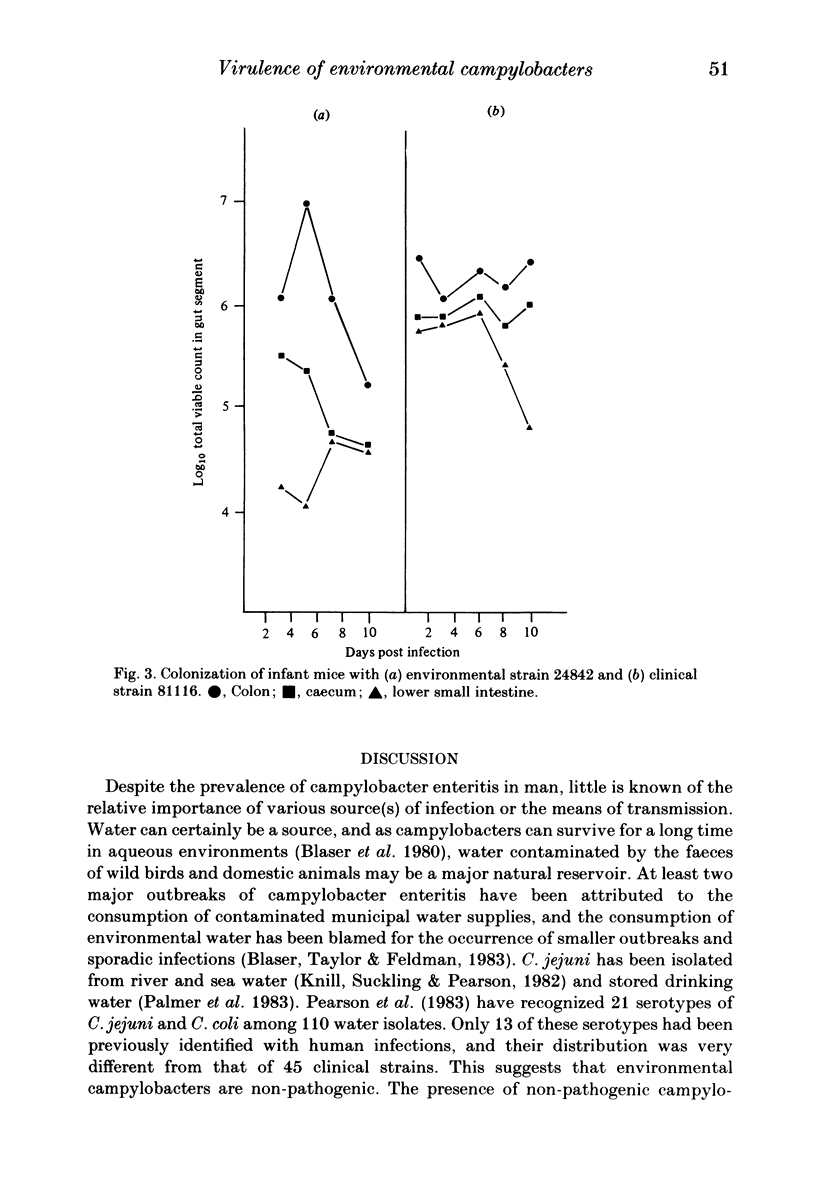



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Hardesty H. L., Powers B., Wang W. L. Survival of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni in biological milieus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):309–313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.309-313.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Berry L. J. The role of gut flora and animal passage in the colonisation of adult mice with Campylobacter jejuni. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Feb;17(1):59–66. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Pope L. M., Berry L. J. Intestinal colonization of neonatal animals by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.884-892.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Pathogenesis of acute bacterial diarrheal disorders. Annu Rev Med. 1981;32:341–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.32.020181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. Toxins produced by Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):229–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E. Infection of HeLa cells with Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR10 bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.290-295.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manninen K. I., Prescott J. F., Dohoo I. R. Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from animals and humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Pearson A. D. The identification of outer membrane proteins and flagella of Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1201–1208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
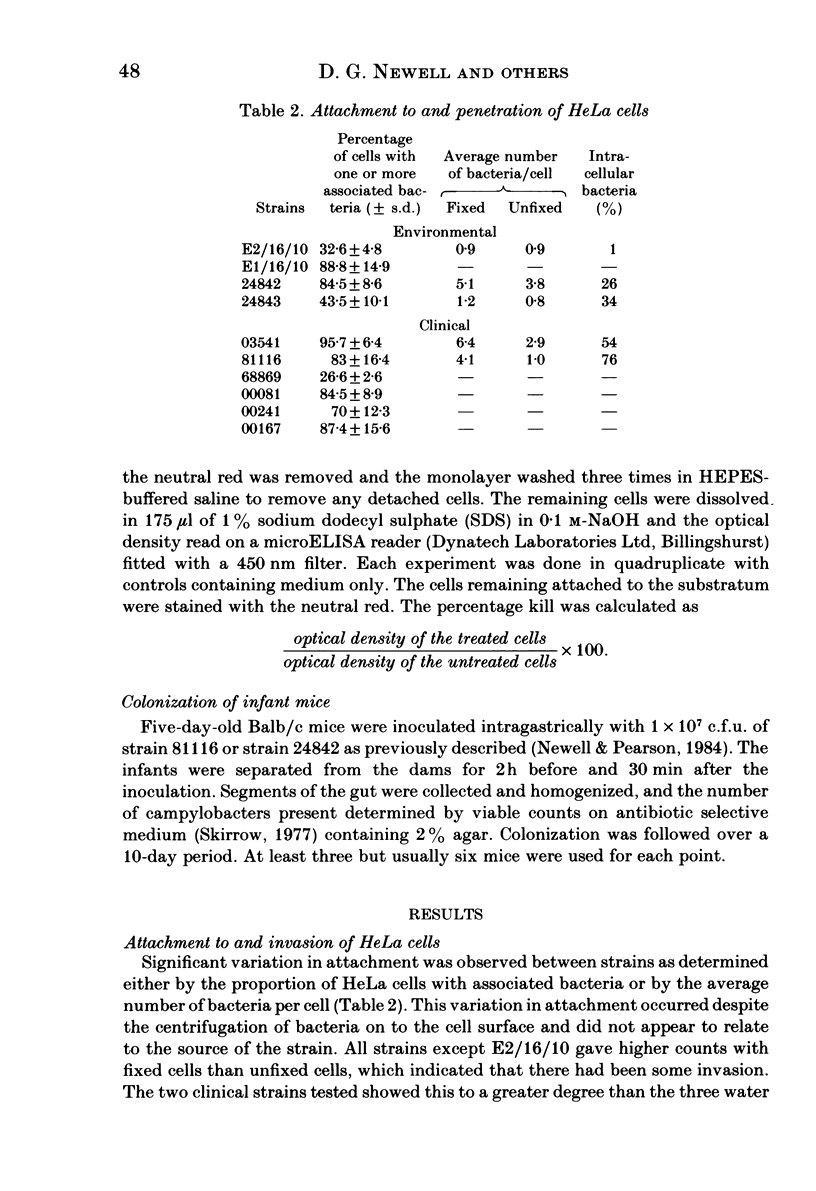
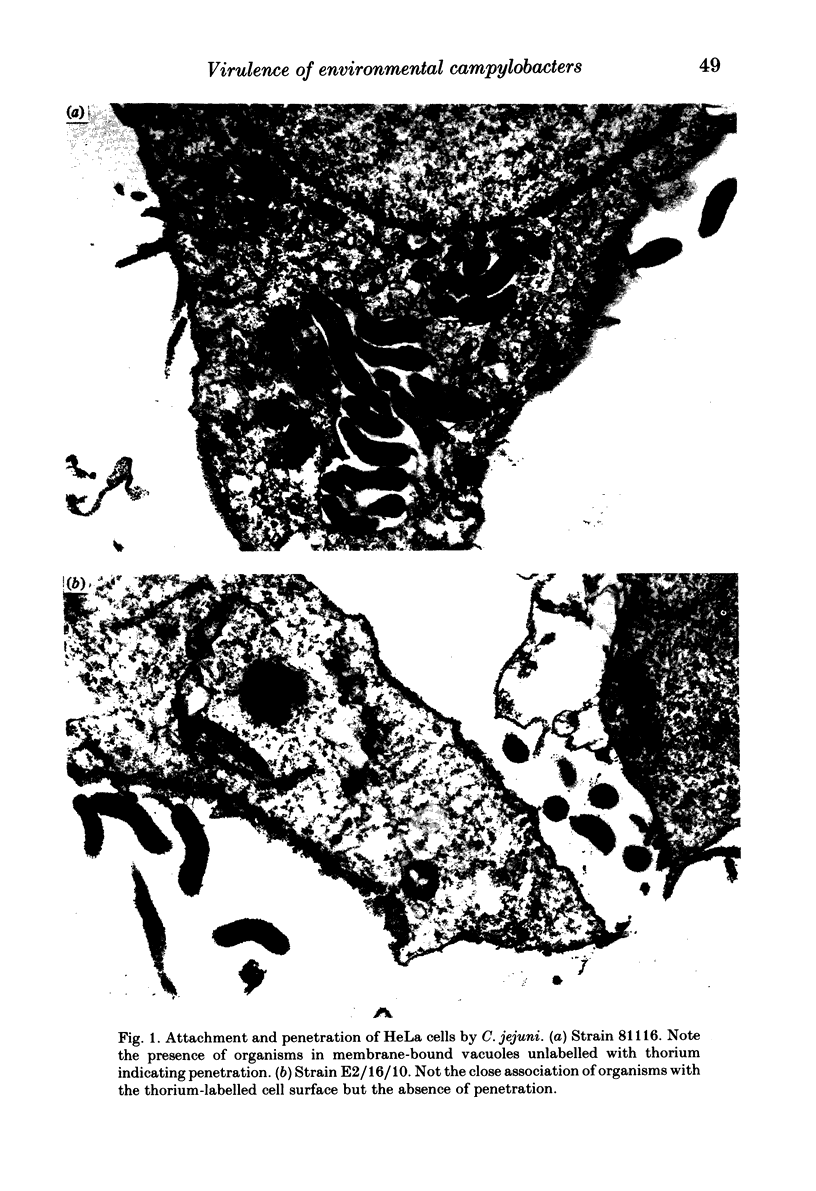
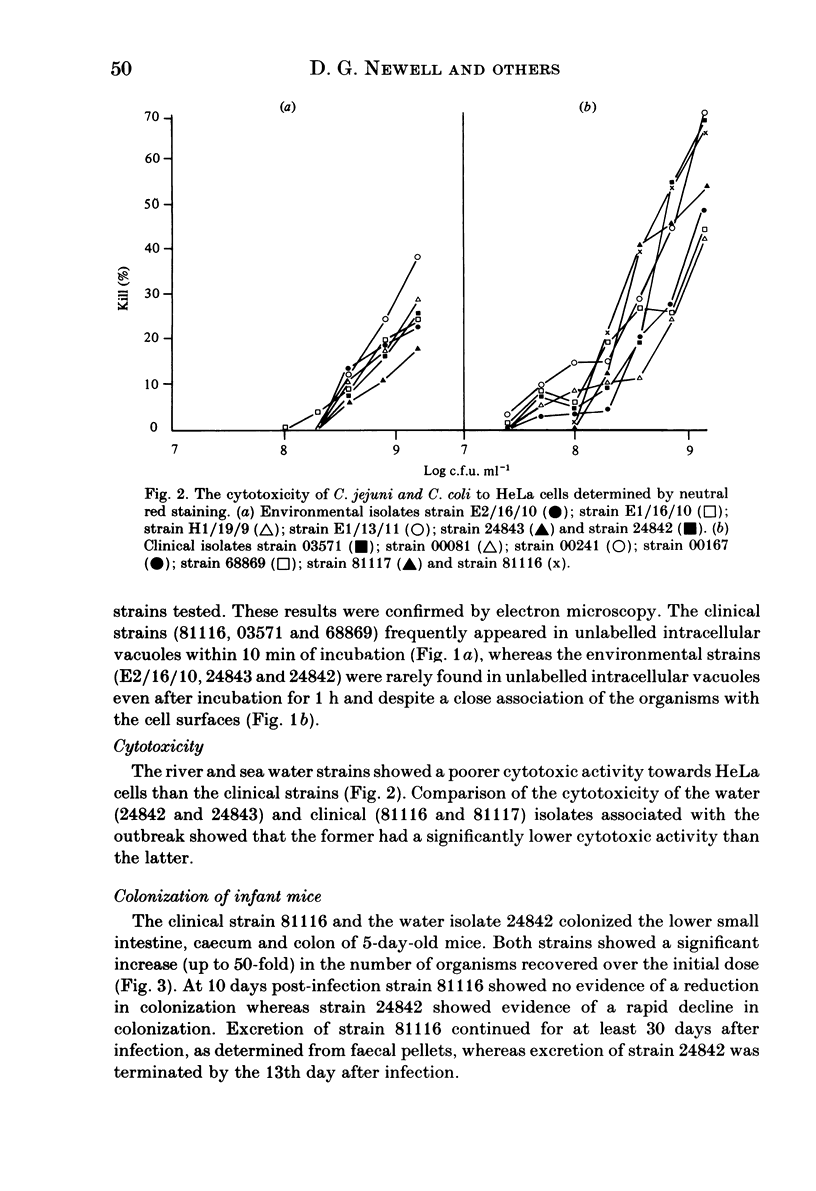
- Newell D. G., Pearson A. The invasion of epithelial cell lines and the intestinal epithelium of infant mice by Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1984 Mar;2(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S. R., Gully P. R., White J. M., Pearson A. D., Suckling W. G., Jones D. M., Rawes J. C., Penner J. L. Water-borne outbreak of campylobacter gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1983 Feb 5;1(8319):287–290. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan D. P., Mathan V. I. Prevalence of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni in healthy populations in southern India. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):749–751. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.749-751.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis - the first five years. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):175–184. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]