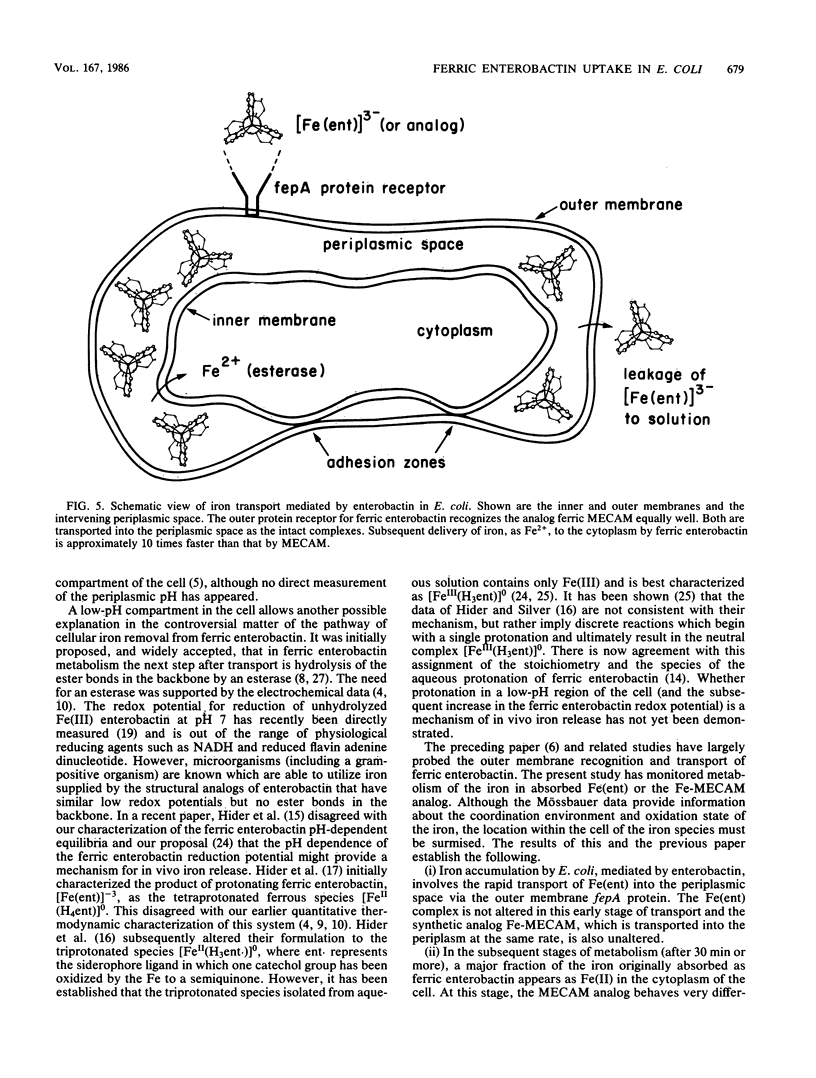
Abstract
Iron uptake by Escherichia coli under aerobic conditions of iron deficiency is mediated by a highly stable ferric enterobactin [Fe(ent)3-] siderophore complex. Mössbauer spectroscopy has been used to monitor the fate of the iron as 57Fe(ent) was taken up by the cells. Osmotic shock experiments were used to distinguish between the iron present in the periplasmic space and that in the cytoplasm of the cell. Iron delivery by a synthetic analog of enterobactin, 1,3,5-N,N',N''- tris-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)triaminomethylbenzene (MECAM), was also studied. Although Fe-MECAM was transported at the same rate as was Fe(ent) across the outer membrane and was apparently accumulated in the periplasmic space, the subsequent behaviors of Fe(ent) and Fe-MECAM were very different. After more than 30 min, a major fraction of the iron originally absorbed as ferric enterobactin appeared as Fe(II), apparently in the cytoplasm of the cell. However, little iron was delivered to the cytoplasm by the MECAM complex. The differences in specificity of these two stages of iron uptake by E. coli are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauminger E. R., Cohen S. G., Dickson D. P., Levy A., Ofer S., Yariv J. Mössbauer spectroscopy of Escherichia coli and its iron-storage protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 26;623(2):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Cohen S. G., Labenski de Kanter F., Levy A., Ofer S., Kessel M., Rottem S. Iron storage in Mycoplasma capricolum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):378–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.378-381.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryce G. F., Brot N. Studies on the enzymatic synthesis of the cyclic trimer of 2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoyl-L-serine in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1708–1715. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. R., McArdle J. V., Raymond K. N. Siderophore electrochemistry: relation to intracellular iron release mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3551–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Matzanke B. F., Raymond K. N. Recognition and transport of ferric enterobactin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.666-673.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood K. T., Luke R. K. Enzymatic hydrolysis of enterochelin and its iron complex in Escherichia Coli K-12. Properties of enterochelin esterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidinger S., Braun V., Pecoraro V. L., Raymond K. N. Iron supply to Escherichia coli by synthetic analogs of enterochelin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.109-115.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Silver J., Nielands J. B., Morrison I. E., Rees L. V. Identification of iron (II) enterobactin and its possible role in Escherichia coli iron transport. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman K. S., Papaefthymiou G. C., Frankel R. B., Rosenthal A. Nature of iron deposits on the cardiac walls in beta-thalassemia by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 22;629(3):522–529. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Gaines C. G., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Non-hydrolytic release of iron from ferrienterobactin analogs by extracts of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B., Erickson T. J., Rastetter W. H. Stereospecificity of the ferric enterobactin receptor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3831–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Enterochelin hydrolysis and iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. R., Mottur G. P., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli. Some observations on the roles of the gene products of BtuC and TonB. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4313–4319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semin B. K., Novakova A. A., Aleksandrov AYu, Ivanov I. I., Rubin A. B., Kuzmin R. N. Mössbauer spectroscopy of iron metabolism and iron intracellular distribution in liver of rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 15;715(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Sperling R., Bauminger E. R., Cohen S. G., Ofer S. The composition and the structure of bacterioferritin of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):171–175. doi: 10.1042/bj1970171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. The sodium/proton antiporter is part of the pH homeostasis mechanism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3687–3691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



