Abstract
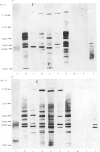
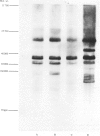
The ELISA and an immunoblotting technique were used to study F38-type mycoplasmas - an important cause of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia - and a number of related mycoplasma species, subspecies, types or serogroups. Two-way ELISA cross-reactivity was demonstrated between five mycoplasmas, namely strain F38, Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides (LC strain), M. equigenitalium, M. primatum and bovine serogroup 7. In addition one-way cross-reactivity was demonstrated between F38 and each of the following mycoplasmas: M. mycoides subsp. mycoides (two SC strains), M. mycoides subsp. capri, and bovine serogroup L. F38 and M. capricolum did not cross-react. Immunoblot analysis, unlike ELISA, revealed that F38 and M. capricolum were closely related. At least four major protein antigens were shared between F38, M. mycoides subsp. mycoides (SC and LC strains), M. mycoides subsp. capri and bovine serogroup 7. The ELISA cross-reactions (above) shown by M. equigenitalium and M. primatum with each other, with F38 and with other mycoplasmas were not apparent by immunoblotting.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen H., Christiansen G., Christiansen C. Electrophoretic analysis of proteins from Mycoplasma capricolum and related serotypes using extracts from intact cells and from minicells containing cloned mycoplasma DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1409–1418. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Ernø H. Classification of the F38 group of caprine Mycoplasma strains by DNA hybridization. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Nov;128(11):2523–2526. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-11-2523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernø H., Leach R. H., MacOwan K. J. Further characterisation of Mycoplasma strain F38. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1979 May;11(2):84–84. doi: 10.1007/BF02237774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernø H., Leach R. H., Salih M. M., MacOwan K. J. The F38-like group, a new group of caprine mycoplasmas? Acta Vet Scand. 1983;24(3):275–286. doi: 10.1186/BF03546731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernø H., Salih M. M. The growth precipitation test as a diagnostic method for differentiation of mycoplasma and acholeplasma species. Acta Vet Scand. 1980;21(4):469–481. doi: 10.1186/BF03546835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbi M. S., El Tahir M. S., Macowan K. J., Nayil A. A. Mycoplasma strain F38 and contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in the Sudan. Vet Rec. 1981 Mar 21;108(12):261–261. doi: 10.1136/vr.108.12.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanyi Kibe M., Smith G. R. A study of F38-type and related mycoplasmas by mycoplasmaemia and cross-immunization tests in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Dec;93(3):465–473. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Marmion B. P., Plackett P. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):691–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacOwan K. J., Minette J. E. A mycoplasma from acute contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in Kenya. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1976 May;8(2):91–95. doi: 10.1007/BF02383376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMartin D. A., MacOwan K. J., Swift L. L. A century of classical contagious caprine pleuropneumonia: from original description to aetiology. Br Vet J. 1980 Sep-Oct;136(5):507–515. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)32196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minion F. C., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Identification of cross-reactive antigens between Mycoplasma pulmonis and Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):115–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.115-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical characterization of a heat-stable surface antigen of Mycoplasma pulmonis expressing both species-specific and strain-specific determinants. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):355–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.355-363.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salih M. M., Ernø H., Simonsen V. Electrophoretic analysis of isoenzymes of mycoplasma species. Acta Vet Scand. 1983;24(1):14–33. doi: 10.1186/BF03546754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavský O., Prescott B., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Serological and immunogenic activities of different fractions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):682–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]