Abstract
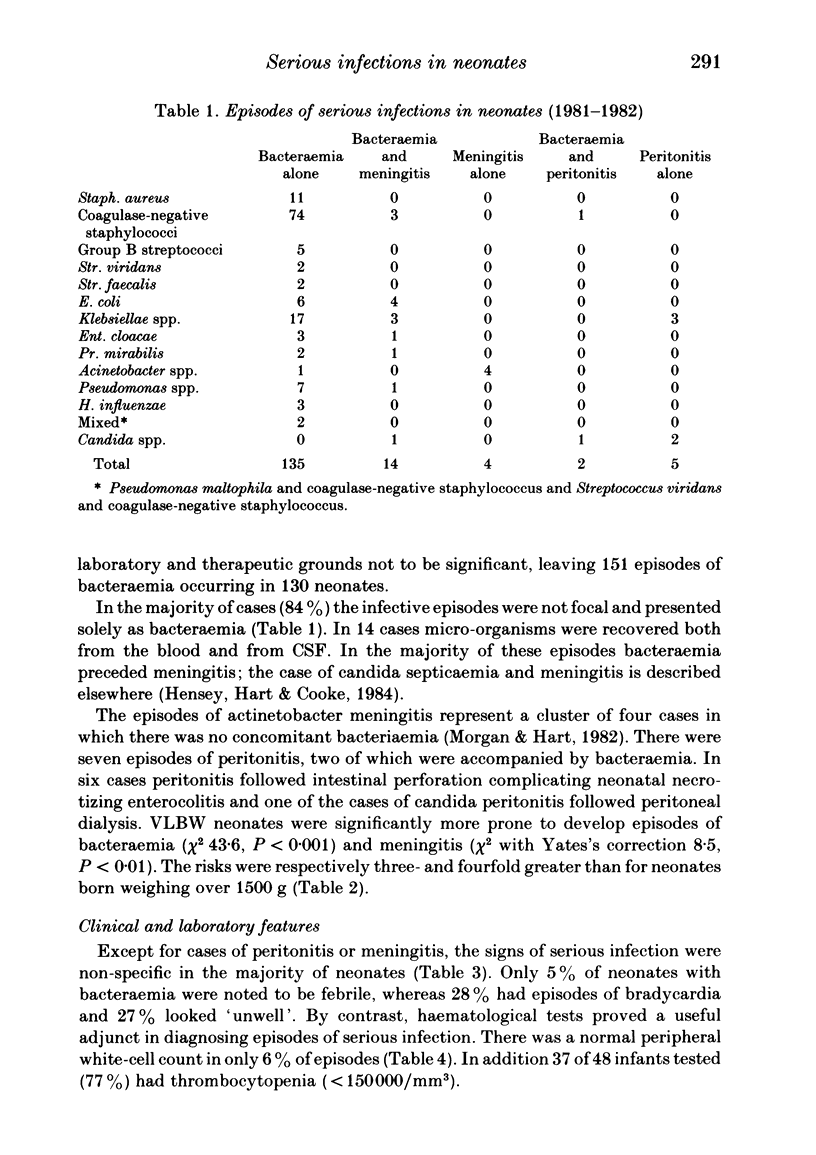
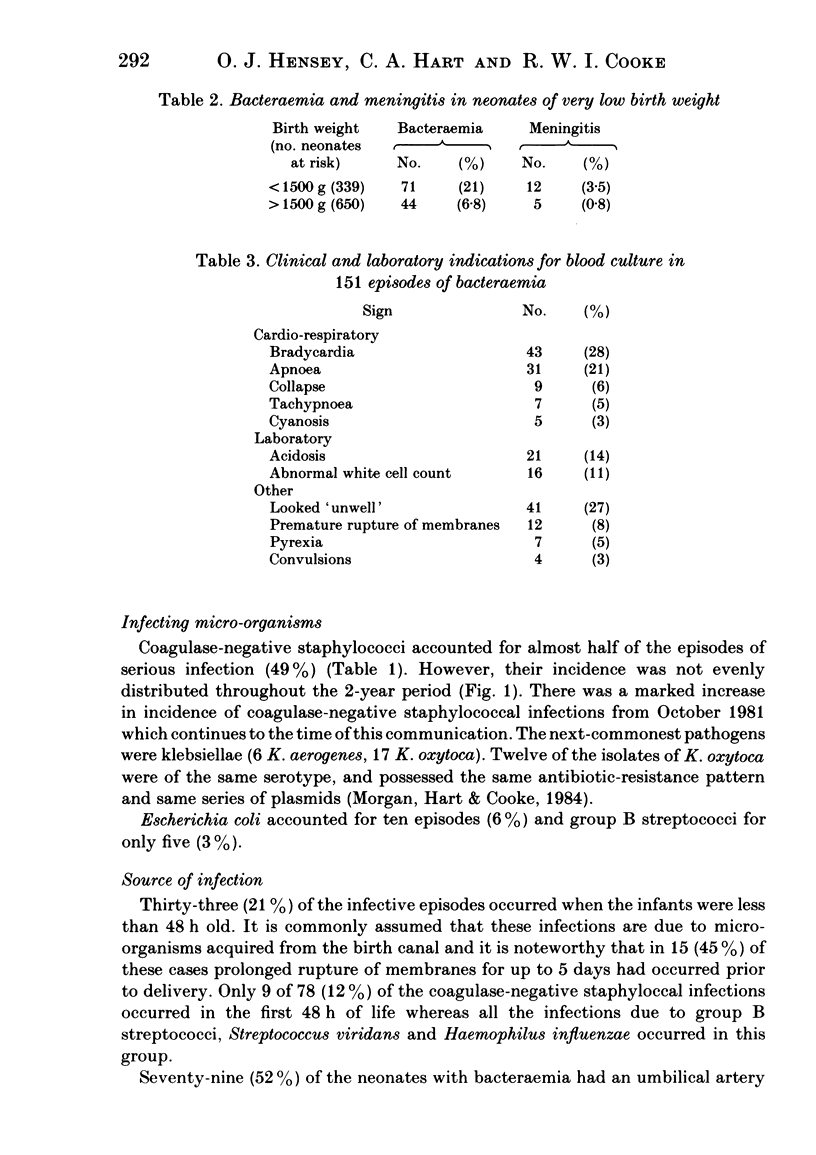
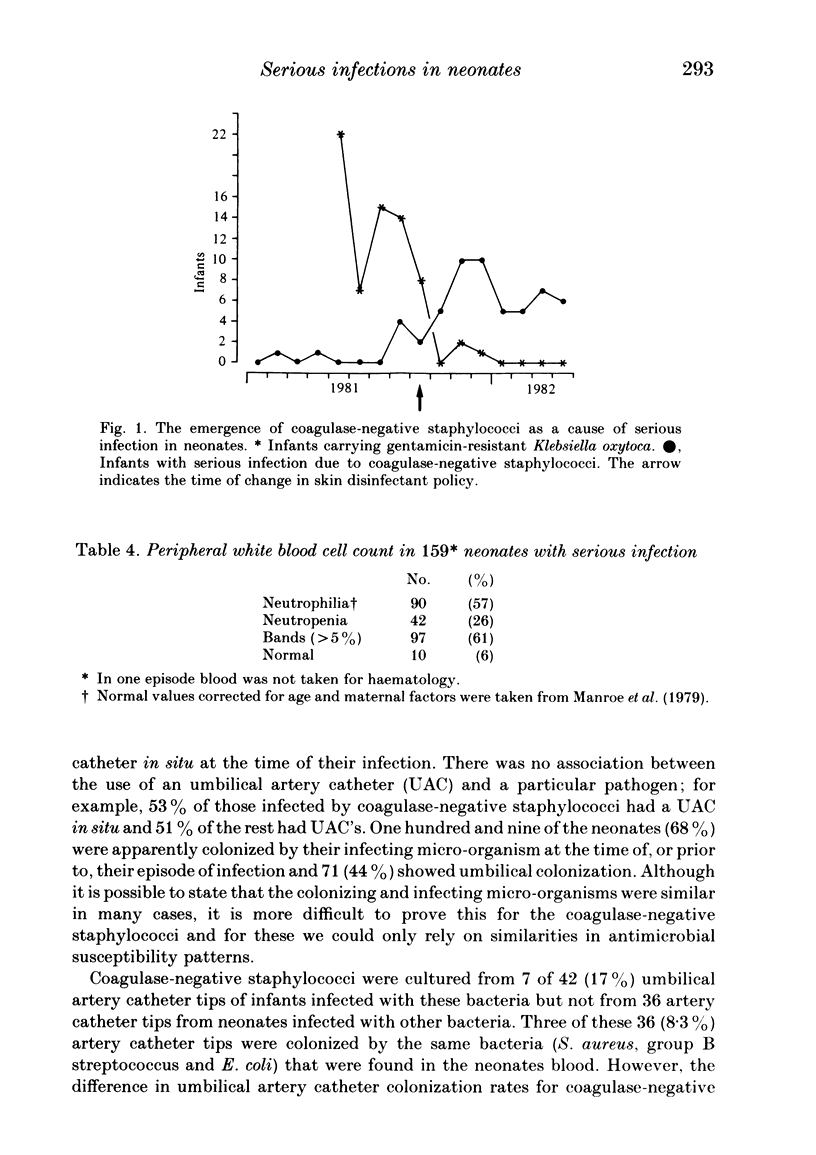
Over a two-year period 160 episodes of serious infection occurred in 139 infants admitted to a regional neonatal intensive-care unit. Eighty-seven (26%) of very low birth weight (VLBW) neonates and 52 (8%) of infants of birth weight greater than 1500 g were infected. The majority (84%) had bacteraemia alone. Though the clinical features of infection were not distinctive, in 94% of episodes the peripheral white blood cell or band counts were abnormal. Thirty-three (21%) of the infections occurred in infants under 48 h old and 15 of these followed prolonged rupture of membranes (greater than 48 h). All of the infections due to group B streptococci (5), Streptococcus viridans (2) and Haemophilus influenzae (3) occurred in this group. Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CONS) accounted for 49% of the infections and there was a marked increase in incidence of such infections during the survey. Infections with CONS were not necessarily associated with parenteral nutrition, the presence of intra-arterial catheters or mechanical ventilation but the rise in incidence was coincident with change in skin disinfectant usage and the general use of a third-generation cephalosporin to which the CONS were resistant. Although VLBW infants with meningitis were more likely to die than those of higher birthweight, the risk for those with bacteriaemia was the same in both groups. Infants with CONS sepsis were less likely to die than those with infections due to Gram-negative bacteria and the time from onset of infection to death was significantly longer for the former.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battisti O., Mitchison R., Davies P. A. Changing blood culture isolates in a referral neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Oct;56(10):775–778. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.10.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLAGHAN R. P., COHEN S. J., STEWART G. T. Septicaemia due to colonization of Spitz-Holter valves by staphylococci. Five cases treated with methicillin. Br Med J. 1961 Mar 25;1(5229):860–863. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5229.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. K., Baillod R. A., Chuah P., Sweny P., Raftery M. J., Varghese Z., Moorhead J. F. Three years' experience of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Lancet. 1981 Jun 27;1(8235):1409–1412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92582-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. J., Ward-Platt M., Kirk R., Marshall R., Speidel B. D., Reeves D. S. Is coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteraemia in neonates a consequence of mechanical ventilation? J Hosp Infect. 1984 Sep;5(3):260–269. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(84)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. W., Gear R. Children of low birthweight in the 1946 national cohort. Behaviour and educational achievement in adolescence. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Nov;51(11):820–827. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.11.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleer A., Senders R. C., Visser M. R., Bijlmer R. P., Gerards L. J., Kraaijeveld C. A., Verhoef J. Septicemia due to coagulase-negative staphylococci in a neonatal intensive care unit: clinical and bacteriological features and contaminated parenteral fluids as a source of sepsis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;2(6):426–431. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198311000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. M., Ingram D. L., Gross I., Ehrenkranz R. A., Warshaw J. B., Baltimore R. S. A half century of neonatal sepsis at Yale: 1928 to 1978. Am J Dis Child. 1981 Feb;135(2):140–144. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130260032010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmann D. A., Maki D. G. Infection control in total parenteral nutrition. JAMA. 1973 Mar 19;223(12):1360–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensey O. J., Hart C. A., Cooke R. W. Candida albicans skin abscesses. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):479–480. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., Cats B., Senders R. C., van Ertbruggen I. Analysis of bacterial infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 1982 Sep;3(3):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(82)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manroe B. L., Weinberg A. G., Rosenfeld C. R., Browne R. The neonatal blood count in health and disease. I. Reference values for neutrophilic cells. J Pediatr. 1979 Jul;95(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. E., Hart C. A. Acinetobacter meningitis: acquired infection in a neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Jul;57(7):557–559. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.7.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. E., Hart C. A., Cooke R. W. Klebsiella infection in a neonatal intensive care unit: role of bacteriological surveillance. J Hosp Infect. 1984 Dec;5(4):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(84)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Sepsis neonatorum. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 12;304(11):642–647. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103123041105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starte D. R., Jones R. A., Hall M. A., Harvey D. R. Survival of preterm babies. Lancet. 1980 Sep 20;2(8195 Pt 1):639–640. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Newman K. A., Wiernik P. H. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an increasing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):503–508. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


