Abstract
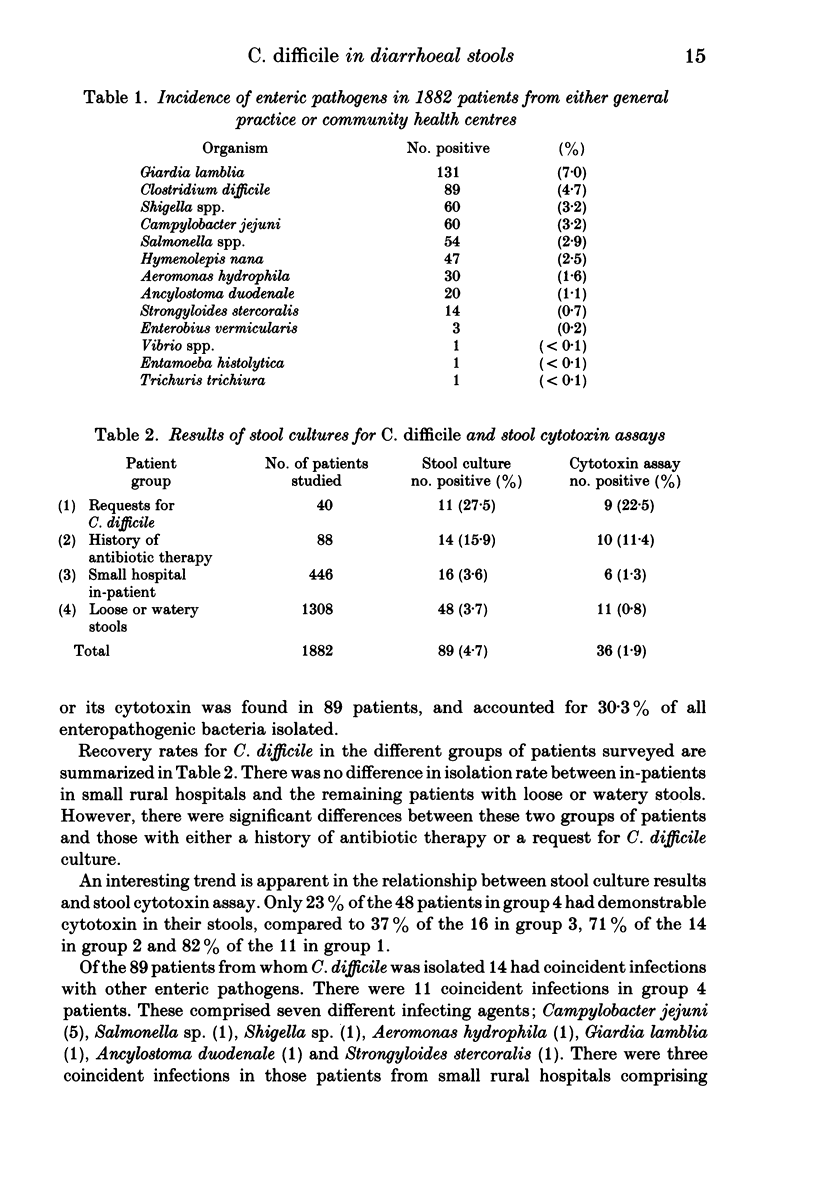
The isolation rate for Clostridium difficile in diarrhoeal stools was investigated in patients from general practice and community health centres over a 14-month period. C. difficile or its cytotoxin was detected in specimens from 89 (4.7%) of 1882 patients studied and accounted for 30.3% of all enteropathogenic micro-organisms isolated. Overall C. difficile was second only to Giardia lamblia in frequency. Recovery rates in the different groups of patients surveyed varied from 3.6 to 27.5%. The relationship between stool culture results and stool cytotoxin assay also varied considerably between groups of patients studied. Coincident infections with a variety of enteropathogenic bacteria and intestinal parasites were diagnosed in 14 of the 89 patients. It was concluded that laboratories servicing this type of practice should be aware that C. difficile may be a cause of diarrhoea. An adequate clinical history should facilitate proper processing of the specimen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Gurwith M., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):531–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T., Taylor N. S., Onderdonk A. B. Colitis induced by Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):370–378. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton R. P., Sherriff R. J., Read A. E. Clostridium difficile associated diarrhoea: a role in inflammatory bowel disease? Lancet. 1980 Feb 23;1(8165):383–384. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90940-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman R. A., Riley T. V. Routine culturing for Clostridium difficile? Pathology. 1984 Jul;16(3):240–242. doi: 10.3109/00313028409068530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brettle R. P., Poxton I. R., Murdoch J. M., Brown R., Byrne M. D., Collee J. G. Clostridium difficile in association with sporadic diarrhoea. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 23;284(6311):230–233. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6311.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon D. W., George R. H., Mogg G. A., Arabi Y., Thompson H., Johnson M., Alexander-Williams J., Keighley M. R. Faecal toxin and severity of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;34(5):548–551. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.5.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Bowman R. A., Riley T. V. A selective broth for Clostridium difficile. Pathology. 1983 Apr;15(2):165–167. doi: 10.3109/00313028309084706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falsen E., Kaijser B., Nehls L., Nygren B., Svedhem A. Clostridium difficile in relation to enteric bacterial pathogens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):297–300. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.297-300.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., McCarthy L. R., Genta V. M. Relative frequency of Clostridium difficile in patients with diarrheal disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):26–31. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.26-31.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Rockhill R. C., Suharyono, Sunoto Aeromonas species as enteric pathogens. Lancet. 1982 Jan 23;1(8265):223–224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90787-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. M., Sullivan S. N., Troster M. Spontaneous pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1980 Aug 2;281(6236):356–356. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6236.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley T. V., Bowman R. A., Carroll S. M. Diarrhoea associated with Clostridium difficile in a hospital population. Med J Aust. 1983 Feb 19;1(4):166–169. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1983.tb104346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald A., Mendelow H., Bartlett J. G. Non-antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing Clostridia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jun;92(6):798–799. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-6-798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



