Abstract
In developing countries tuberculous meningitis is a difficult infection to differentiate from other central nervous system (CNS) infections. This paper presents the history, physical findings, laboratory data, and clinical course of 100 patients who were admitted to a special ward and had CSF cultures positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Fifty-four patients were comatose when admitted and 76 had meningeal signs. Mean admission CSF values were WBC 531, glucose 23 mg/dl, and protein 166 mg/dl. Only two CSF AFB smears were positive. Sixty-one percent of the chest X-rays taken were consistent with pulmonary tuberculous and 39% were normal. Twenty-four patients died within the first week after admission, before the clinical diagnosis was made and anti-tuberculous therapy could be started. Fifty-three of 76 patients given antituberculous therapy died. Neurologic sequelae developed in 48% of the survivors. The high mortality and morbidity rates in this patient-group were due to the severity of illness on admission and the predominance of children (54%).
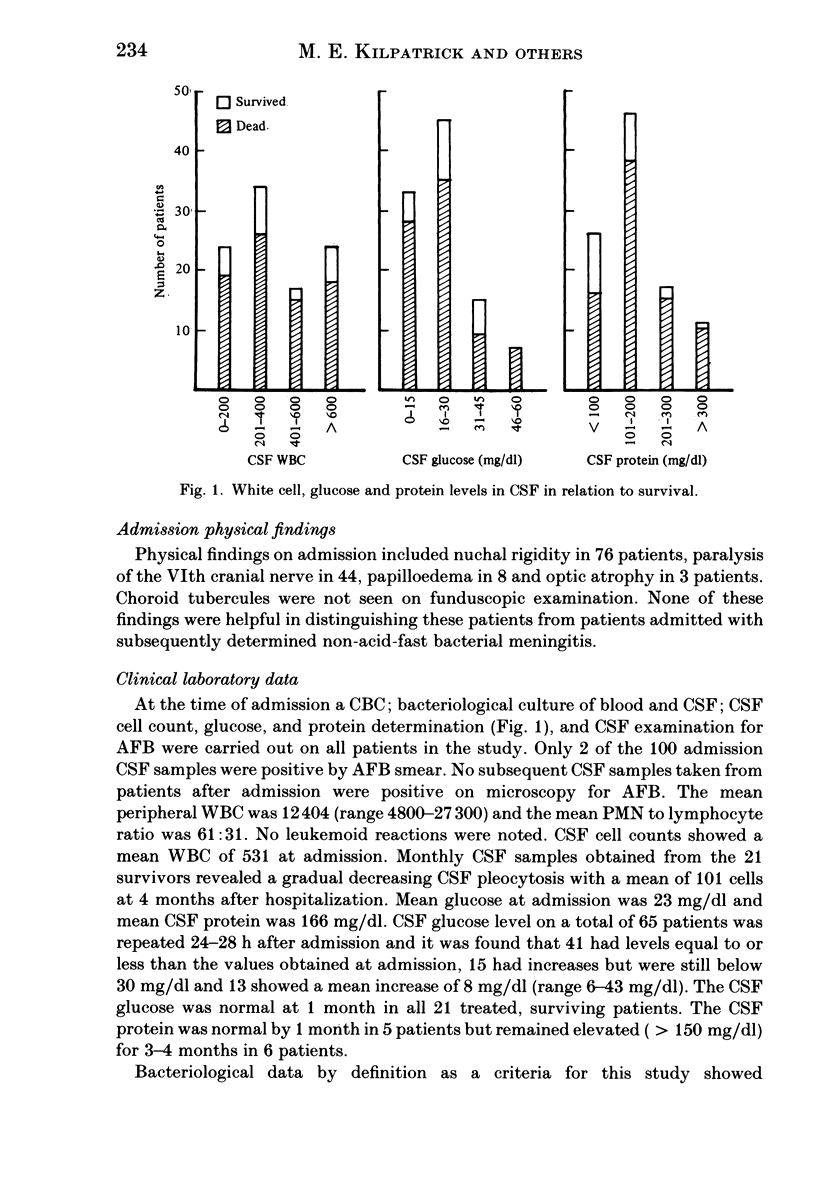
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bwibo N. O. Tuberculous meningitis--diagnostic problems. East Afr Med J. 1979 Dec;56(12):646–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCCHI C. Cortisone and corticotropin in the treatment of tuberculosis in infancy and childhood. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Aug;74(2 Pt 2):209-16; discussion, 216-20. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.2-2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardozo L. J., Raidoo S., Patel B. P. Tuberculous meningitis in adult Africans-problems of diagnosis and management. East Afr Med J. 1976 Mar;53(3):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Oliveira J. J. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of rifampin in meningeal tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Sep;106(3):432–437. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBRE R., BRISSAUD H. E. Present method and results of treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Aug;74(2 Pt 2):221–224. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.2-2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emond R. T., McKendrick G. D. Tuberculosis as a cause of transient aseptic meningitis. Lancet. 1973 Aug 4;2(7823):234–236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar J. A., Belsey M. A., Dueñas A., Medina P. Mortality from tuberculous meningitis reduced by steroid therapy. Pediatrics. 1975 Dec;56(6):1050–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZSIMONS J. M., SMITH H. Tuberculous meningitis: special features of treatment. Tubercle. 1963 Mar;44:103–111. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(63)80064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freiman I., Geefhuysen J. Evaluation of intrathecal therapy with streptomycin and hydrocortisone in tuberculous meningitis. J Pediatr. 1970 Jun;76(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girgis N. I., Yassin M. W., Sippel J. E., Sorensen K., Hassan A., Miner W. F., Farid Z., Abu el Ella A. The value of ethambutol in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis. J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Jan;79(1):14–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E. J., Madhavan T., Quinn E. L., Cox F., Fisher E., Burch K. Tuberculous meningitis in an urban general hospital. Arch Intern Med. 1977 Nov;137(11):1518–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna L. S., Girgis N. I., Hassan A., Yassin W., Sippel J. E. The incidence of ocular complications in meningococcal meningitis. J Egypt Med Assoc. 1975;58(1-2):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan A., Abdel-Wahab M. F. Tuberculous meningitis in U.A.R. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 1969;44(4):303–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockaday J. M., Smith H. M. Corticosteroids as an adjuvant to the chemotherapy of tuberculous meningitis. Tubercle. 1966 Mar;47(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(66)80052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ILLINGWORTH R. S., LORBER J. Tubercles of the choroid. Arch Dis Child. 1956 Dec;31(160):467–469. doi: 10.1136/adc.31.160.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idriss Z. H., Sinno A. A., Kronfol N. M. Tuberculous meningitis in childhood. Forty-three cases. Am J Dis Child. 1976 Apr;130(4):364–367. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1976.02120050022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. H., Fallon R. J. Tuberculous meningitis. JAMA. 1979 Jan 19;241(3):264–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINCOLN E. M., SIFONTES J. E. Tuberculous meningitis in children. Med Clin North Am. 1953 Mar;37(2):345–362. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)35018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINCOLN E. M., SORDILLO V. R., DAVIES P. A. Tuberculous meningitis in children. A review of 167 untreated and 74 treated patients with special reference to early diagnosis. J Pediatr. 1960 Dec;57:807–823. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORBER J. Treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Br Med J. 1960 Apr 30;1(5182):1309–1312. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5182.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORBER J. Tuberculous meningitis in children treated with streptomycin and P.A.S. Lancet. 1954 May 29;266(6822):1104–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)92155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naughten E., Weindling A. M., Newton R., Bower B. D. Tuberculous meningitis in children. Recent experience in two English centres. Lancet. 1981 Oct 31;2(8253):973–975. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow J. H. Levels of rifampin in cerebrospinal fluid. Chest. 1973 Apr;63(4):648–649. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuntokun B. O., Adeuja A. O., Familusi J. B. Tuberculous meningitis in Nigerians. A study of 194 patients. Trop Geogr Med. 1971 Sep;23(3):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Place V. A., Pyle M. M., De la Huerga J. Ethambutol in tuberculous meningitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 May;99(5):783–785. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.5.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAADE F., KRISTENSEN K. P. Purulent meningitis. A review of 658 cases. Acta Med Scand. 1962 May;171:543–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner P., Portugaleza C. Tuberculous meningitis in children. A review of 25 cases observed between the years 1965 and 1970 at the Kings County Medical Center of Brooklyn with special reference to the problem of infection with primary drug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jan;107(1):22–29. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumaya C. V., Simek M., Smith M. H., Seidemann M. F., Ferriss G. S., Rubin W. Tuberculous meningitis in children during the isoniazid era. J Pediatr. 1975 Jul;87(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Management of bacterial meningitis. Mil Med. 1976 Sep;141(9):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLJAVEC B. F., ORTON S. P., CORPE R. F. Tuberculous meningitis; prognosis and treatment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Sep;80:388–397. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.3.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visudhiphan P., Chiemchanya S. Evaluation of rifampicin in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis in children. J Pediatr. 1975 Dec;87(6 Pt 1):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80924-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS W., FLIPPIN H. F. THE CHANGING INCIDENCE AND PROGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS. Am J Med Sci. 1965 Jul;250:46–59. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196507000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



