Abstract
Fresh human and bovine milk are bacteriostatic in vitro for only some (milk-sensitive) strains of E. coli. The addition of bicarbonate to the test system potentiates the bacteriostasis so that otherwise milk-resistant strains are inhibited. By titration of the bicarbonate in the milk, it is possible to determine the minimum concentration that will activate milk aganinst a milk resistant strain but be ineffective in boiled milk, i.e. it potentiates a heat-labile system in milk and does not merely exert a direct toxic effect. This concentration is lower for human milk than for cow's milk and can be reduced even further by the addition of more iron-binding protein. Lactoferrin and bicarbonate may be present in the gut of the newborn. In an attempt to imitate conditions in the infant gut, we therefore reinvestigated, in vitro and in the presence of added bicarbonate and transferrin, the bacteriostatic activity against E. coli of fresh breast-milk, commercial bottle-milk, and mixtures of these as fed to infants in the study. The results, and information about events in vivo deduced from the ratio of milk-sensitive to milk-resistant strains of E. coli isolated from babies' stool suggest that neonatal intestinal secretions may contribute to the bacteriostatic activity of their feeds so that (1) in fully breastfed babies all strains of E. coli are inhibited to the same extent; there is no selection on the basis of milk sensitivity and equal numbers of strains resistant and sensitive to milk are found in the stools; (2) in fully bottle-fed babies E. coli is not inhibited since the milk is non-bacteriostatic and again there is no selection; (3) in babies fed at the breast but bottle-milk supplemented, only milk-sensitive strains are inhibited; milk-resistant strains are not, and preferentially colonize the large intestines.
Full text
PDF


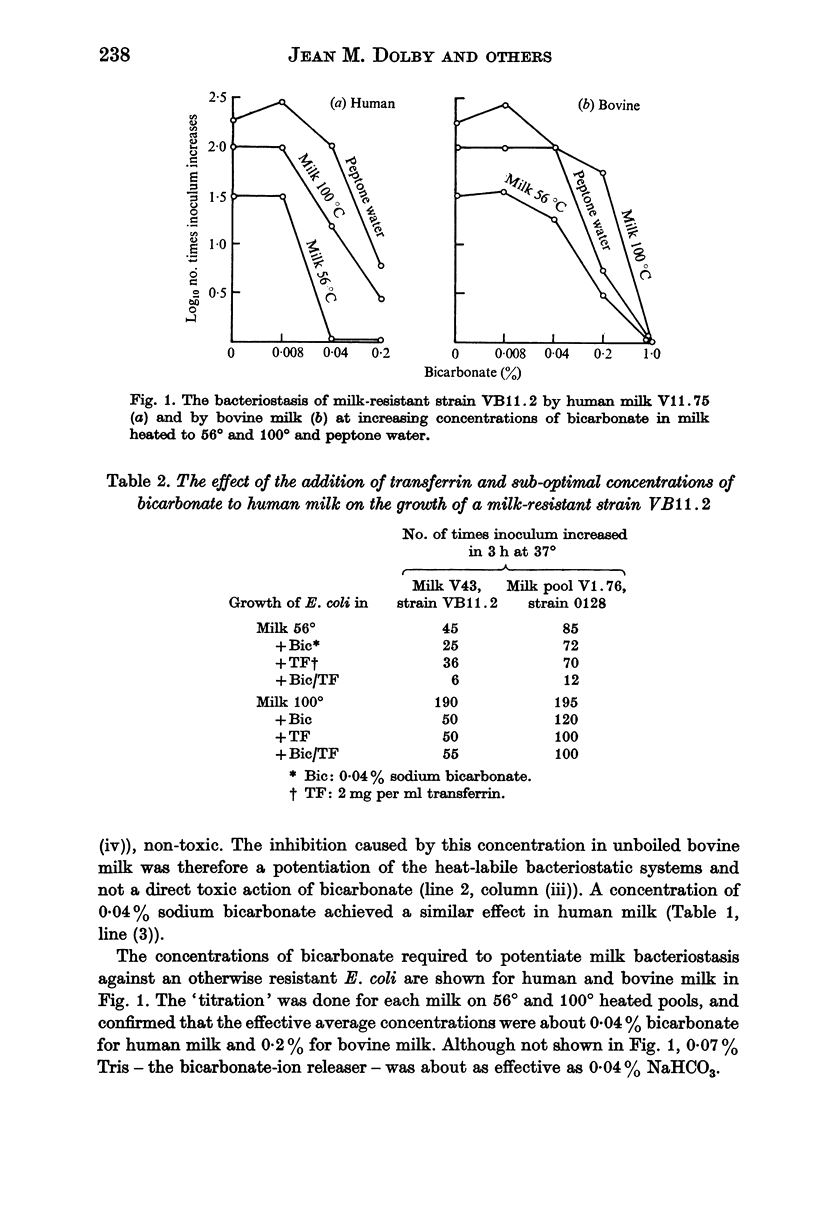



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Aasa R., Malmström B. G., Vänngård T. Bicarbonate and the binding of iron to transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2484–2490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delachaume-Salem E., Sarles H. Evolution en fonction de l'age de la sécrétion pancréatique humaine normale. Biol Gastroenterol (Paris) 1970;2:135–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolby J. M., Honour P., Valman H. B. Bacteriostasis of Escherichia coli by milk. I. Colonization of breast-fed infants by milk resistant organisms. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Feb;78(1):85–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS G. E. Secretin tests with bilumen gastroduodenal drainage in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1950 Jun;5(6):941–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Biasucci A. Development of gamma G, gamma A, gamma M, beta IC-beta IA, C 1 esterase inhibitor, ceruloplasmin, transferrin, hemopexin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, alpha 1-antitrypsin, orosomucoid, beta-lipoprotein, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and prealbumin in the human conceptus. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1433–1446. doi: 10.1172/JCI106109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gothefors L., Carlsson B., Ahlstedt S., Hanson L. A., Winberg J. Influence of maternal gut flora and colostral and cord serum antibodies on presence of Escherichia coli in faeces of the newborn infant. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Mar;65(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb16542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Metal-combining properties of human lactoferrin (red milk protein). 1. The involvement of bicarbonate in the reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Dec 5;6(4):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter B., Brock J. H., Steel E. D. Inhibition of Escherichia coli by bovine colostrum and post-colostral milk. II. The bacteriostatic effect of lactoferrin on a serum susceptible and serum resistant strain of E. coli. Immunology. 1975 Jan;28(1):83–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidmon E. J., Mosovich L. L., Neter E. Colonization by Enterobacteriaceae of the respiratory tract of children with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and their antibody response. J Pediatr. 1975 Oct;87(4):528–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80814-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen P., Rossi T., Hirvonen T. The concentration of Gc globulin and transferrin in human fetal and infant sera. Scand J Haematol. 1969;6(2):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1969.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


