Abstract
A simple method for the bacteriocine typing of Serratia marcescens without the use of induction was sought. The results of a mutual inhibition experiment with 89 unrelated cultures indicated that a bacteriocine-susceptibility method would give more discrimination between strains than would a bacteriocine-production method. A cross-streaking technique for bacteriocine-susceptibility typing without previous induction was developed, and its performance was compared with that of another susceptibility-typing method in which cell-free lysates of the producer strains were obtained by induction with mitomycin C.
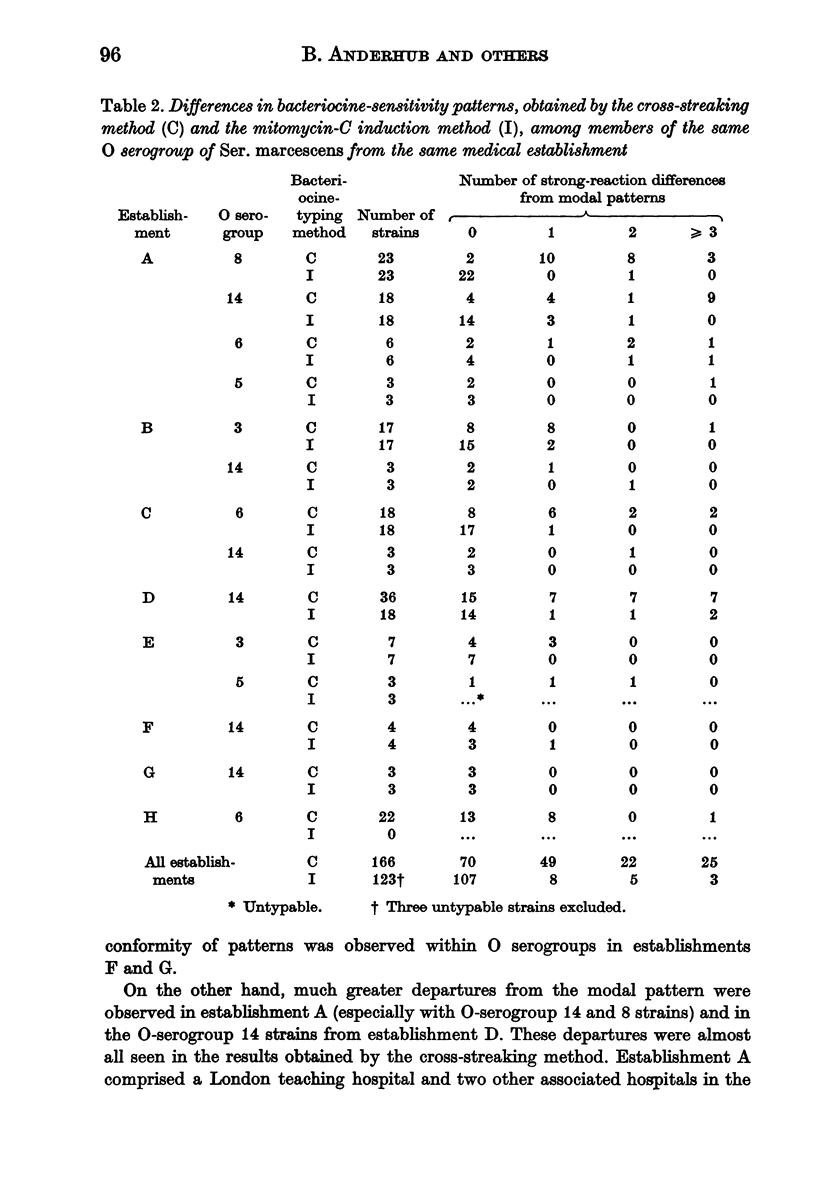
Replicate typing of the same collection of cultures by both methods indicated that small variations in pattern were common and that larger variations occurred occasionally. Differences in pattern of less than two strong reactions in the mitomycin-C induction method, and of less than three strong reactions in the cross-streaking method, should therefore not be taken as evidence that strains can be distinguished.
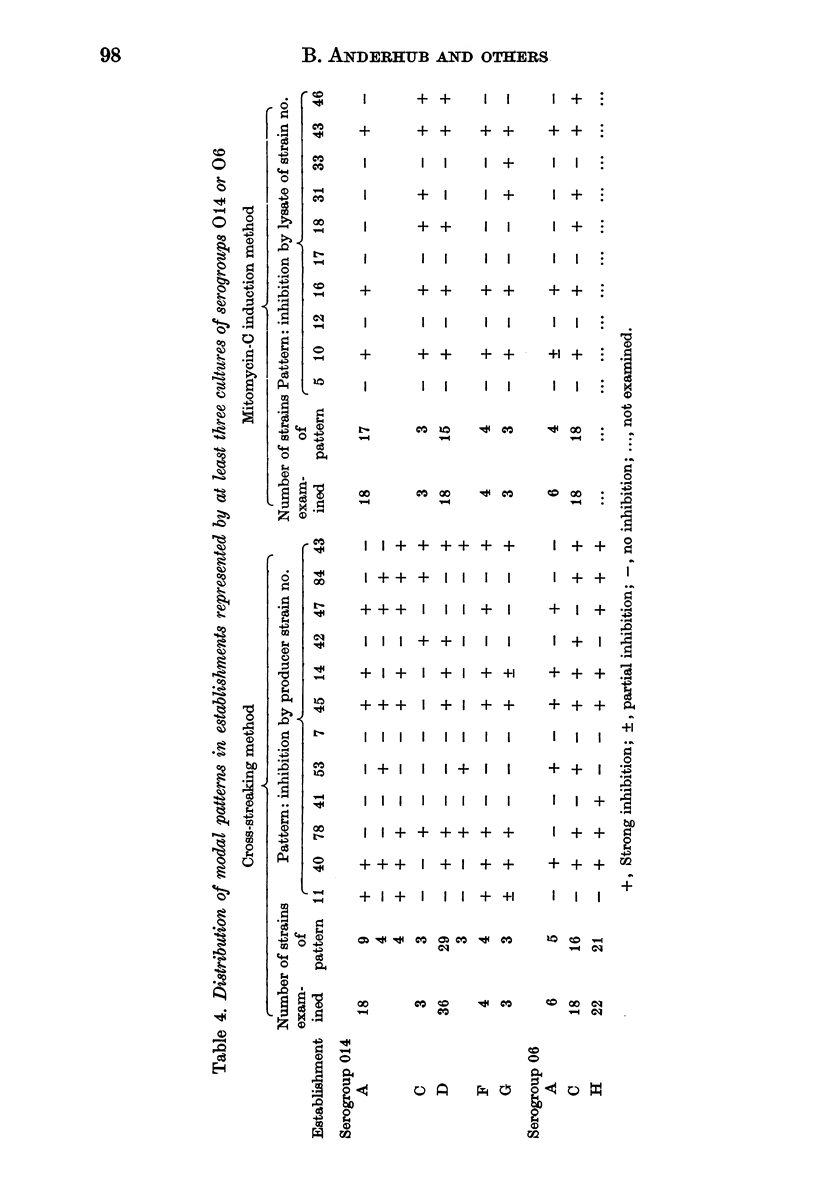
Sets of cultures of Ser. marcescens, 178 in total, from a number of supposed incidents of infection in hospitals, were used to evaluate the two bacteriocine-typing methods; all of the cultures were also O serogrouped. Comparison of the typing patterns of members of the same O serogroup from clear-cut incidents of infection confirmed that results of acceptable reliability could be obtained by either bacteriocine-typing method by the application of the appropriate `difference' rule. When so interpreted, the cross-streaking method appeared to be slightly the more discriminatory.
The greatest discrimination between strains was obtained by the use of a `hierarchical' typing system in which the strains were first O serogrouped, and the cross-streaking method of bacteriocine typing was then used to make subdivisions within O serogroups.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT J. D., SHANNON R. A method for typing Shigella sonnei, using colicine production as a marker. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jan;11(1):71–77. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Culbertson W. R., Fullen W. D., McDonough J. J. Serratia marcescens septicemia. A new threat in surgery. Arch Surg. 1969 Aug;99(2):232–238. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340140104015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daschner F., Senska-Euringer C. Kontaminierte Infusionen als Ursache nosokomialer Serratia-marcescens-Sepsis bei Kindern. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1975 Nov 7;100(45):2324–2328. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Spink W. W. Infections due to gram-negative organisms: an analysis of 860 patients with bacteremia at the University of Minnesota Medical Center, 1958-1966. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jul;48(4):307–332. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Epidemiological differentiation of Serratia marcescens: typing by bacteriocin production. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):218–225. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.218-225.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Herman L. G. Epidemiological fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the production of and sensitivity of pyocin and bacteriophage. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):760–765. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.760-765.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. R., Govan J. R. Typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by pyocine production. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):339–345. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. F., Thomas E. T., Stinnett J. D., Gilardi G. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd Pyocin sensitivity of Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):288–289. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.288-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meitert T., Meitert E. Utilisation combinée du sérotypage et de la lysotypie des souches de Psuedomonas aeruginosa en vue d'approfondir les investigations épidémiologiques. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1966 Jun;25(2):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinsloo H. E. Bacteriocins and phages produced by Serratia marcescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):205–212. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampling A., Whitby J. L., Wildy P. Pyocin-sensitivity testing as a method of typing Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of "phage-free" preparations of pyocin. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):531–541. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Raymond E. A., Startsman T. S. Bacteriocin (Marcescin) typing of clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):837–840. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.837-840.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAHBA A. H. THE PRODUCTION AND INACTIVATION OF PYOCINES. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Dec;61:431–441. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. O., RIPPON J. E. Bacteriophage typing of Staphylococcus aureus. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Sep;50(3):320–353. doi: 10.1017/s002217240001963x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfert J. N., Barrett F. F., Ewing W. H., Finland M., Kass E. H. Serratia marcescens: biochemical, serological, and epidemiological characteristics and antibiotic susceptibility of strains isolated at Boston City Hospital. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Feb;19(2):345–352. doi: 10.1128/am.19.2.345-352.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfert J. N., Barrett F. F., Kass E. H. Bacteremia due to serratia marcescens. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 8;279(6):286–289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808082790604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Martin W. J., Ritts R. E., Jr Serratia marcescens. Biochemical characteristics, antibiotic susceptibility patterns, and clinical significance. JAMA. 1970 Dec 21;214(12):2157–2162. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.12.2157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


