Abstract
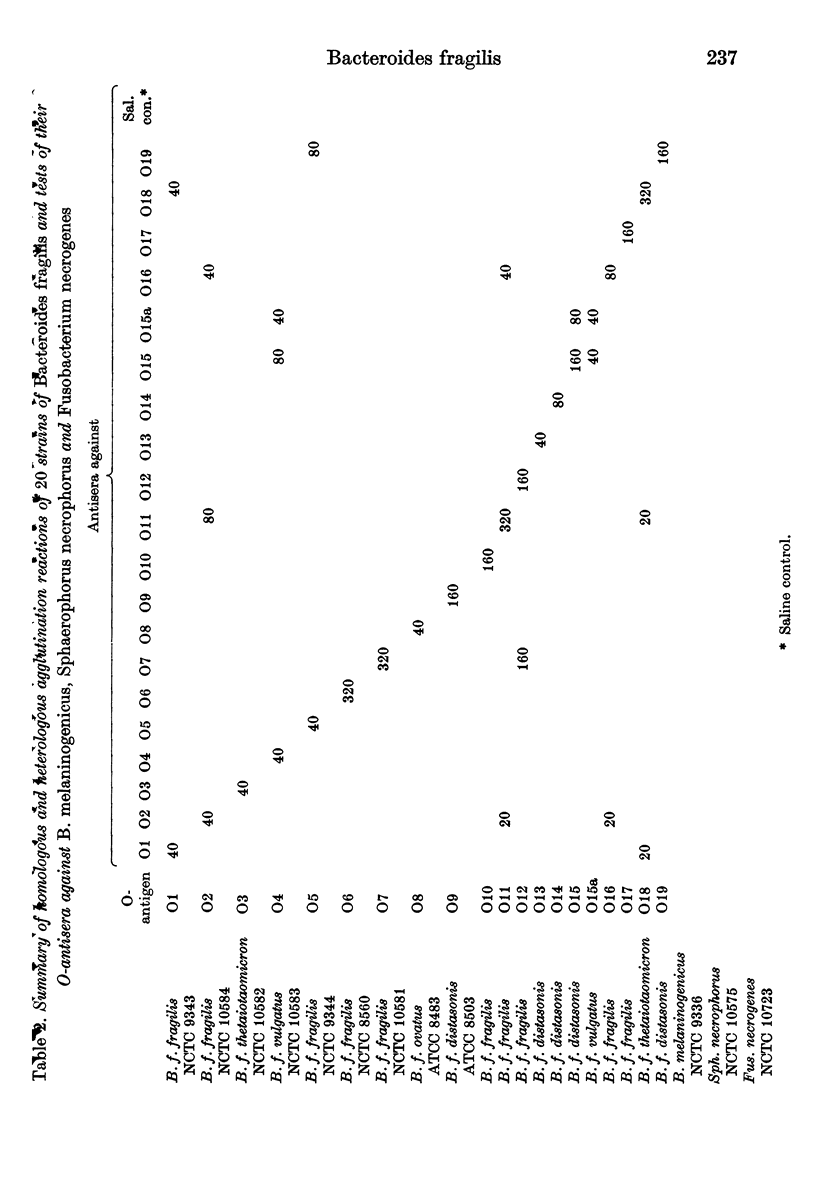
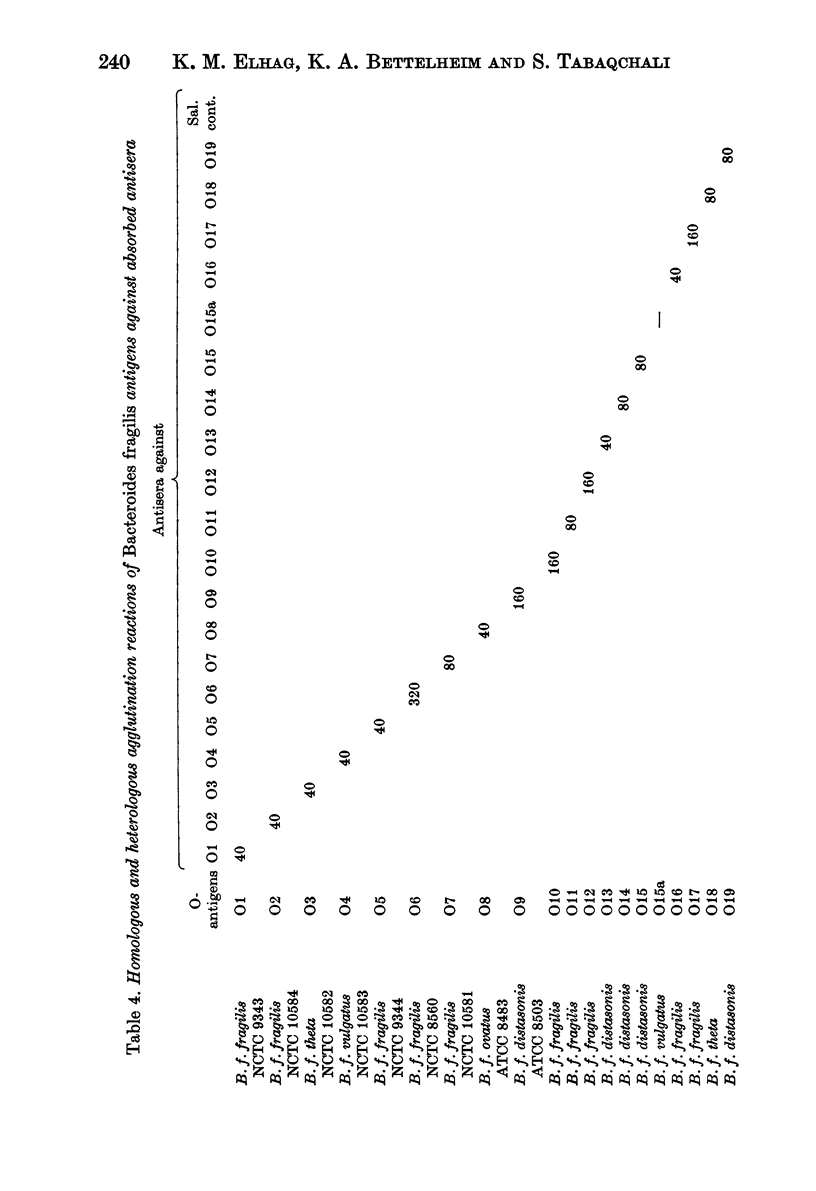
Using direct agglutination methods, a simple serological scheme for the classification of Bacteroides fragilis is described. Twenty strains of B. fragilis were selected by a process of sucessive screening from 151 strains obtained from various sources. O-antigens were prepared from the 20 strains, and used to raise antisera in rabbits. Each of the 20 antisera reacted with its homologous antigen and eight antisera cross-reacted with other subspecies. These cross-reactions were successfully removed after absorption of the antisera with the cross-reacting antigens, resulting in 19 type-specific antisera, titres ranging from 40 to 320, and 19 distinct serotypes of B. fragilis. There was no correlation between the antigenic and the biochemical characteristics of these strains and no cross-reactions occurred with other gram-negative anaerobes, B. melaninogenicus, Sphaerophorus necrophorus and Fusobacterium necrogenes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beerens H., Wattre P., Shinjo T., Romond C. Premiers résultats d'un essai de classification sérologique de 131 souches de Bacteroïdes du groupe fragilis (eggerthella. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Aug;121(2):187–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M. Infections due to anaerobes. Med Times. 1968 Feb;96(2):174–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Anaerobic infections (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1237–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. Chemical and biological characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Moroz D. A. Serogrouping of Bacteroides fragilis subsp. fragilis by the agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):586–592. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.586-592.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. A. Incidence and isolation of Bacteroides species from clinical material and their sensitivity to antibiotics. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Oct;26(10):738–741. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.10.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. E. Serology of rumen bacteroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Aug;67(3):273–288. doi: 10.1099/00221287-67-3-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Thompson F. S., Dowell V. R., Jr, Balows A. Micromethod system for identification of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.713-717.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H. A serological study of strains belonging to Sphaerophorus necrophorus, Sph. varius, and Sph. freundii. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1972;157(4):315–324. doi: 10.1007/BF02121123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H. Das serologische Verhalten von Stämmen der Species Bacteroides convexus, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus und B. distasonis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969 Jun;210(2):192–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


