Abstract
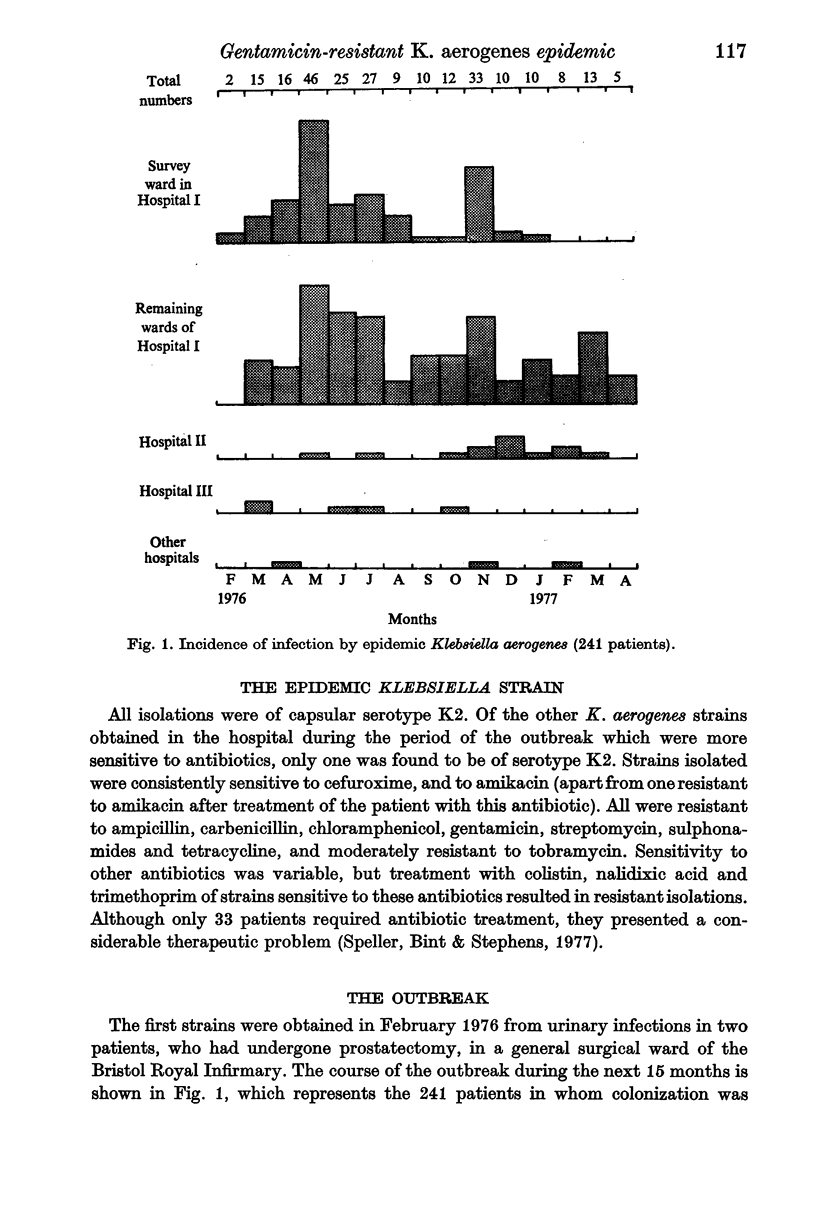
In the 15 months, February 1976 to April 1977, more than 241 patients became colonized with a strain of Klebsiella aerogenes, capsular serotype K2, resistant to most antibiotics. Urinary tract infection was the most common clinical manifestation but bacteraemia and, occasionally, infections of other sites were encountered. The main reservoir of the epidemic klebsiella was the gut, urine and skin of colonized patients. Gut carriage among staff was very uncommon. The most susceptible patients were elderly males, with debilitating illnesses and urinary tract abnormalities, especially if they were catheterized or receiving antibiotics. Likely vehicles for spread were the hands of staff, and contaminated bedpans and urinals. Control measures were directed at these factors. At the end of April 1977 no new cases had occurred for 3 months in the ward in which the outbreak began, and which had been the main focus of infection, and only 5 patients in the affected hospitals were known to be colonized by the epidemic klebsiella.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Detection of type-specific pneumococcal antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. I. Methodology and immunologic properties of pneumococcal antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):770–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes I., Gray A., Hurse A., Pavillard R. The emergence of gentamicin-resistant klebsiellae in a large general hospital. Med J Aust. 1977 Jan 1;1(1-2):14–16. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb130463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Sleigh J. D. Control of infection due to Klebsiella aerogenes in a neurosurgical unit by withdrawal of all antibiotics. Lancet. 1970 Dec 12;2(7685):1213–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Duncan I. B. Emergence of gentamicin-resistant Klebsiella in a general hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):179–184. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Weinstein R. A., Stamm W. E. Epidemics of nosocomial urinary tract infection caused by multiply resistant gram-negative bacilli: epidemiology and control. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):363–366. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. Nosocomial klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):657–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speller D. C., Raghunath D., Stephens M., Viant A. C., Reeves D. S., Wilkinson P. J., Broughall J. M., Holt H. A. Epidemic infection by a gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in three hospitals. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):464–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


