Abstract
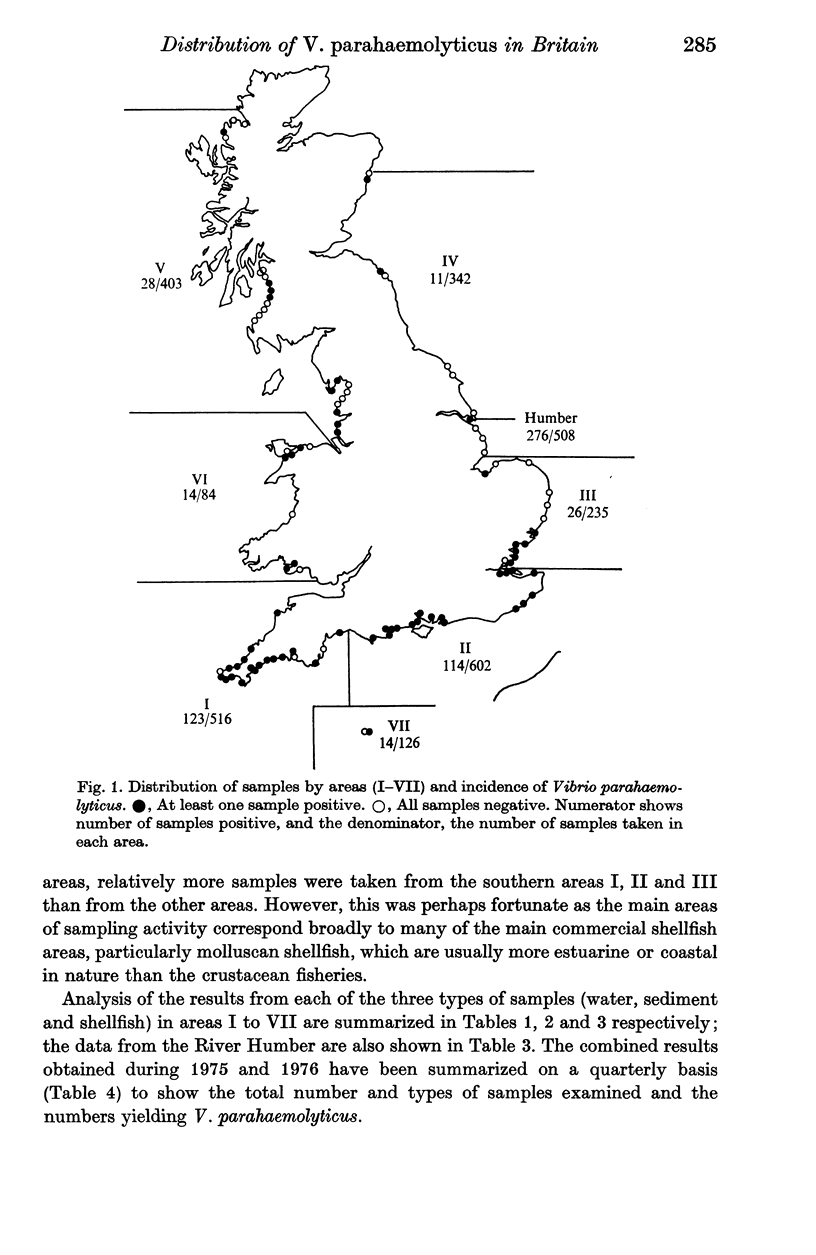
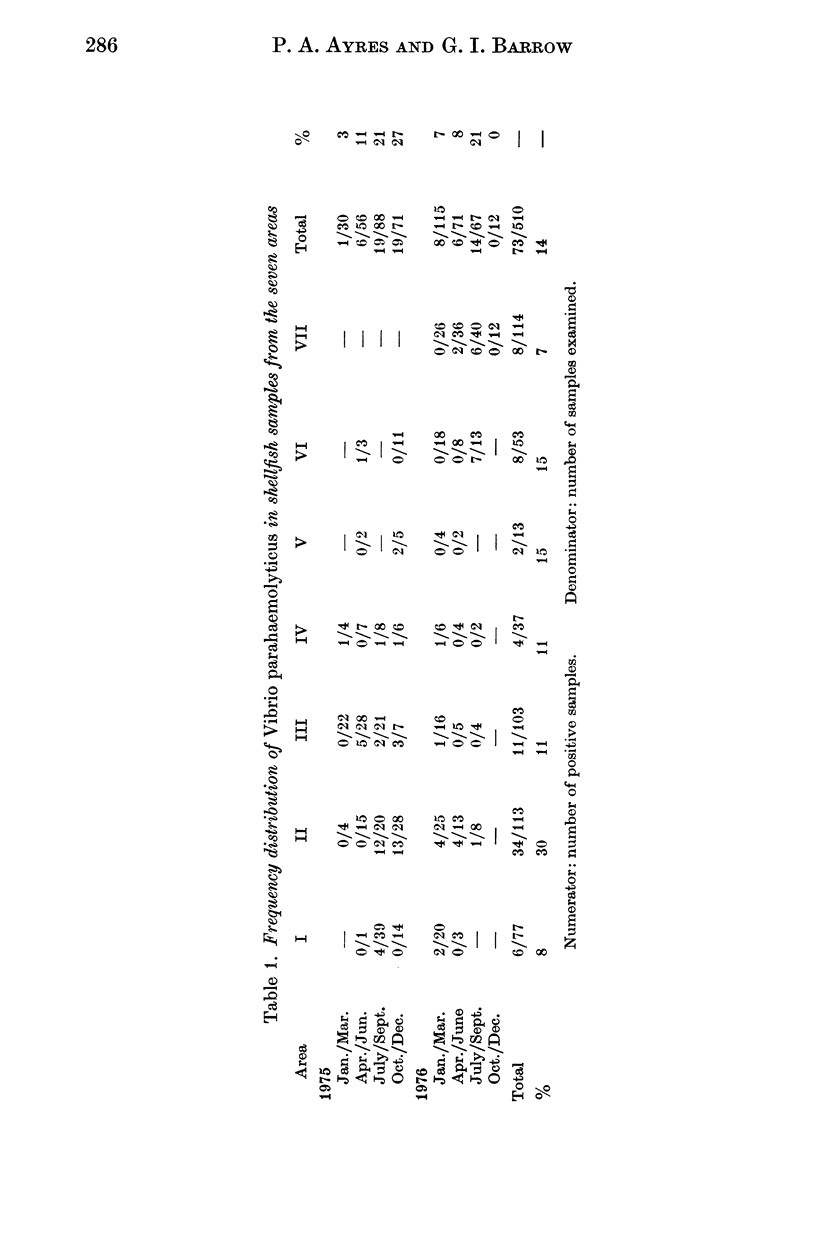
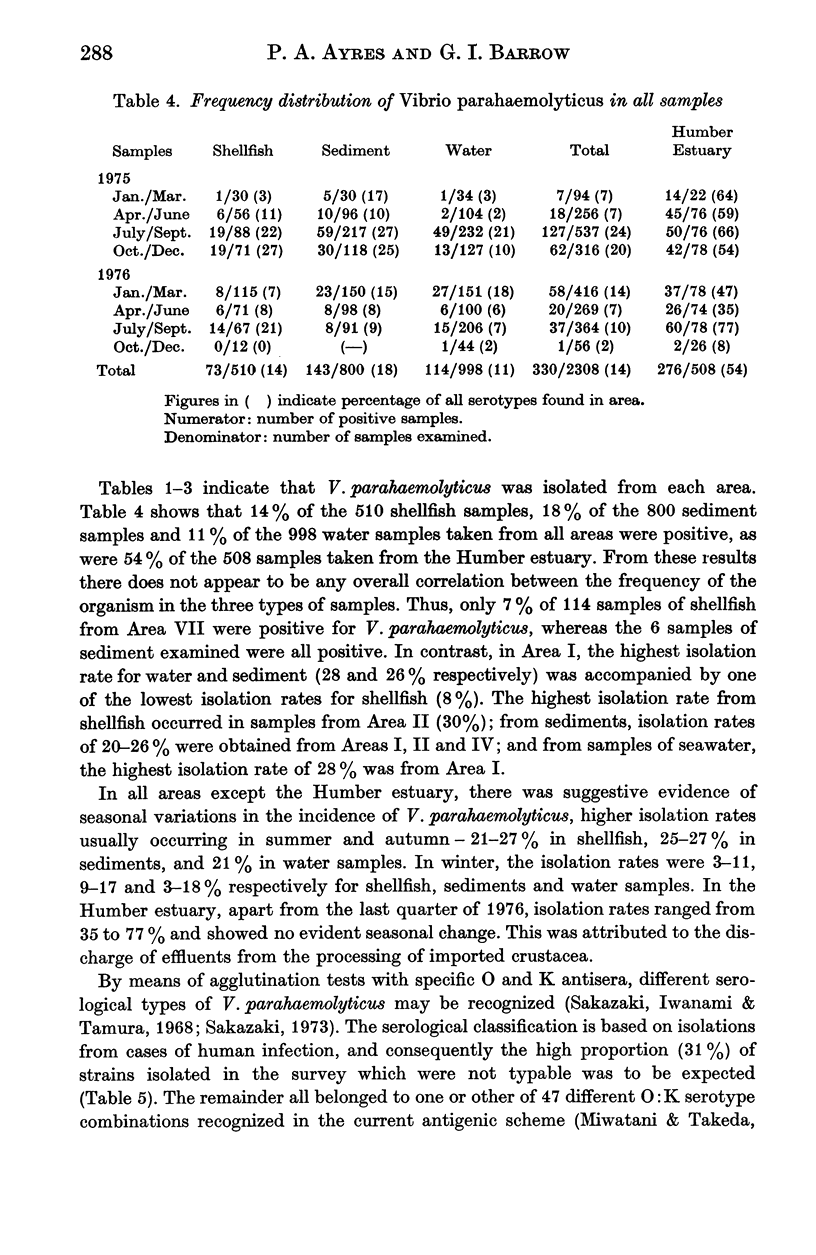
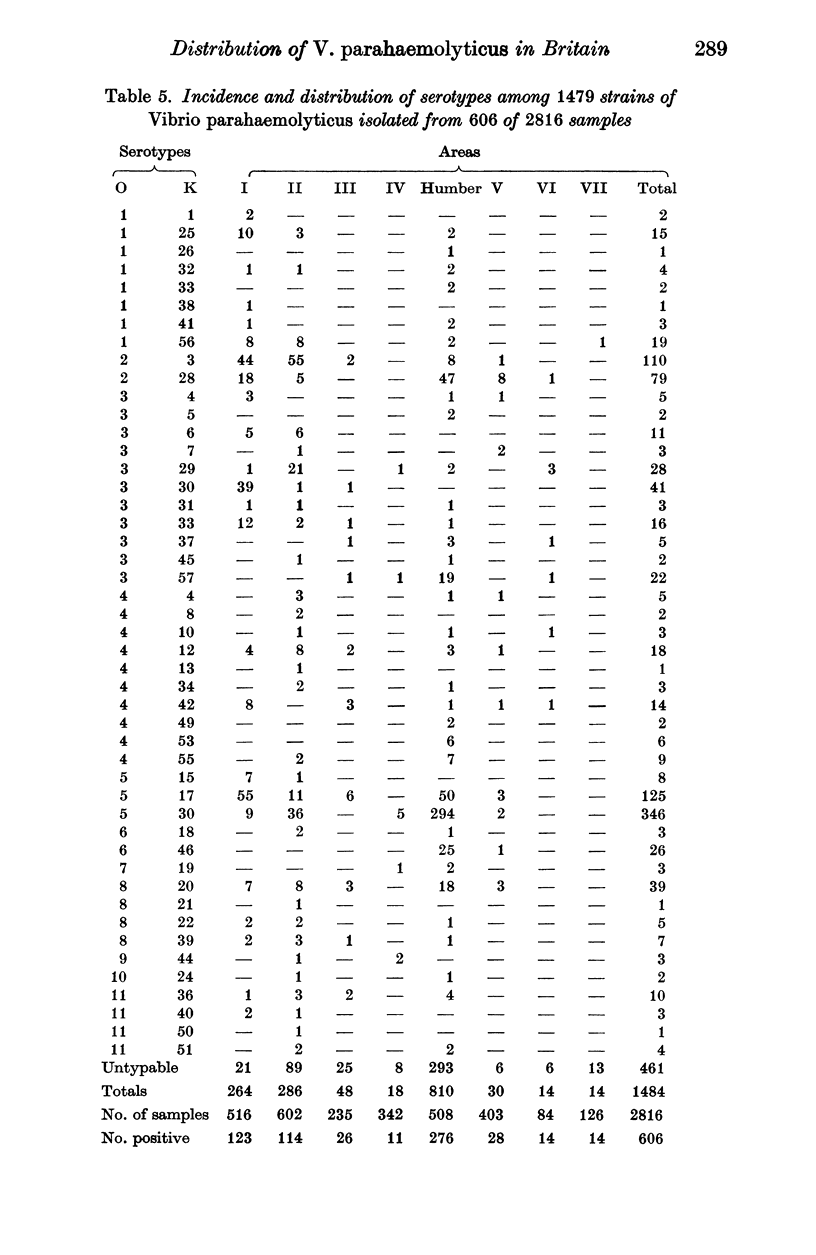
A collaborative survey has shown that V. parahaemolyticus is widely distributed in British coastal waters, sediments and shellfish, especially in southern and western areas. The relatively small numbers in the environment do not present significant health hazards from marine products, provided that processing, storage and distribution are adequate. The presence of this organism in small numbers in British coastal waters or in shellfish should not in itself be regarded as cause for concern.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker W. H., Jr Vibrio parahaemolyticus outbreaks in the United States. Lancet. 1974 Mar 30;1(7857):551–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92727-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baross J., Liston J. Isolation of vibrio parahaemolyticus from the Northwest Pacific. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1263–1264. doi: 10.1038/2171263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow G. I., Miller D. C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a potential pathogen from marine sources in Britain. Lancet. 1972 Feb 26;1(7748):485–486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey Y. M., Wallace R. B., Allan B. C., Keeffe B. M. Gastro-enteritis in Australia caused by a marine vibrio. Med J Aust. 1970 Feb 28;1(9):430–433. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1970.tb77967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockemühl J., Amédomé A., Triemer A. Gastro-enterites cholériformes dues à Vibrio parahaemolyticus sur la cote du Togo (Afrique occidentale. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1972 Sep;23(3):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubb H. D. Vibrio parahaemolyticus -- a marine pathogen detected in South African coastal waters. S Afr Med J. 1975 Aug 30;49(37):1514–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun D., Chung J. K., Seol S. Y., Tak R. Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the Republic of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Nov;23(6):1125–1130. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper W. L., Barrow G. I., McNab D. J. Vibrio parahaemolyticus food-poisoning in Britain. Lancet. 1974 Jun 1;1(7866):1100–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampelmacher E. H., van Noorle Jansen L. M., Mossel D. A., Groen F. J. A survey of the occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and V. alginolyticus on mussels and oysters and in estuarine waters in the Netherlands. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;35(3):431–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Adsorption of Vibrio parahaemolyticus onto chitin and copepods. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):269–274. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.269-274.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Ecology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.24-32.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Incidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.251-257.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAZAKI R., IWANAMI S., FUKUMI H. STUDIES ON THE ENTEROPATHOGENIC, FACULTATIVELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA, VIBRIO PARAHAEMOLYTICUS. I. MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND ITS TAXONOMICAL POSITION. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1963 Aug;16:161–188. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.16.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Iwanami S., Tamura K. Studies on the enteropathogenic, facultatively halophilic bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Serological characteristics. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):313–324. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKIKAWA I. Studies on pathogenic halophilic bacteria. Yokohama Med Bull. 1958 Oct;9(5):313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen-Yoji H., Le Clair R. A., Ota K., Montague T. S. Comparison of Vibrio parahaemolyticus cultures isolated in the United States with those isolated in Japan. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):237–241. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


