Abstract
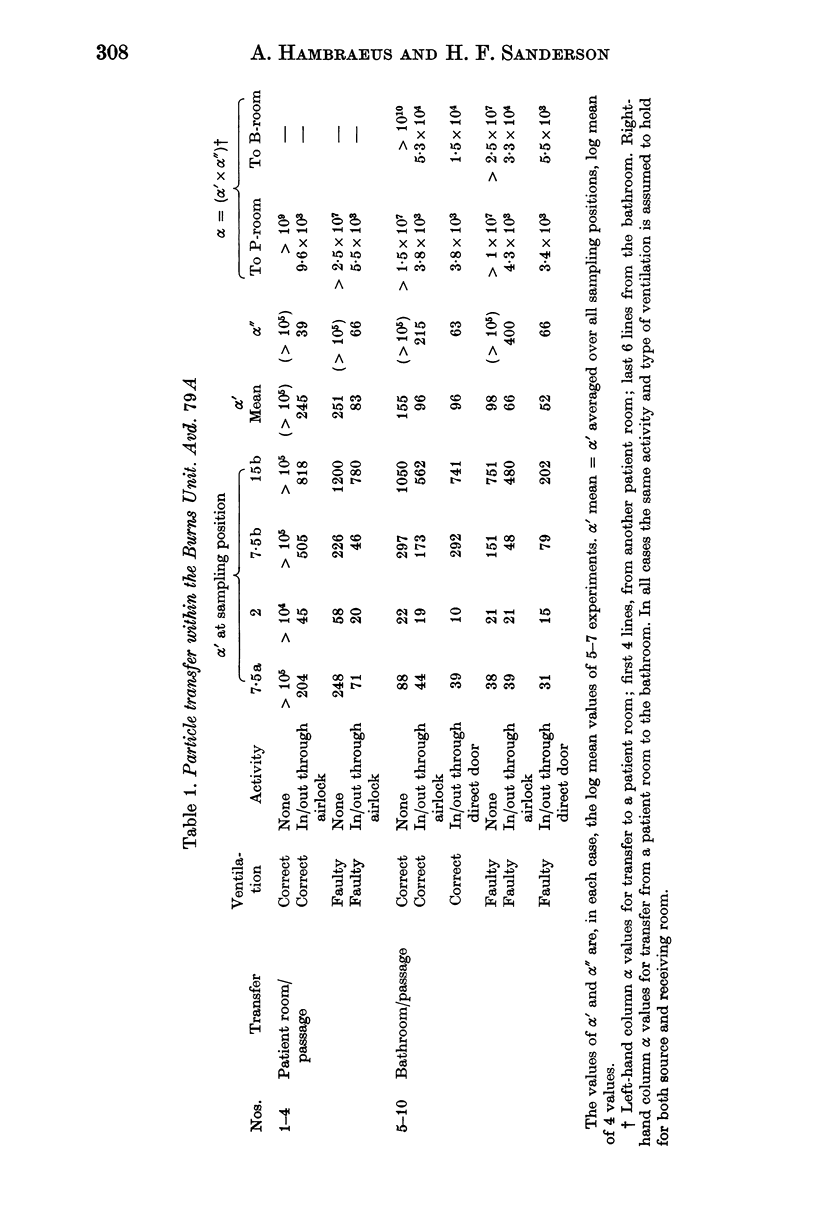
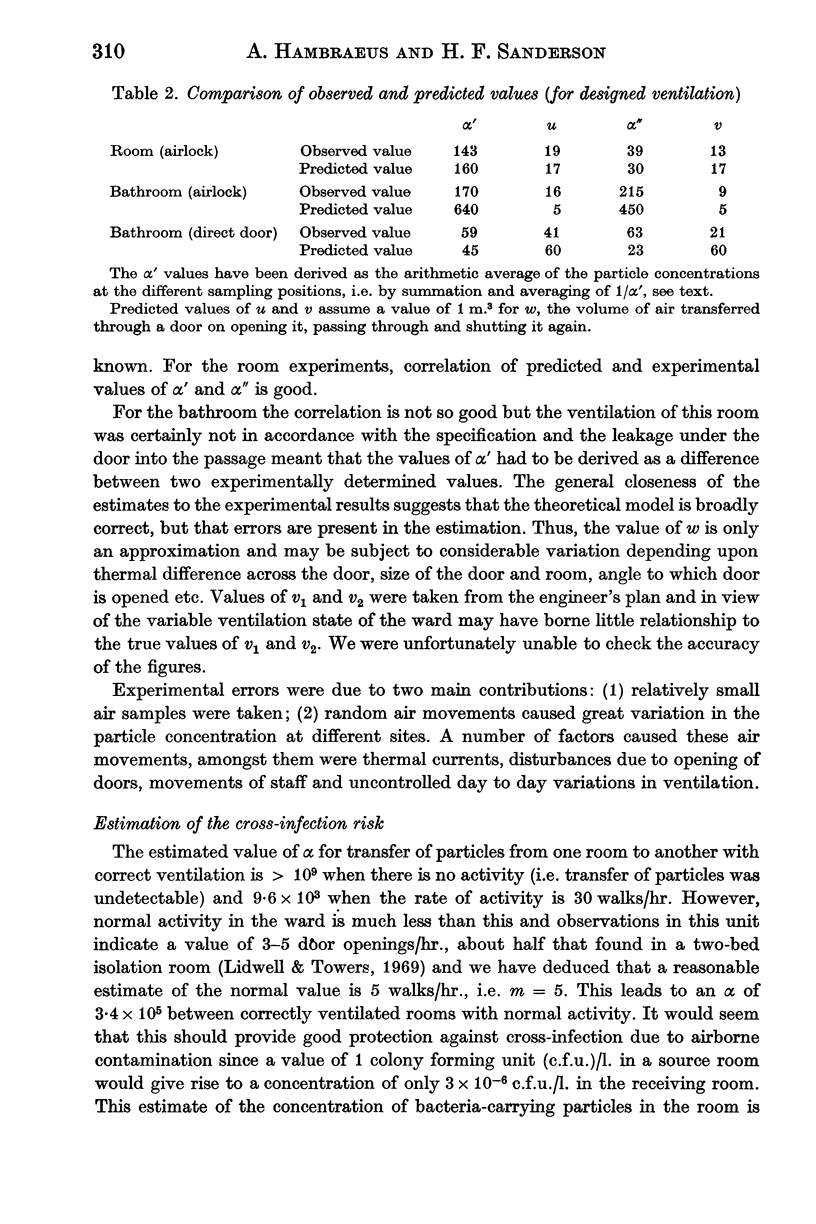
Airborne-particle transfer has been studied in a burns unit using potassium iodide particles. The observed rates of transfer were in good agreement with the values predicted by a theoretical model.
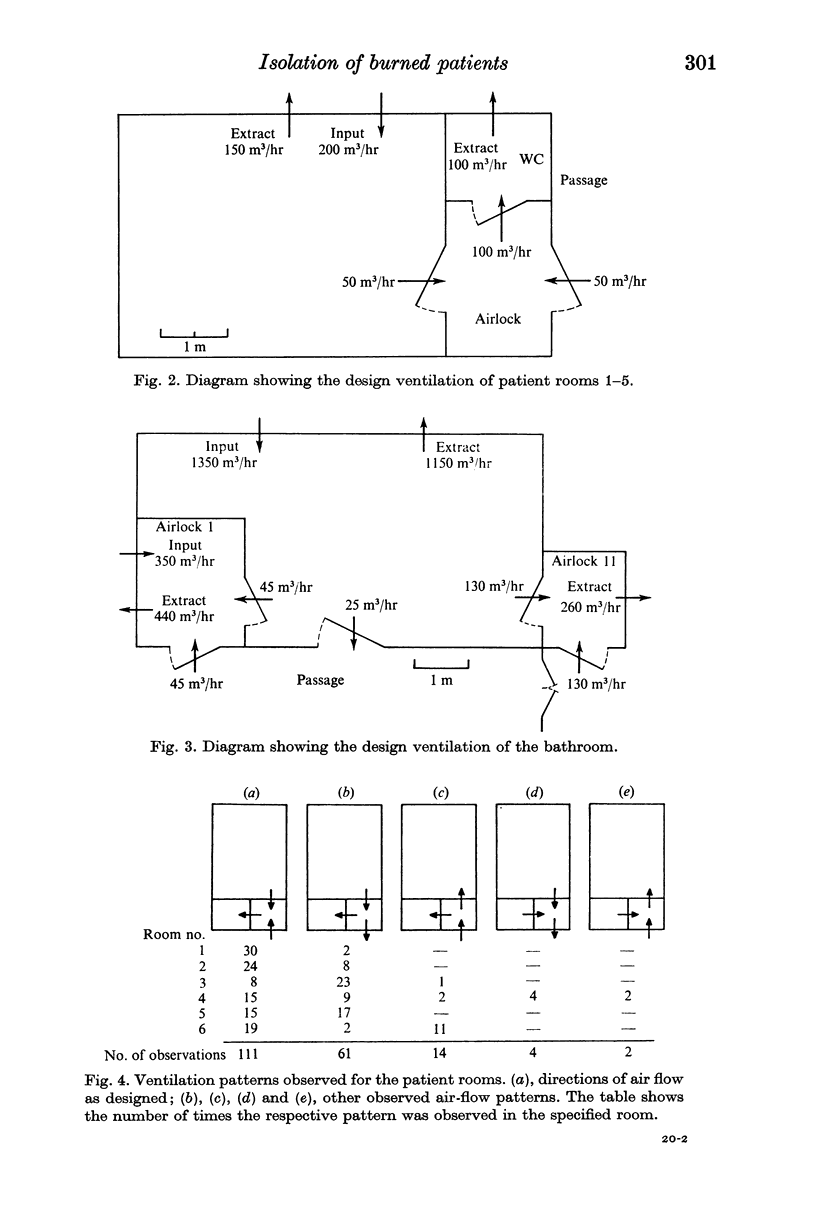
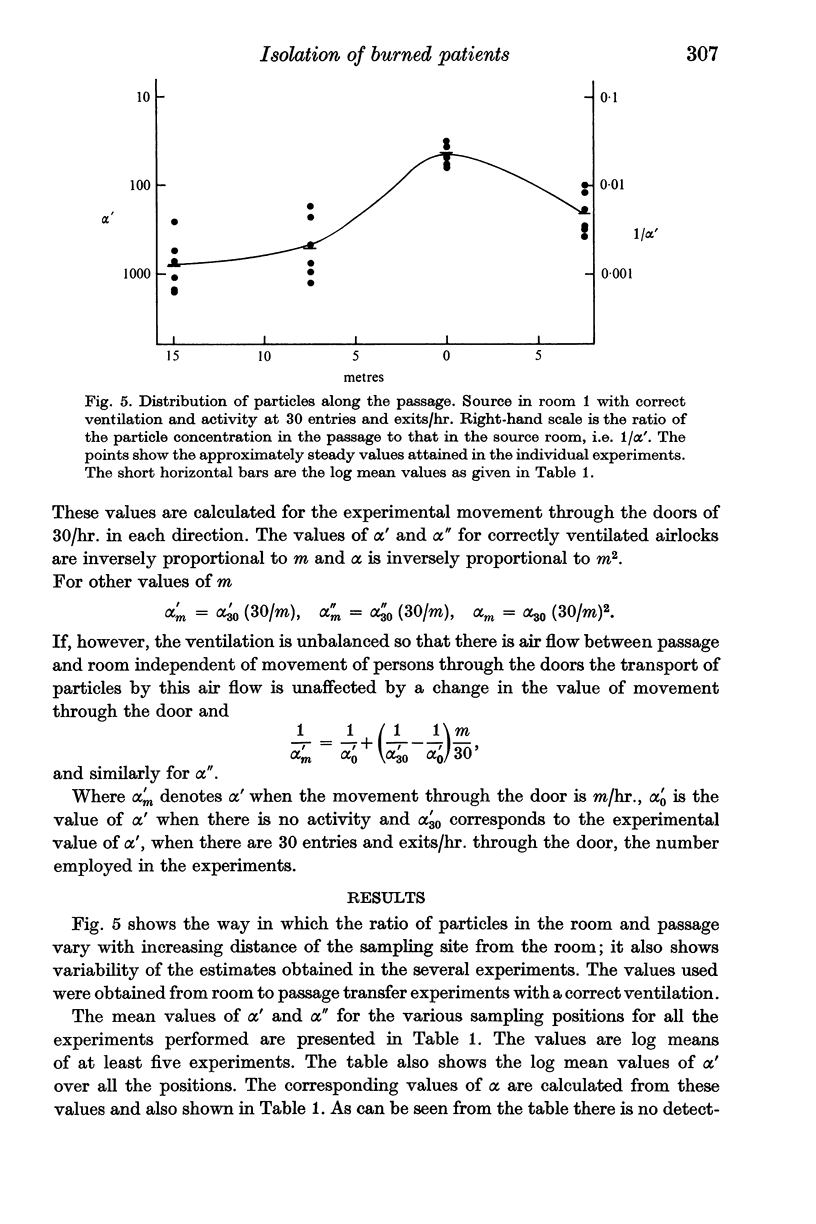
An estimate of the average transfer between rooms under conditions of normal activity and with correctly functioning ventilation showed that the isolation system was highly efficient, the proportion transferred being probably less than 1 in 105. However, the ventilation often did not function as designed and under these conditions the efficiency was reduced by a maximum of a factor of ten. These rates of transfer do not seem great enough to account for the high rate of cross-infection found in this unit.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Foord N., Lidwell O. M. The control by ventilation of airborne bacterial transfer between hospital patients, and its assessment by means of a particle tracer. I. An airborne-particle tracer for cross-infection studies. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Jun;70(2):279–286. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidwell O. M., Polakoff S., Davies J., Hewitt J. H., Shooter R. A., Walker K. A., Gaya H., Taylor G. W. Nasal acquisition of Staphylococcus aureus in a subdivided and mechanically ventilated ward: endemic prevalence of a single staphylococcal strain. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):417–433. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidwell O. M. The control by ventilation of airborne bacterial transfer between hospital patients, and its assessment by means of a particle tracer. II. Ventilation in subdivided isolation units. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Jun;70(2):287–297. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidwell O. M., Towers A. G. Protection from microbial contamination in a room ventilated by a uni-directional air flow. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Mar;67(1):95–106. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400041474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE W. C., LIDWELL O. M., KINGSTON D. THE SIZE DISTRIBUTION OF AIRBORNE PARTICLES CARRYING MICRO-ORGANISMS. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Dec;61:385–391. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


