Abstract
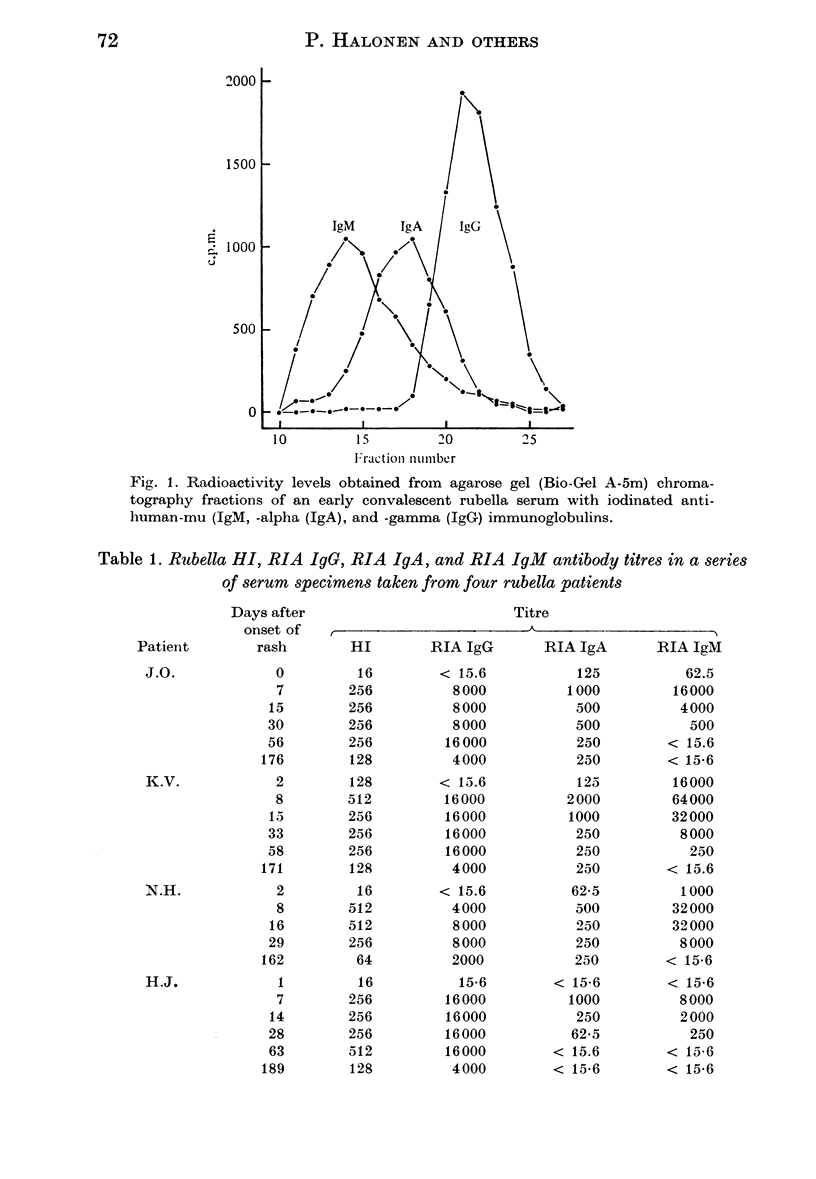
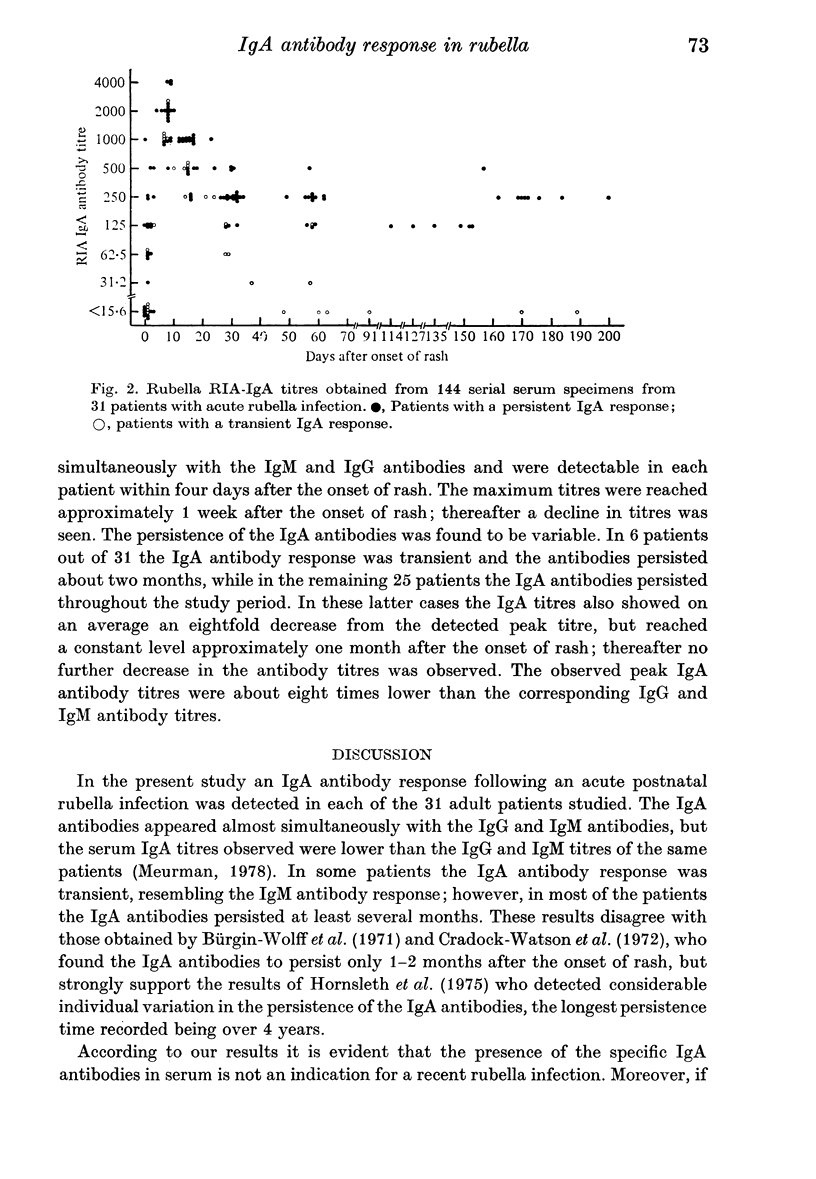
A solid-phase radioimmunoassay (RIA) for detecting rubella virus IgA serum antibodies was developed. Purified rubella virus grown in roller cultures of Vero cells was adsorbed onto polystyrene beads. The coated beads were then incubated with dilutions of serum, and rubella IgA antibodies which attached to the virus antigen on the solid-phase were subsequently detected with 125I-labelled anti-human-alpha antibodies. The specificity of the iodinated anti-human immunoglobulins was confirmed by RIA analysis of fractions obtained by chromatography of an early convalescent serum on an agarose column. A complete separation of IgM, IgA, and IgG was observed. A total of 144 serial serum specimens from 31 adult patients with an acute rubella infection were tested for rubella IgA antibodies, and the results were compared with the RIA IgG and IgM titres reported earlier from the same specimens. The RIA IgA response was detected in each of the 31 patients and the IgA antibodies appeared almost simultaneously with the IgG and IgM antibodies. The maximum titres, which were lower than the IgG and IgM titres, were reached in about 1 week after the onset of rash. In 6 patients out of 31 the IgA antibody response was transient and persisted approximately two months, while in the remaining 25 patients the IgA antibodies persisted throughout the study period of more than 5 months. The results obtained indicate that the presence of rubella IgA antibodies in serum is not an indication for a recent rubella infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Nakib W., Best J. M., Banatvala J. E. Rubella-specific serum and nasopharygeal immunoglobulin responses following naturally acquired and vaccine-induced infection. Prolonged persistence of virus-specific IgM. Lancet. 1975 Jan 25;1(7900):182–185. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ankerst J., Christensen P., Kjellén L., Kronvall G. A rountine diagnostic test for IgA and IgM antibodies to rubella virus: absorption of IgG with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):268–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgin-Wolff A., Hernandez R., Just M. Separation of rubella IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies by gel filtration on agarose. Lancet. 1971 Dec 11;2(7737):1278–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Bourne M. S., Vandervelde E. M. IgG, IgA and IgM responses in acute rubella determined by the immunofluorescent technique. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Sep;70(3):473–485. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsleth A., Leerhoy J., Grauballe P., Spanggaard H. Persistence of rubellavirus-specific immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies: investigation of successive serum samples with lowered immunoglobulin G concentration. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):804–808. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.804-808.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Meurman O. H., Halonen P. E., Ziola B. R., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K., Toivanen P. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella virus immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):117–123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.117-123.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H. Antibody responses in patients with rubella infection determined by passive hemagglutination, hemagglutination inhibition, complement fixation, and solid-phase radioimmunoassay tests. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):369–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.369-372.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella virus immunoglobulin M antibodies: comparison with sucrose density gradient centrifugation test. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):257–262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.257-262.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Ziola B. R. IgM-class rheumatoid factor interference in the solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella-specific IgM antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):483–487. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Kerr-Grant D., Umana G., Dzierba J., Weintraub D. Antibody response in serum and nasopharynx after naturally acquired and vaccine-induced infection with rubella virus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 9;285(24):1333–1339. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112092852401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J. R., Mace J. E. Elution patterns of rubella IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies from a dextran and an agarose gel. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Aug;28(8):670–673. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.8.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggendorf M., Schneweis K. E., Wolff M. H. Zum Nachweis Röteln-spezifischer IgM im Hämagglutinations-hemmungstest. Vergleichende Untersuchungen mit der Absorption von IgG durch Protein A-haltige Staphylokokken und der Dichtegradienten-Ultrazentrifugation. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Aug;235(4):363–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Shimizu H., Kampa D., Doerr H. W. Rapid method to detect rubella immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):132–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.132-135.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


