Abstract
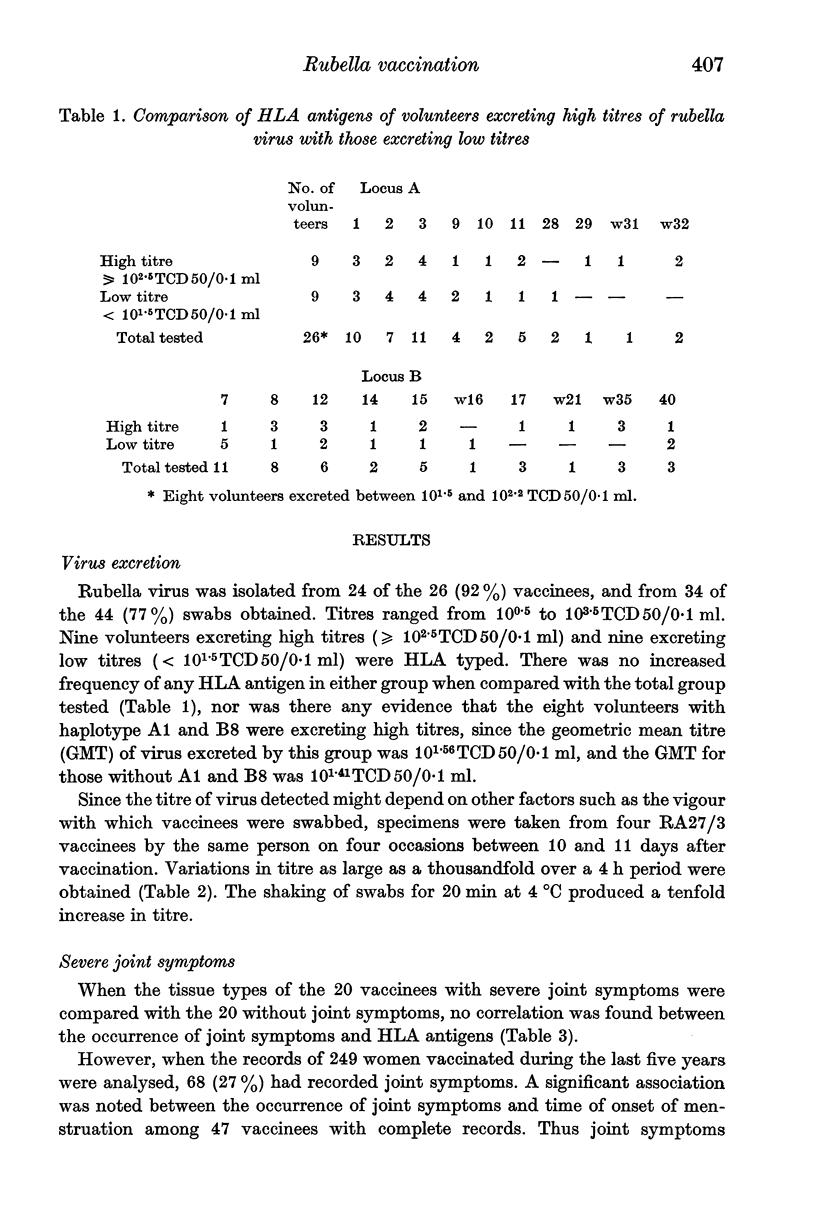
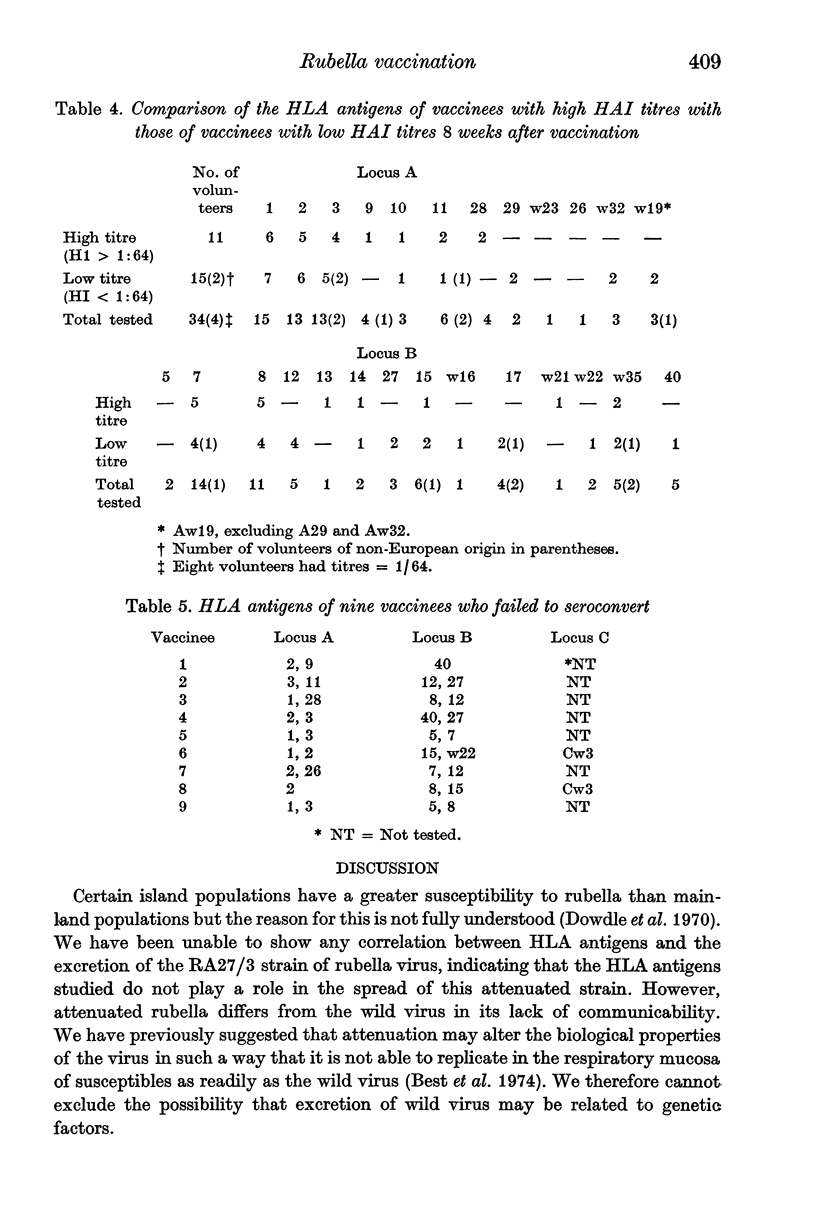
Attempts were made to correlate virus excretion, joint symptoms and antibody response with human leukocyte antigens (HLA) in seronegative adult women given attenuated rubella vaccine. No association was shown between HLA antigens of the A and B loci and excretion of either high or low titres of RA27/3 vaccine among 26 volunteers. However, virus excretion was influenced by such factors as the time of day at which specimens were collected and the method of virus isolation. Our study therefore failed to confirm the hypothesis that certain persons are good 'spreaders' of rubella virus and that this capacity is associated with HLA-A1 and B8. The study of joint symptoms following vaccination with Cendehill, HPV77.DE-5, RA27/3 or To-336 vaccines showed no association between such symptoms and HLA antigens. However, joint symptoms occurred within 7 days of the onset of menstruation in 33 of 47 (70%) vaccinees (P less than 0.01) and it is therefore suggested that hormonal factors must play a role. No association between HLA antigens and haemagglutination inhibition (HAI) antibody titres, 8 weeks after vaccination with RA27/3, was found amongst 34 volunteers.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. M., Banatvala J. E., Bowen J. M. New Japanese rubella vaccine: comparative trials. Br Med J. 1974 Jul 27;3(5925):221–224. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5925.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. M., Banatvala J. E. Studies on rubella virus strain variation by kinetic haemagglutination-inhibition tests. J Gen Virol. 1970 Dec;9(3):215–223. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-9-3-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. L. Measles endemicity in insular populations: critical community size and its evolutionary implication. J Theor Biol. 1966 Jul;11(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W. C. World aspects of the epidemiology of rubella. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jul;118(1):112–122. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040114019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. Z., Matters B., Rosenblum J. K., Krugman S. Experience with a modified rubella hemagglutination inhibition antibody test. JAMA. 1969 Jan 6;207(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle W. R., Ferrera W., De Salles Gomes L. F., King D., Kourany M., Madalengoitia J., Pearson E., Swanston W. H., Tosi H. C., Vilches A. M. WHO collaborative study on the sero-epidemiology of rubella in Caribbean and Middle and South American populations in 1968. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(3):419–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. L., Detels R., Kim K. S., Beasley R. P., Grayston J. T. Epidemiology of rubella on Taiwan. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jul;118(1):143–145. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040145024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. M., Spruance S. L., Ogra P. L., Thompson G. R., DeWitt C. W. HLA and recurrent episodic arthropathy associated with rubella vaccination. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1192–1197. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., Diwan A. R., Oda A. I. Susceptibility of rubella among adolescents and adults in Hawaii. JAMA. 1969 Dec 8;210(10):1881–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman M. C., Dorman D. C., Menser M. A., Forrest J. M., Guinan J. J., Clark P. HL-A antigens in congenital rubella and the role of antigens 1 and 8 in the epidemiology of natural rubella. Tissue Antigens. 1975 Feb;5(1):12–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1975.tb00520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman M. C., Menser M. A. Ethnicity is a significant factor in the epidemiology of rubella and Hodgkin's disease. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):441–442. doi: 10.1038/251441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Kimura M., Takakura I., Sakakibara T., Inouye H., Tsuji K. Possible associations between HLA antigens and the immune responsiveness to attenuated rubella vaccine. Tissue Antigens. 1978 May;11(5):475–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono R., Hayakawa Y., Hibi M., Ishii K. Experimental vertical transmission of rubella virus in rabbits. Lancet. 1969 Feb 15;1(7590):343–347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts O. M., Ravenel J. M., Finklea J. F. Rubella immunity in Trinidad. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Mar;89(3):271–276. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. E., Banatvala J. E., Best J. M. Interferon studies with Japanese and U.S. rubella virus strains. Br Med J. 1973 Jan 27;1(5847):197–199. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5847.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L., Bradstreet C. M., Bailey M., Ferris A. A., Lehmann N. I., Nagler F. P., Furesz J., Kono R., Ohtawara M. WHO collaborative study on the sero-epidemiology of rubella. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(1):79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugishita C., O'Shea S., Best J. M., Banatvala J. E. Rubella serology by solid-phase radioimmunoassay: its potential for screening programmes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):50–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


