Abstract
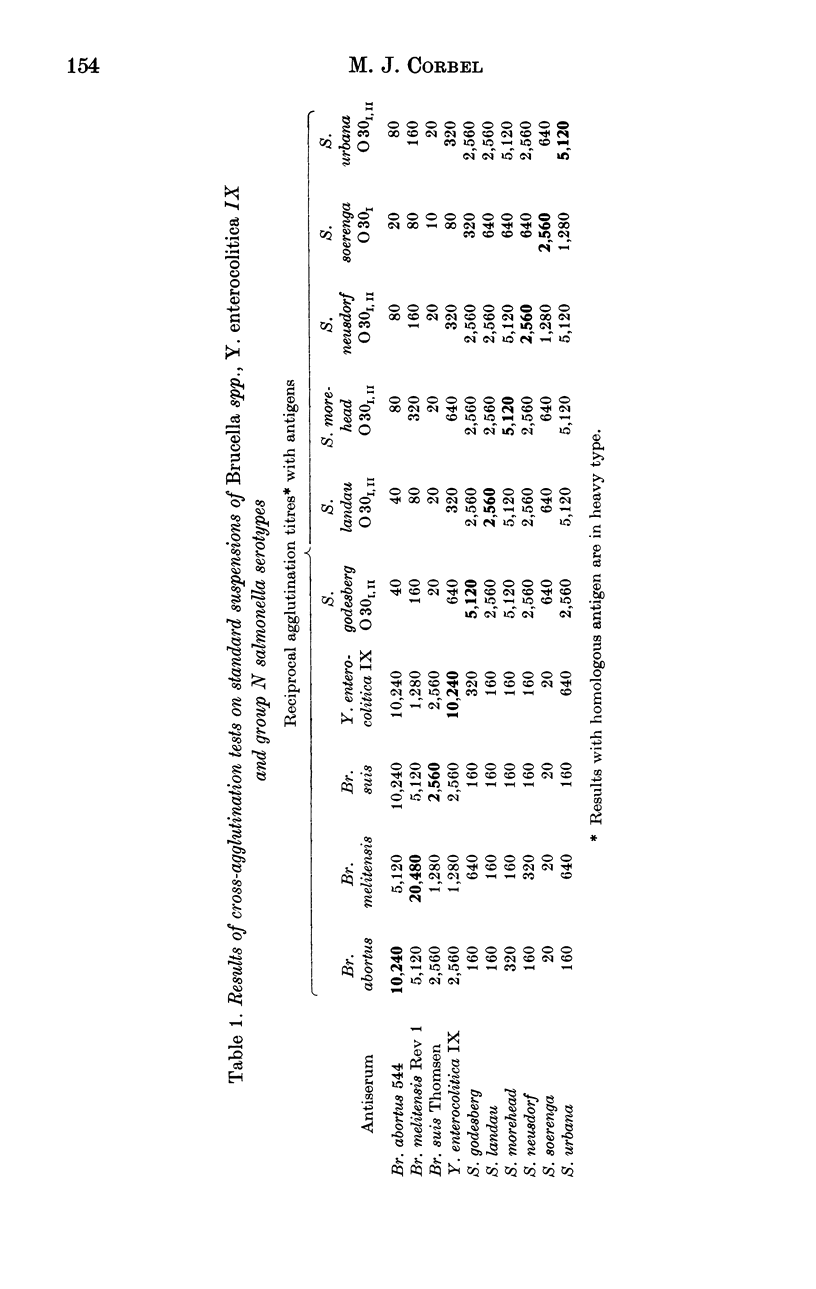
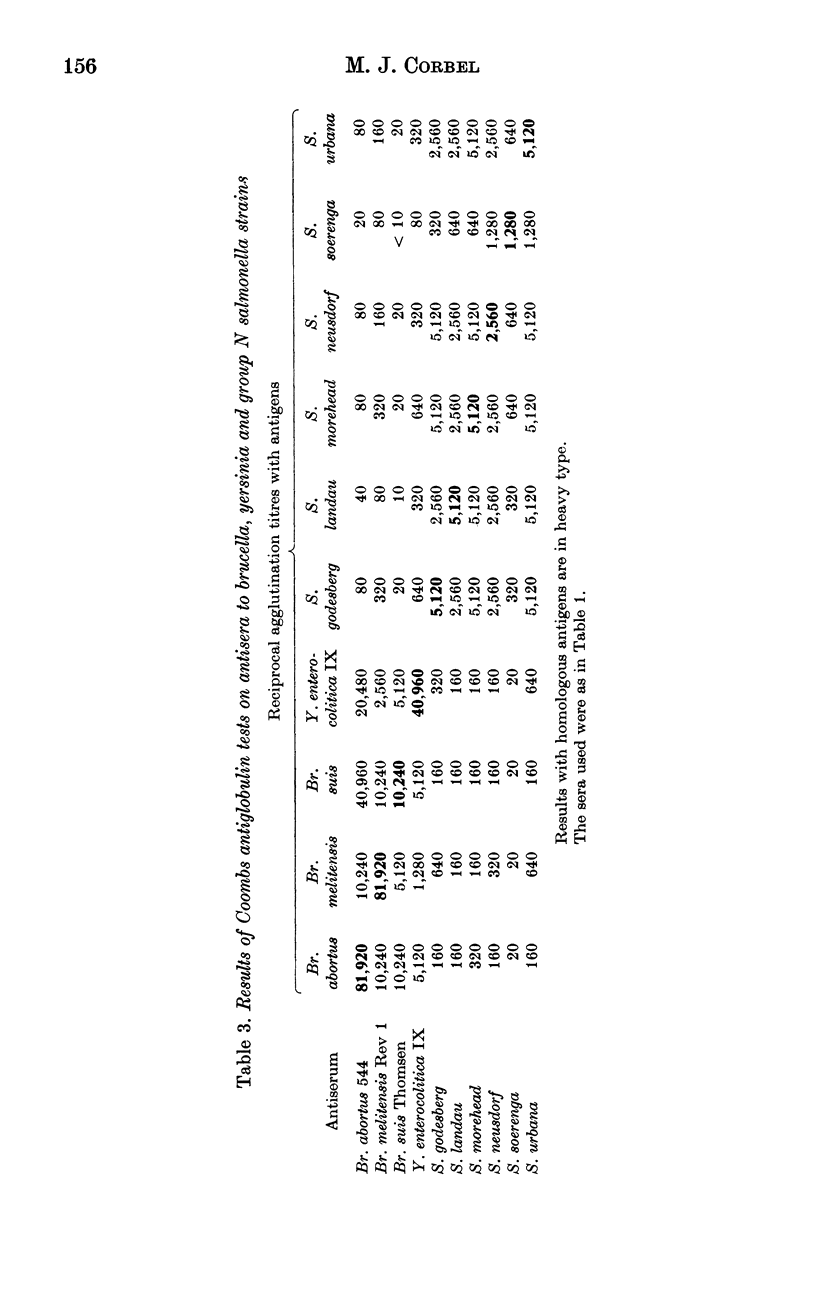
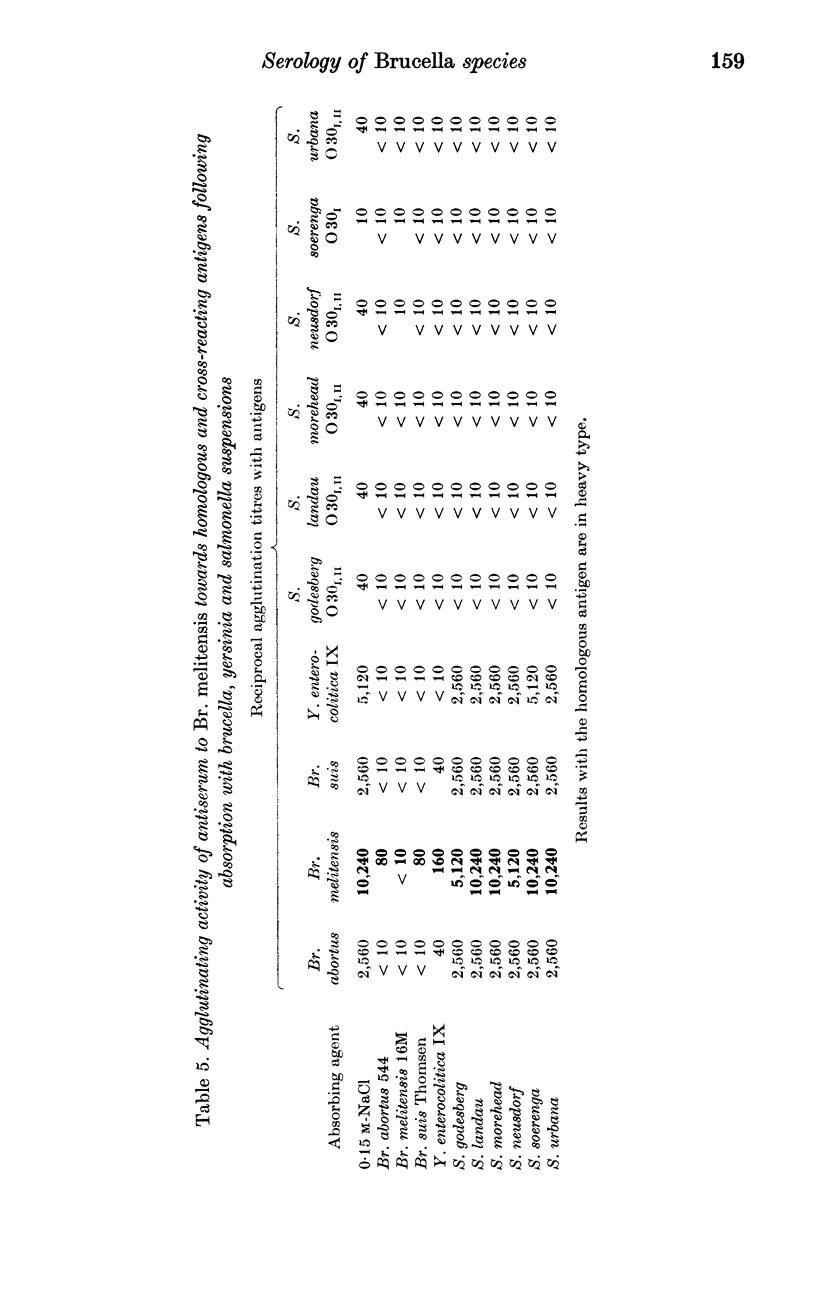
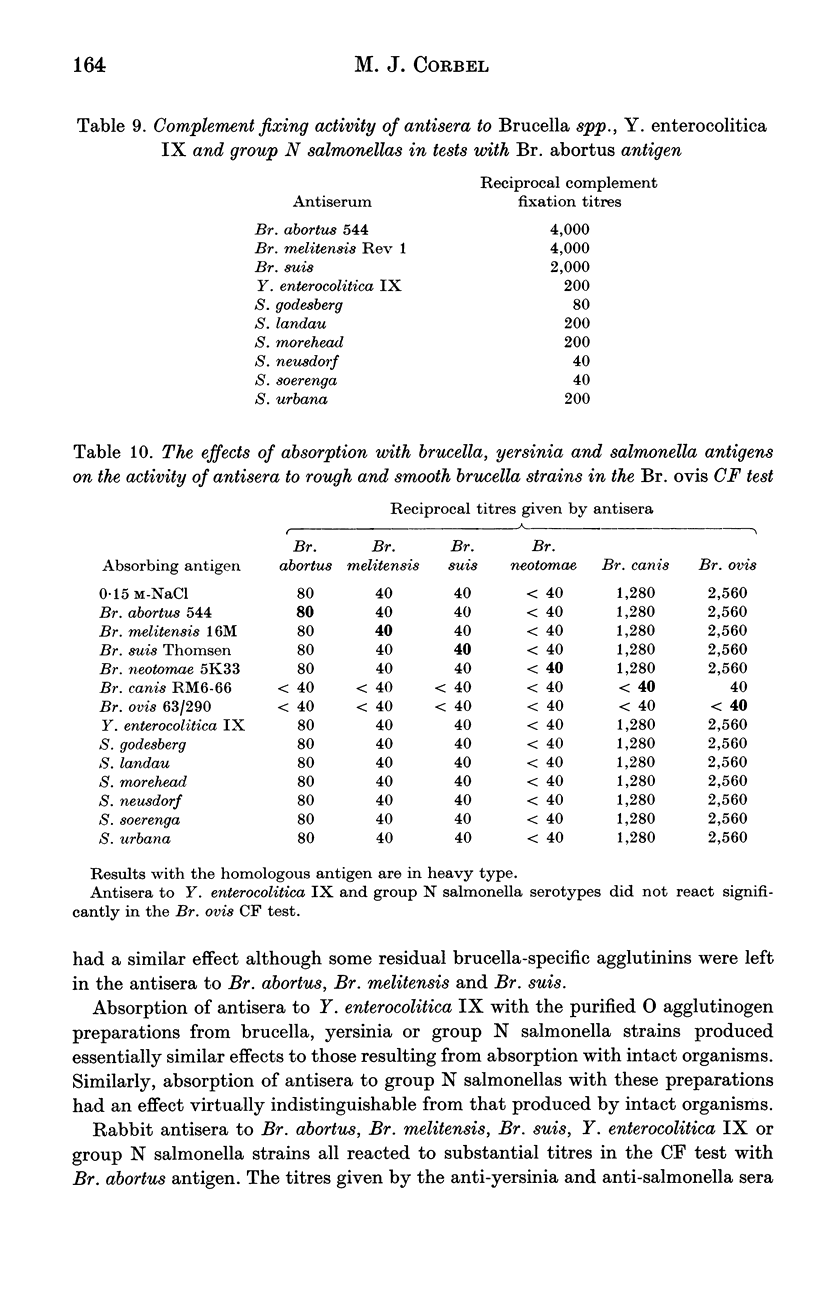
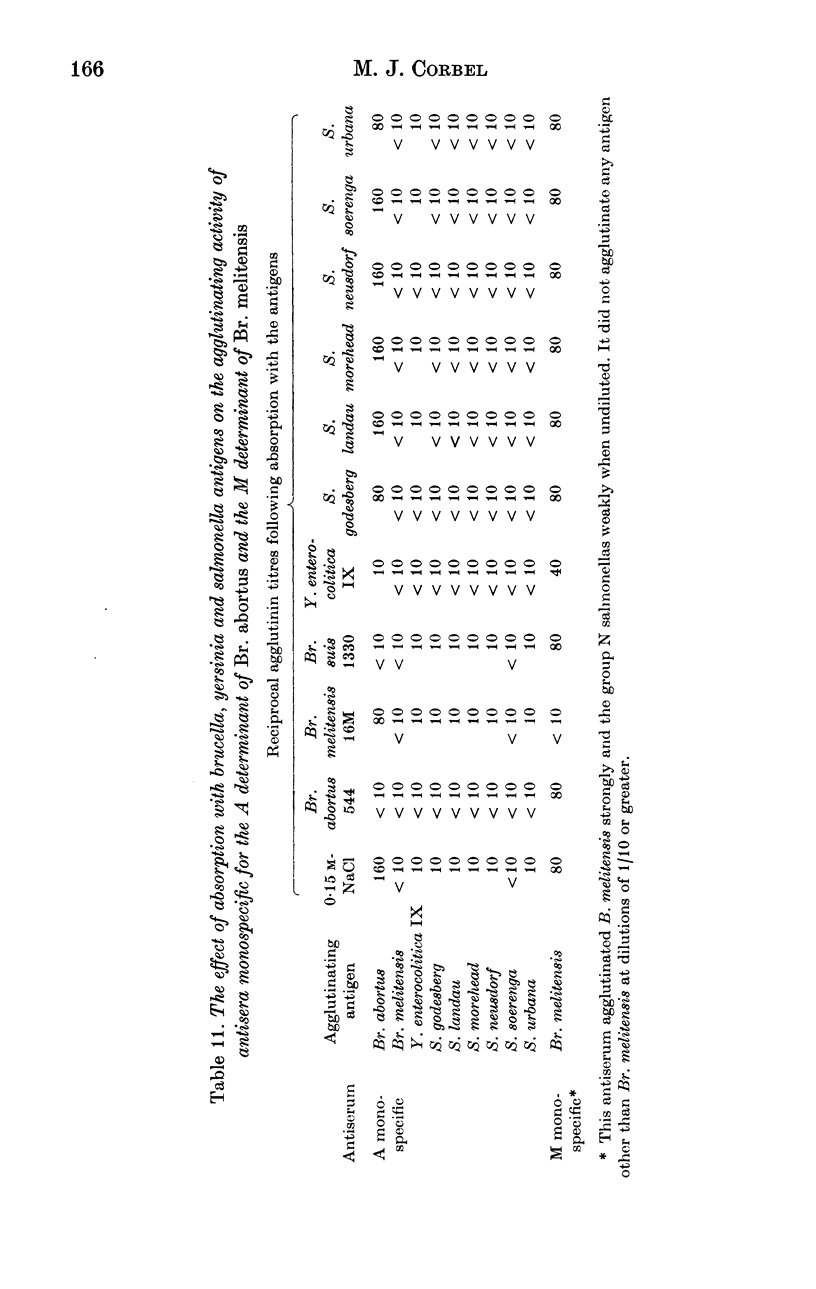
The serological relationship between Brucella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica IX, and the group N salmonella serotypes S. godesberg, S. landau, S. morehead, S. neusdorf, S. soerenga and S. urbana was examined using agglutination, antiglobulin, complement fixation, immunodiffusion and fluorescent antibody methods. Antisera to the group N salmonella serotypes all reacted to significant titres in agglutination and complement fixation, but not antiglobulin or immunodiffusion tests with smooth brucella antigens. These antisera also reacted in agglutination, but not antiglobulin, tests with Y. enterocolitica IX. They did not react significantly in any tests with rough brucella antigens. Conversely, antisera to smooth Brucella spp. agglutinated group N salmonellas to low titre and Y. enterocolitica IX to titres similar to those given against the homologous strain. Antiserum to Y. enterocolitica IX on the other hand reacted with smooth brucella antigens to high titre in agglutination, complement fixation and antiglobulin tests, and with the group N salmonella antigens to substantial titres in agglutination tests. In direct fluorescent antibody tests, smooth Brucella strains and Y. enterocolitica IX reacted strongly with FITC-labelled antibody to Br. abortus whereas the group N salmonella strains reacted weakly. In tests with monospecific antisera to the A and M determinants of Br. abortus and Br. melitensis respectively, Y. enterocolitica IX reacted only with the antiserum to the A determinant whereas group N salmonellas reacted to low titre with both A and M antisera. The results of cross-absorption tests confirmed this relationship and suggested that the O30 antigens of group N salmonella serotypes contained antigenic determinants similar to, but not identical with, the antigenic structure shared by smooth Brucella spp. and Y. enterocolitica IX.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahvonen P., Jansson E., Aho K. Marked cross-agglutination between Brucellae and a subtype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(2):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIBERSTEIN E. L., McGOWAN B. Epididymitis in rams; studies on laboratory diagnosis. Cornell Vet. 1958 Jan;48(1):31–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J., Cullen G. A. Differentiation of the serologicl response to Yersinia enterocolitica and Brucella abortus in cattle. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Dec;68(4):519–530. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J., Day C. A. Assessment of indirect haemagglutination procedures for the serological diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. Br Vet J. 1973 Sep-Oct;129(5):480–492. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)36389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J., Phillip J. I. The relationship of Brucella abortus agglutinogenic antigens to the receptor sites for Tbilisi phage. Res Vet Sci. 1972 Jan;13(1):91–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J. The direct fluorescent antibody test for detection of Brucella abortus in bovine abortion material. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Mar;71(1):123–129. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J. The nature of the antibody response to Yersinia enterocolitica serotype IX in cattle. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Jun;71(2):309–323. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELTYNOWSKI A., LAZUGA K., MIERZEJEWSKI T., PARNAS J. Badania porównawcze nad właściwościami pałeczek: Pasteurella tularemiae, Pasteurella multocida, Pasteurella rodentium i Brucella brucei. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med. 1955;10:207–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C. Somatic O antigen relationship of Brucella and Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):645–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.645-649.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fribourg-Blanc A. Etude par immunofluorescence des antigènes somatiques de Yersinia enterocolitica. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1971;29(3):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Hoghooghi N. The presence of snails of veterinary importance in Isfahan, Iran. Br Vet J. 1973 Mar-Apr;129(2):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)36560-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. SEPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF A COMMON ANTIGEN IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:565–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Chalon A. M., Véron M. Recherches sur la présence de l'antigène commun des "Enterobacteriaceae" (antigène Kunin) chez les "Yersinia", "Levinea", "Aeromonas" et "Vibrio". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):761–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., MILNER K. C., PERRINE T. D. Endotoxic and antigenic fractions from the cell wall of Salmonella enteritidis; methods for separation and some biologic activities. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusu V., Stănescu C., Muscan A., Lăzăroae D., Popescu M. Infection humaine à Yersinia enterocolitica sérotype 9. Implications épidémiologiques. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1970 Sep;29(3):507–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. The immunochemistry of Salmonella chemotype VI O-antigens. The structure of oligosaccharides from Salmonella group N (o 30) lipopolysaccharides. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):815–819. doi: 10.1042/bj0970815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


