Abstract
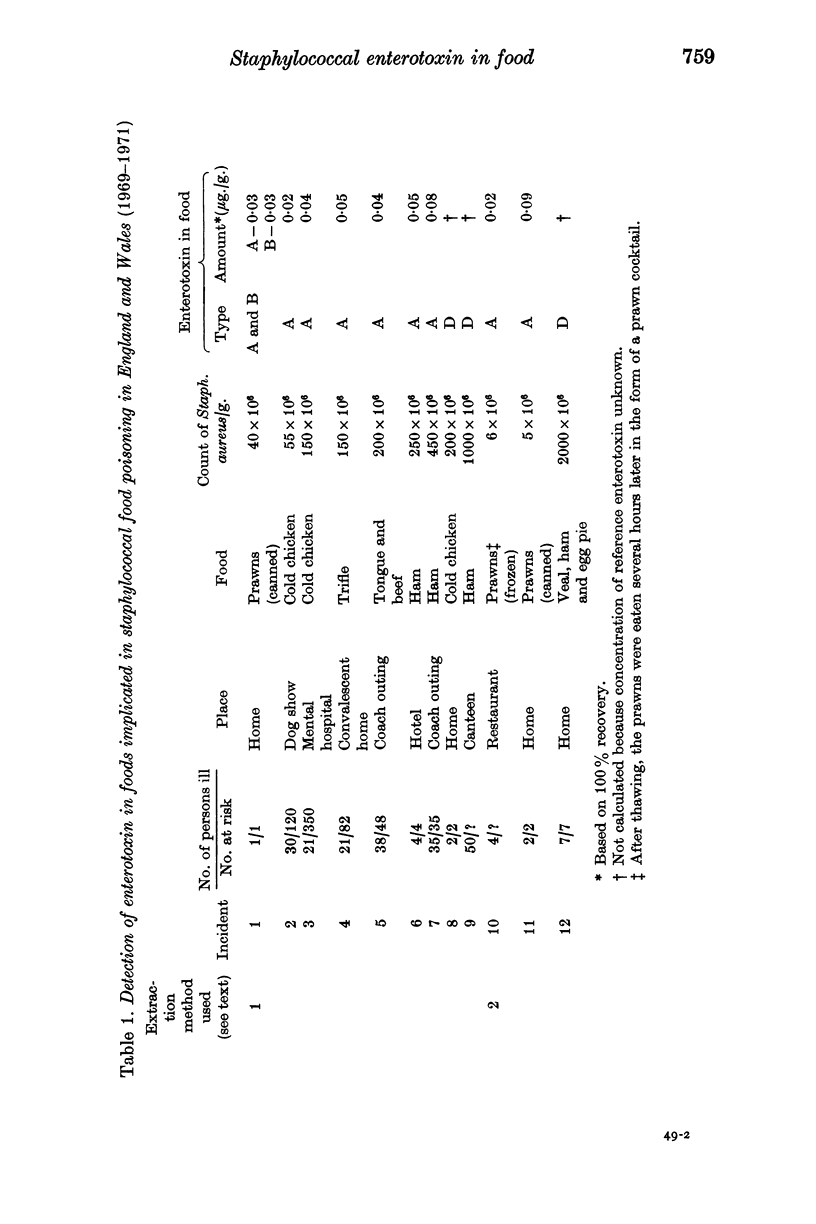
Two methods are described for the extraction of enterotoxin from foods incriminated in incidents of staphylococcal food poisoning. Enterotoxin was detected serologically in 12 of 24 food samples from 20 separate incidents: eight samples contained enterotoxin A, three contained D and one both A and B. The amount of enterotoxin in nine foods, based on 100% recovery, varied from 0·02 to 0·09 μg./g.
Data are also given on the numbers of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from samples of food from 39 food poisoning incidents. Colony counts varied between 7·5 × 105 and 9 × 109/g. with a median value of 7 × 107/g.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASMAN E. P., BENNETT R. W. DETECTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN IN FOOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:181–189. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.181-189.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Issa J. A. Identification of a fourth staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1875–1882. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1875-1882.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Stone J. E. The micro-slide gel double diffusion test for the detection and assay of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Oct;6(4):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P. Staphylococcal food poisoning. Health Lab Sci. 1967 Oct;4(4):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL H. E., ANGELOTTI R., LEWIS K. H. DETECTION OF THE STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXINS IN FOOD. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBBS B. C. The laboratory investigation of non-sterile canned hams. Ann Inst Pasteur Lille. 1955;7:190–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs B. C., Kendall M., Gilbert R. J. Use of phenolphthale in diphosphate agar with polymyxin as a selective medium for the isolation and enumeration of coagulase-positive staphylococci from foods. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Mar;16(3):535–535. doi: 10.1128/am.16.3.535-.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus Z. H., Silverman G. J. Factors affecting the secretion of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):492–496. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.492-496.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus Z., Silverman G. J. Enterotoxin B synthesis by replicating and nonreplicating cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.506-512.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Mah R. A., Dobrogosz W. J. Regulation of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):4–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.4-9.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj H. D., Bergdoll M. S. Effect of enterotoxin B on human volunteers. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):833–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.833-834.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


