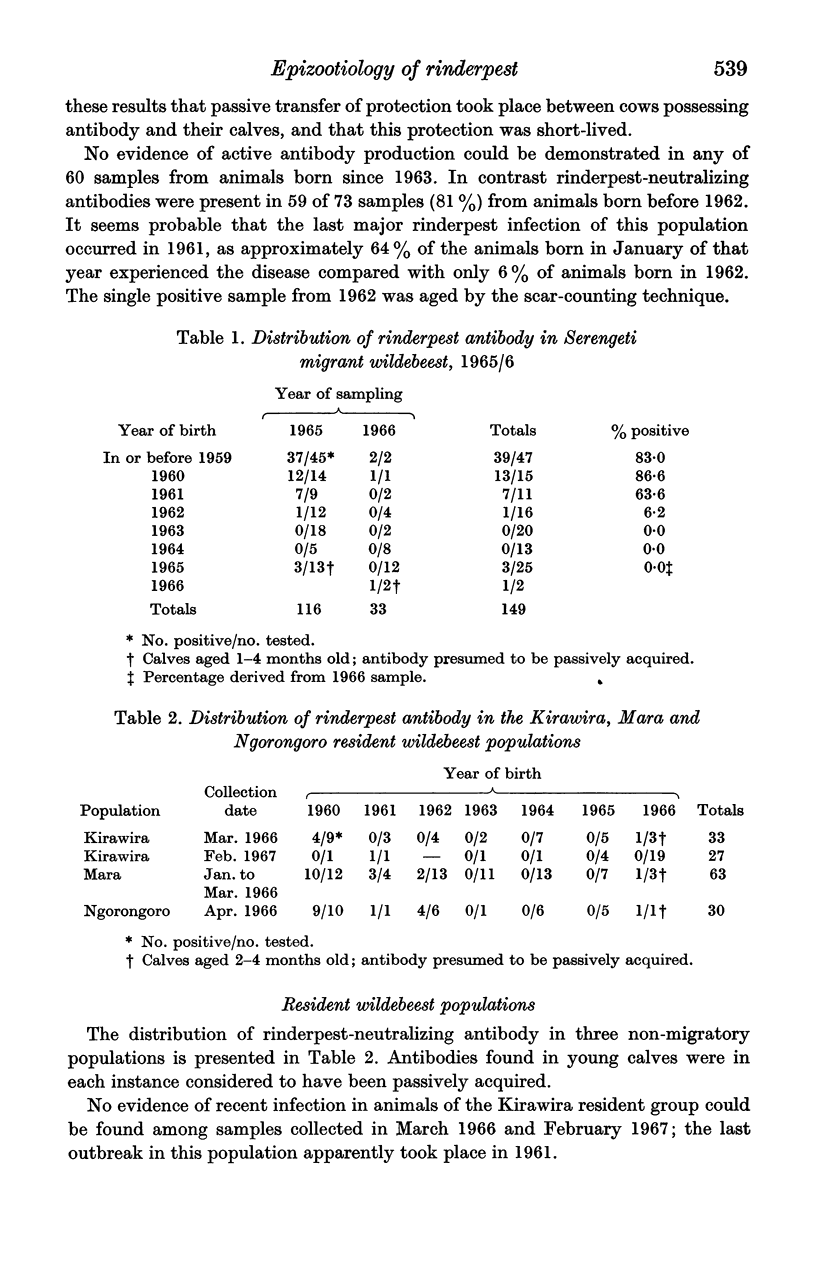
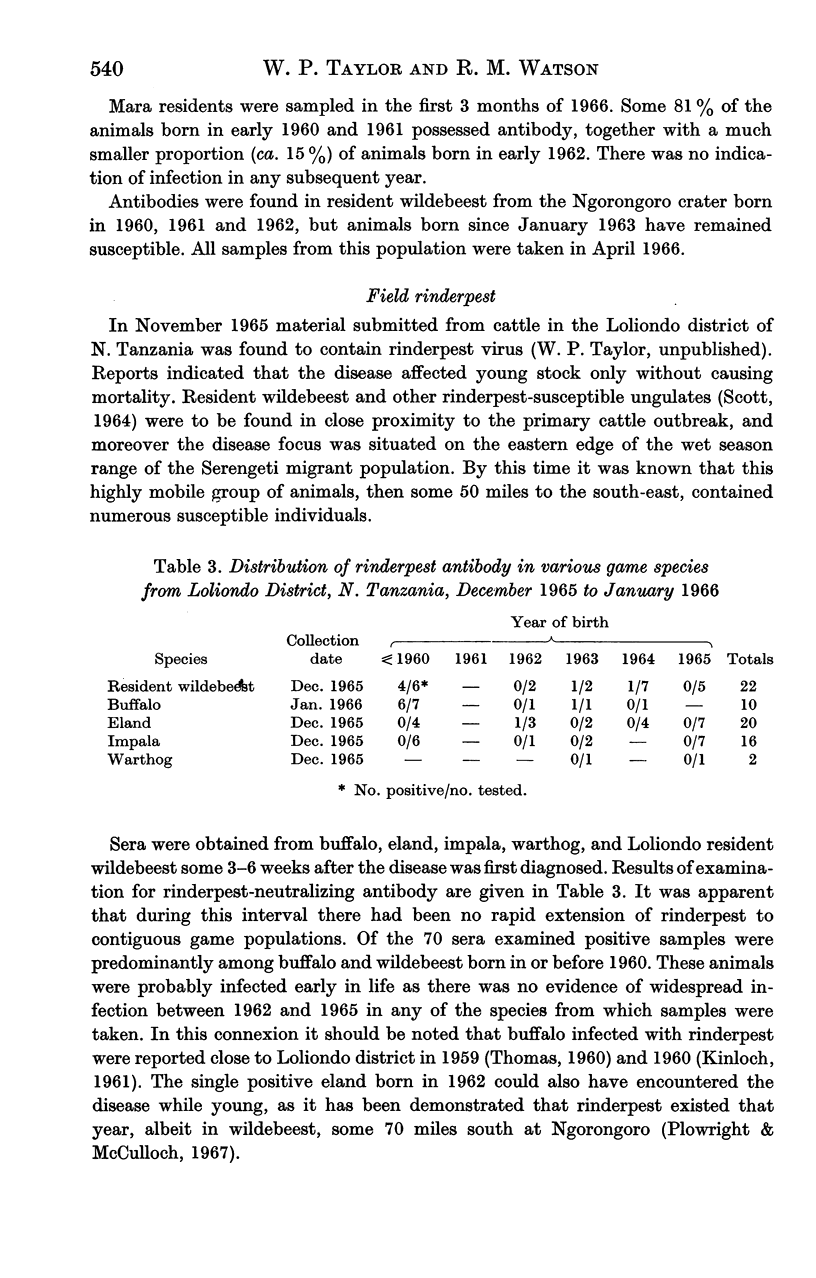
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branagan D., Hammond J. A. Rinderpest in Tanganyika: a review. Bull Epizoot Dis Afr. 1965 Sep;13(3):225–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOWRIGHT W., FERRIS R. D. Studies with rinderpest virus in tissue culture. III. The stability of cultured virus and its use in virus neutralization tests. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1962;11:516–533. doi: 10.1007/BF01241304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOWRIGHT W., LAWS R. M., RAMPTON C. S. SEROLOGICAL EVIDENCE FOR THE SUSCEPTIBILITY OF THE HIPPOPOTAMUS (HIPPOPOTAMUS AMPHIBIUS LINNAEUS) TO NATURAL INFECTION WITH RINDERPEST VIRUS. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Sep;62:329–336. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowright W., McCulloch B. Investigations on the incidence of rinderpest virus infection in game animals of N. Tanganyika and S. Kenya 1960-63. J Hyg (Lond) 1967 Sep;65(3):343–358. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400045861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowright W. The role of game animals in the epizootiology of rinderpest and malignant catarrhal fever in East Africa. Bull Epizoot Dis Afr. 1963 Jun;11(2):149–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. R. USE OF MOVING AVERAGES AND INTERPOLATION TO ESTIMATE MEDIAN-EFFECTIVE DOSE: I. Fundamental Formulas, Estimation of Error, and Relation to Other Methods. Bacteriol Rev. 1947 Jun;11(2):115–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


