Abstract
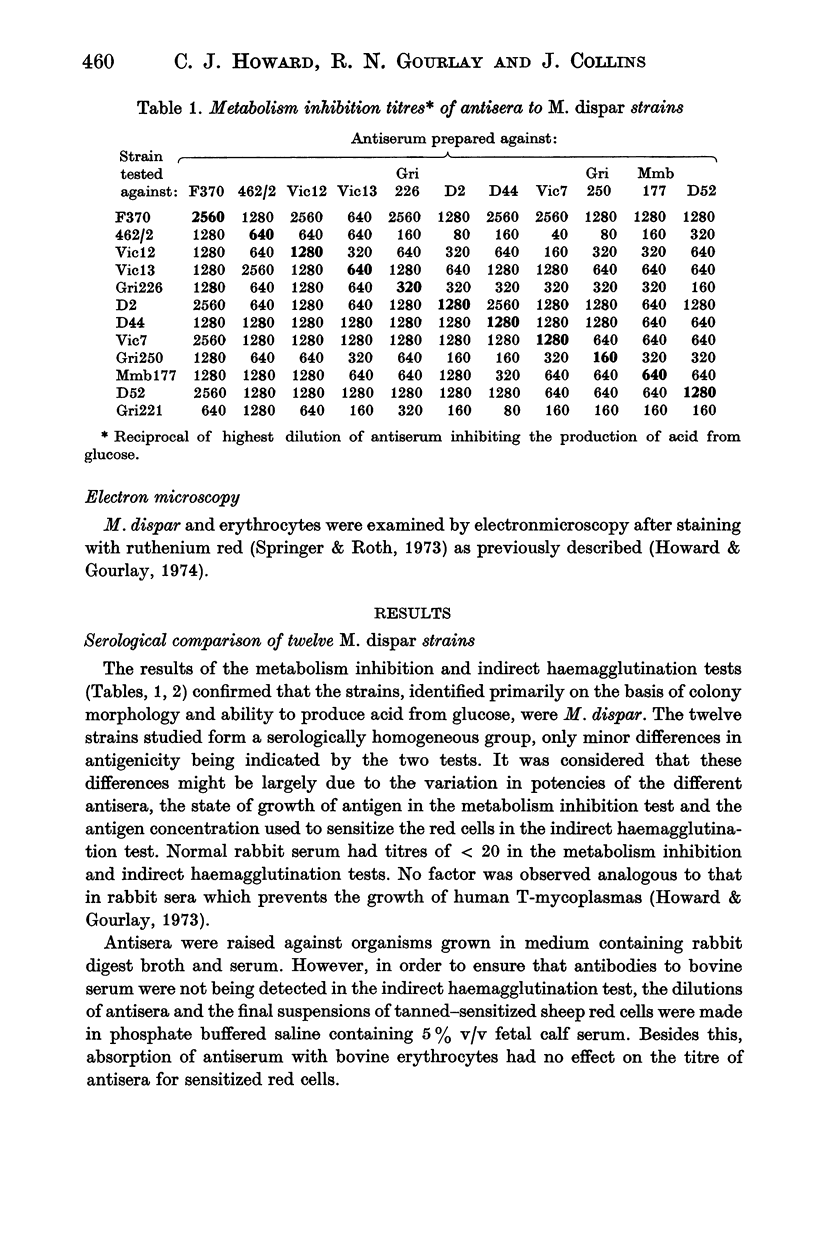
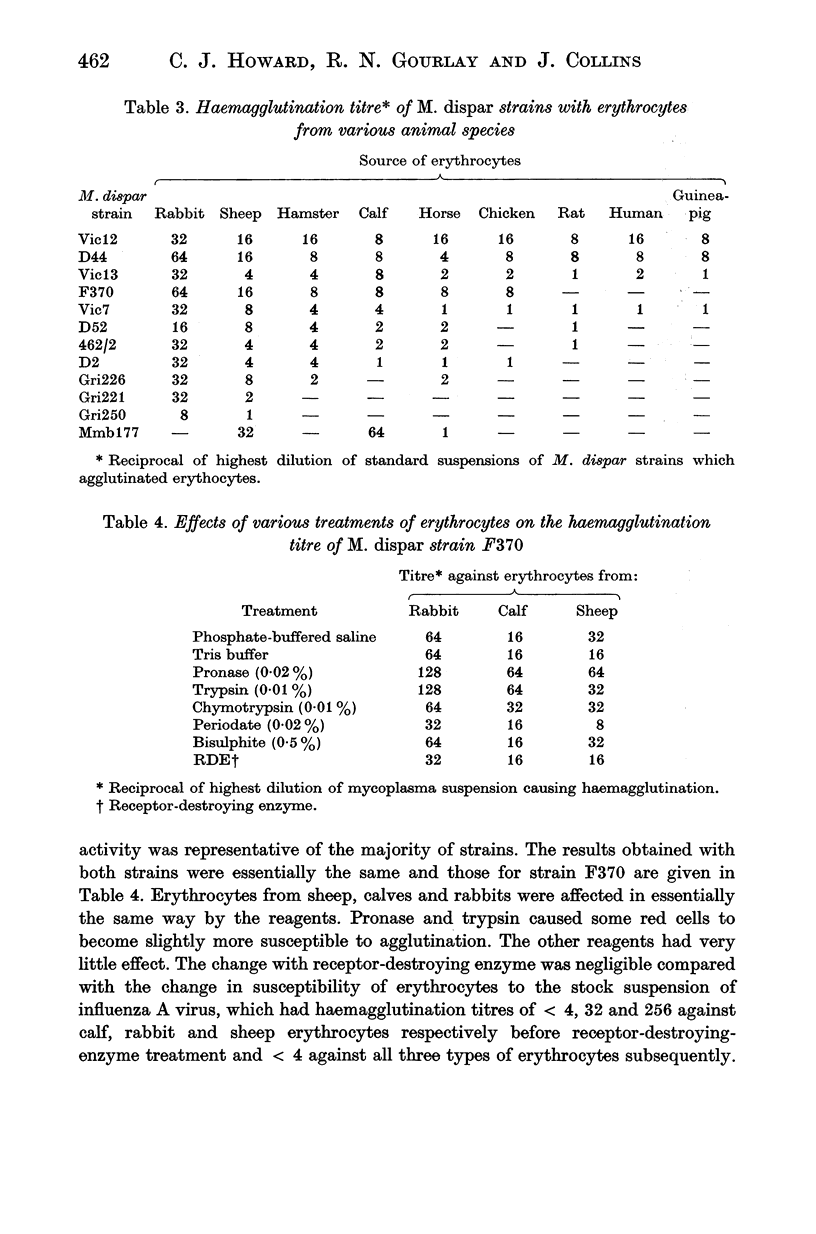
A comparison of twelve strains of Mycoplasma dispar by the metabolism inhibition and indirect haemagglutination tests has shown them to form a serologically homogeneous group of micro-organisms. The twelve strains vary in their haemagglutinating activity against erythrocytes from different animal species, and certain of the strains can be distinguished by the erythrocytes they agglutinate. Haemagglutination may thus provide a method by which certain strains can be typed. The erythrocyte receptor site does not appear to contain sialic acid and is not sensitive to proteolytic enzymes. On the mycoplasma cell two attachment sites have been demonstrated. One, by which it attaches to sheep and bovine erythrocytes, is a protein or contains a protein moiety. The chemical nature of the other attachment site, by which M. dispar attaches to rabbit erythrocytes, is unknown.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. E., Leach R. H., Gourlay R. N., Howard C. J. Enhanced isolation of Mycoplasma dispar by substitution of ampicillin for benzylpenicillin in growth media. Vet Rec. 1973 Dec 8;93(23):603–603. doi: 10.1136/vr.93.23.603-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKLAND F. E., TYRRELL D. A. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VIRUS HAEMAGGLUTININS. THE STABILITY OF HAEMAGGLUTININS AND RED CELL RECEPTORS TO CERTAIN PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TREATMENTS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:241–253. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erno H., Stipkovits L. Bovine mycoplasmas: cultural and biochemical studies. II. Acta Vet Scand. 1973;14(3):450–463. doi: 10.1186/BF03547432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw K. A., Fallon R. J. Serological heterogeneity of Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):501–510. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George T. D., Horsfall N., Sullivan N. D. A subclinical pneumonia of calves associated with Mycoplasma dispar. Aust Vet J. 1973 Dec;49(12):580–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1973.tb06738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesner B., Thomas L. Sialic acid binding sites: role in hemagglutination by Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Science. 1966 Feb 4;151(3710):590–591. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3710.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N. Isolation of a Mycoplasma-like organism from pneumonic calf lungs. Vet Rec. 1969 Mar 1;84(9):229–230. doi: 10.1136/vr.84.9.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Leach R. H. A new mycoplasma species isolated from pneumonic lungs of calves (Mycoplasma dispar sp. nov.). J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):111–123. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Mackenzie A., Cooper J. E. Studies of the microbiology and pathology of pneumonic lungs of calves. J Comp Pathol. 1970 Oct;80(4):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(70)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Thomas L. H. Experimental pneumonia in calves produced by inoculation of mycoplasmas. Vet Rec. 1969 Nov 22;85(21):583–583. doi: 10.1136/vr.85.21.583-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Manchee R. J. The role of mycoplasma membrane proteins in the adsorption of animal cells to Mycoplasma hominis colonies. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):391–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Gourlay R. N. Inhibition by normal rabbit sera of the growth of T-mycoplasma strains isolated from different animal species. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):277–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Gourlay R. N. Serology of bovine T-mycoplasmas. Br Vet J. 1972 Sep;128(9):xxxvii–xl. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Haemadsorption and haemagglutination by mycoplasmas. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):465–478. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Studies on the nature of receptors involved in attachment of tissue culture cells to mycoplasmas. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Feb;50(1):66–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Utilization of neuraminic acid receptors by mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):914–919. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.914-919.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D., Chanock R. M., Taylor-Robinson D., Canchola J., Valdesuso J. Significance of antibody to mycoplasma as measured by metabolic-inhibition techniques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):664–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
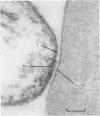
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. The ultrastructure of the capsules of Diplococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae stained with ruthenium red. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Berry D. M. The evaluation of the metabolic-inhibition technique for the study of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jan;55(1):127–137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. H., Howard C. J. Effect of Mycoplasma dispar, Mycoplasma bovirhinis, Acholeplasma laidlawii and T-mycoplasmas on explant cultures of bovine trachea. J Comp Pathol. 1974 Apr;84(2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(74)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. H., Smith G. S. Distribution of mycoplasmas in the non-pneumonic bovine respiratory tract. J Comp Pathol. 1972 Jan;82(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(72)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]