Full text
PDF







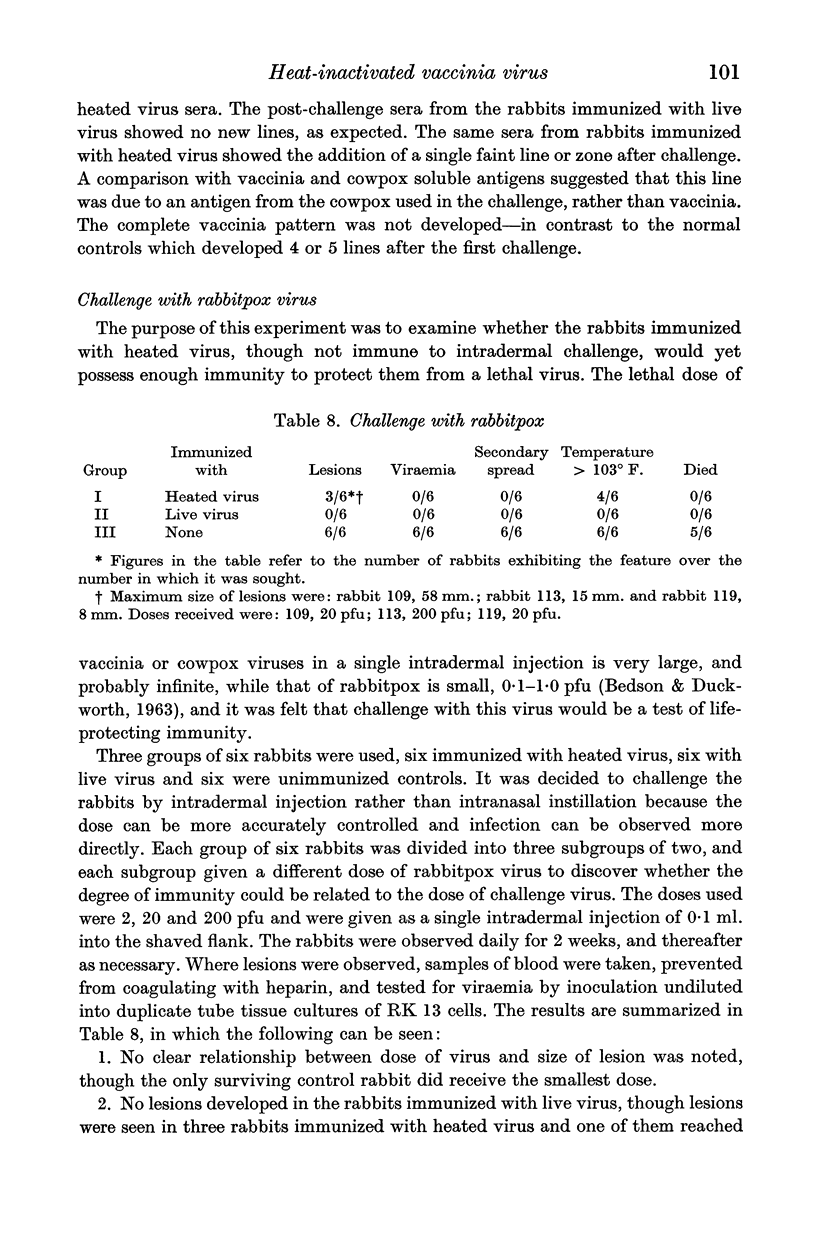





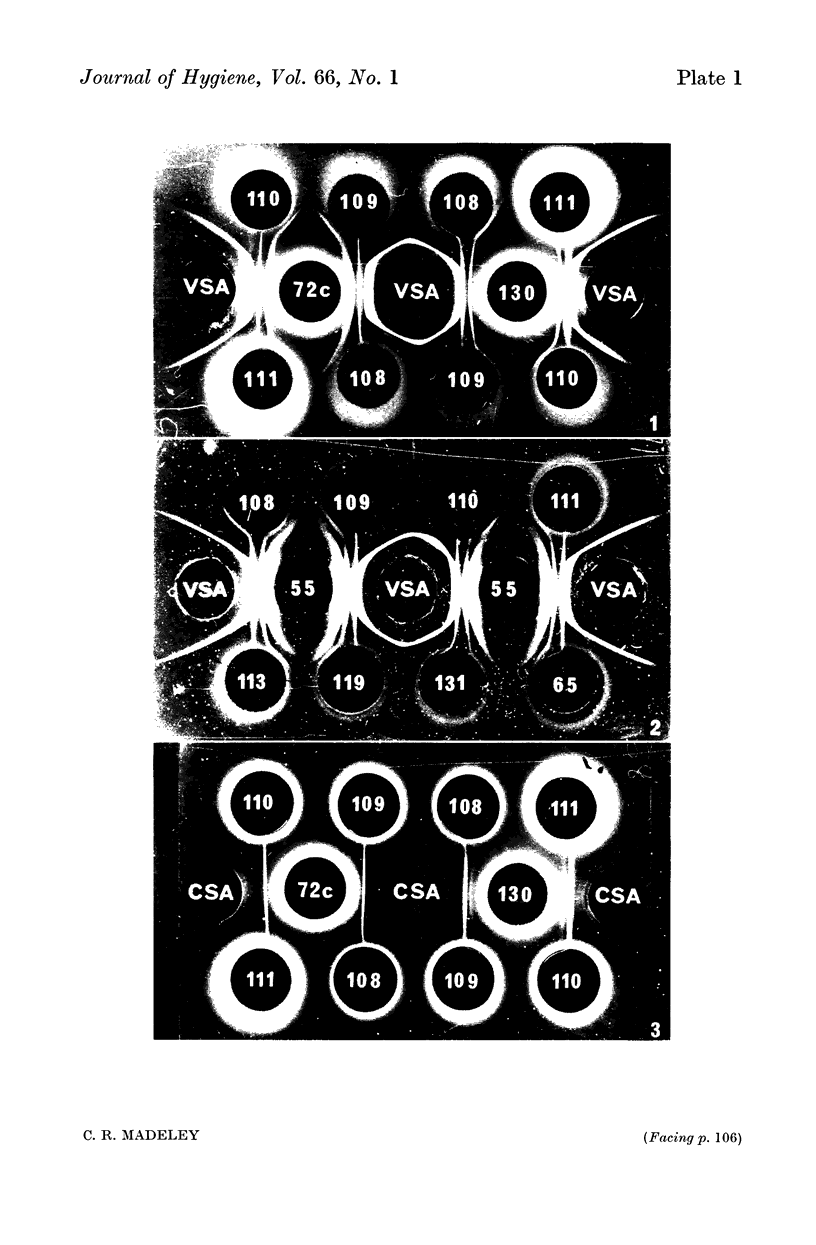
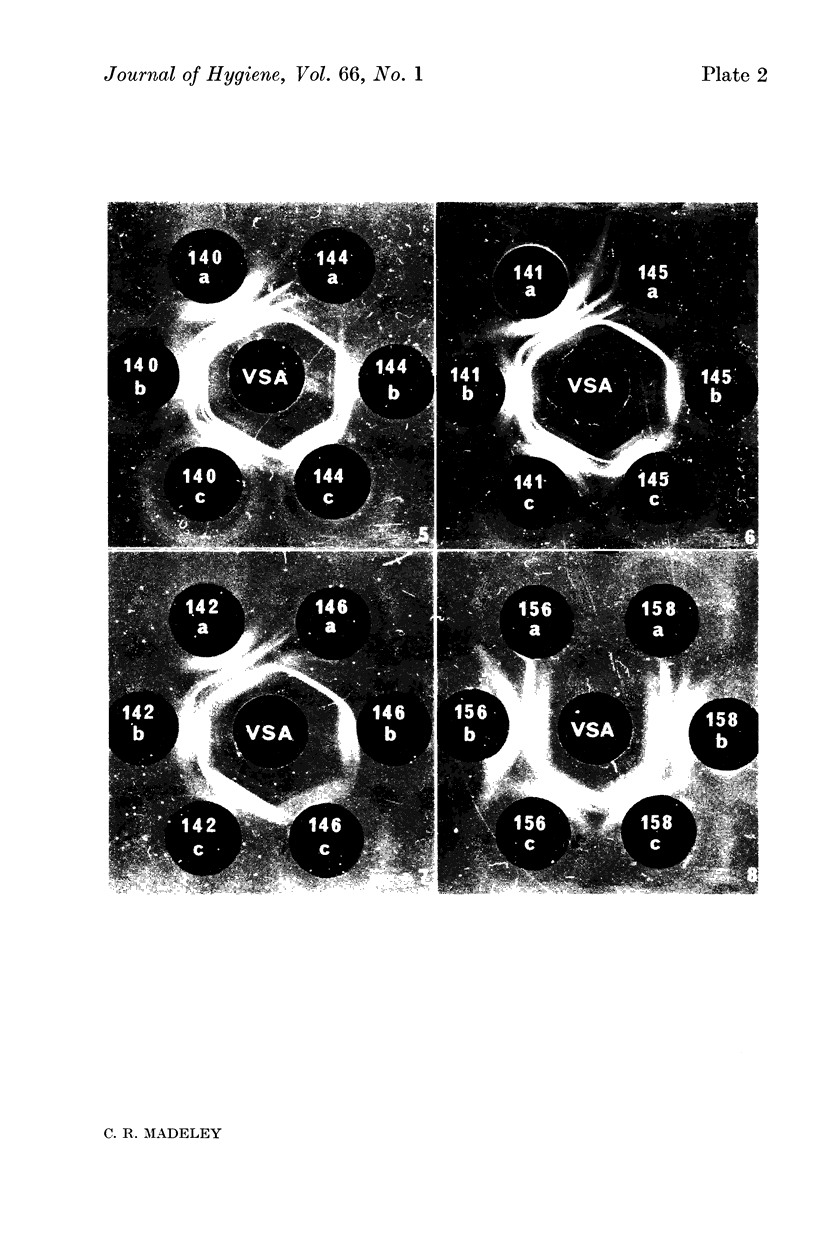

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMIES C. R. Loss of immunogenic properties of vaccinia virus inactivated by formaldehyde. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Apr;7:141–152. doi: 10.1139/m61-019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPLEYARD G. An immunizing antigen from rabbit-pox and vaccinia viruses. Nature. 1961 Apr 29;190:465–466. doi: 10.1038/190465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEDSON H. S., DUCKWORTH M. J. Rabbit pox: an experimental study of the pathways of infection in rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER L. H., MCCLEAN D., VALLET L. The antigenicity of ultra-violet irradiated vaccinia virus. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Dec;53(4):513–534. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400001017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S., KAJIOKA R. THE CYCLE OF MULTIPLICATION OF VACCINIA VIRUS IN EARLE'S STRAIN L CELLS. I. UPTAKE AND PENETRATION. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:278–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNIE A. W., MACDONALD A. A study of the pox viruses by complement fixation and inhibition of complement-fixation methods. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;62(3):389–401. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENNER F., BURNET F. M. A short description of the poxvirus group (vaccinia and related viruses). Virology. 1957 Oct;4(2):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALASSO G. J., SHARP D. G. Homologous inhibition with heated and ultraviolet-treated vaccinia virus in cultures of L cells. Virology. 1963 May;20:1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRLICH A. Uber Vakzine-Antigen; versuch einer Prophylaxe neuraler Impfschäden. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1959 Jan 2;101(1):12–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRLICH A. WELCHEN NUTZEN HAT DIE PROPHYLAXE DER POSTVAKZINALEN ENZEPHALITIS? EINE VERGLEICHENDE WERTUNG DER HEUTIGEN METHODEN. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1964 May 15;89:968–974. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1111245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN C., BENSON P. F., BUTLER N. R. IMMUNOGENICITY OF ULTRAVIOLET-IRRADIATED, NON-INFECTIOUS, VACCINIA-VIRUS VACCINE IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN. Lancet. 1965 Mar 13;1(7385):573–574. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeill T. A. The antibody response of rabbits to inactivated vaccinia virus. J Hyg (Lond) 1965 Dec;63(4):525–535. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400045411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUH L. W., SCHMIDT R. MEASLES IMMUNIZATION WITH KILLED VIRUS VACCINE. SERUM ANTIBODY TITERS AND EXPERIENCE WITH EXPOSURE TO MEASLES EPIDEMIC. Am J Dis Child. 1965 Mar;109:232–237. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1965.02090020234007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODROOFE G. M. The heat inactivation of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1960 Mar;10:379–382. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]