Abstract
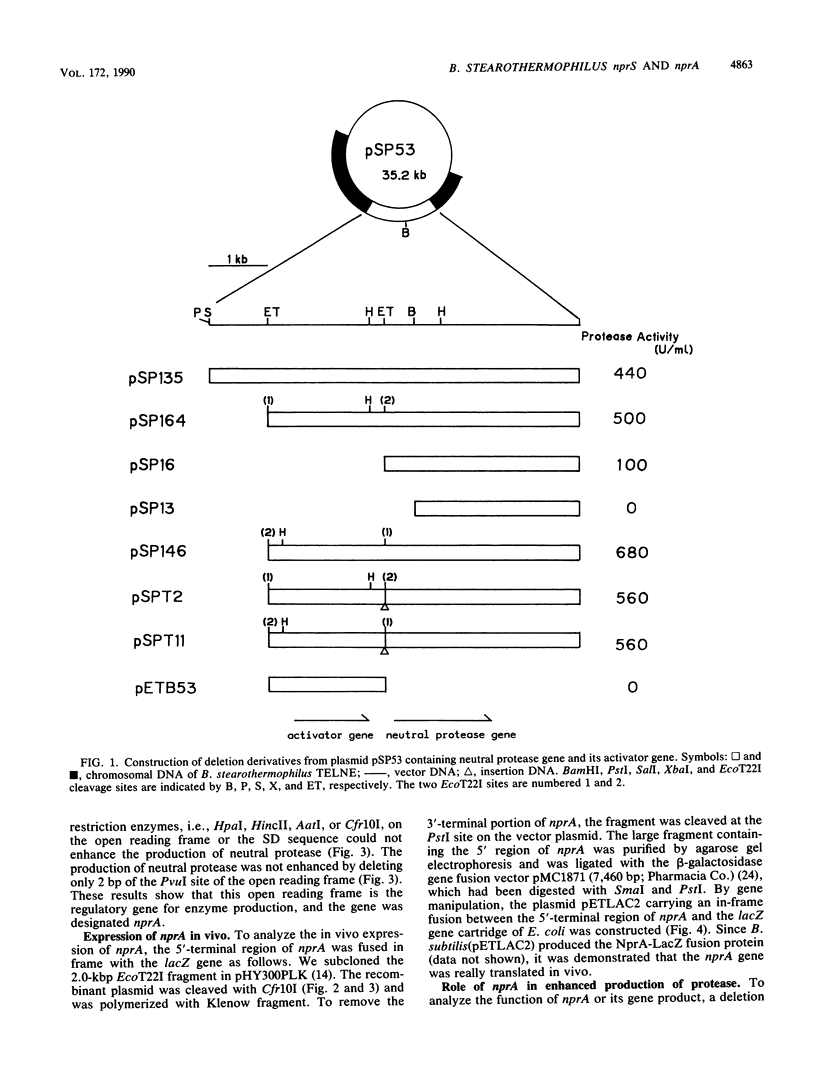
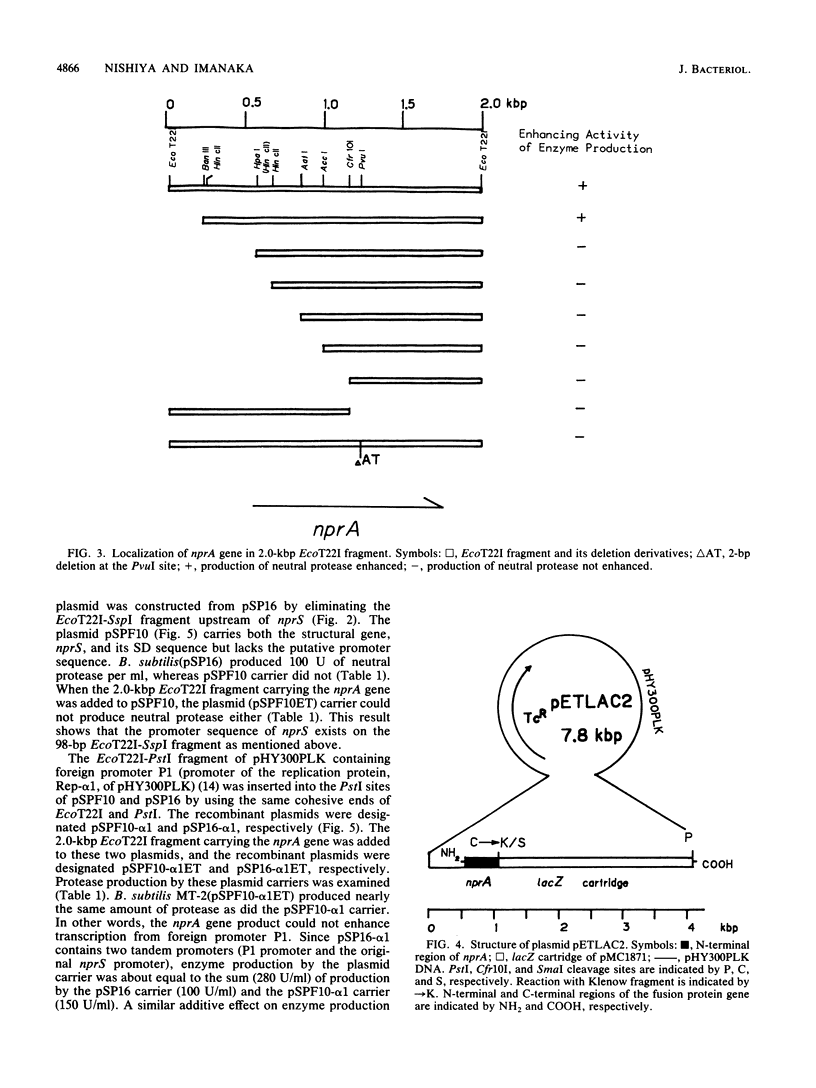
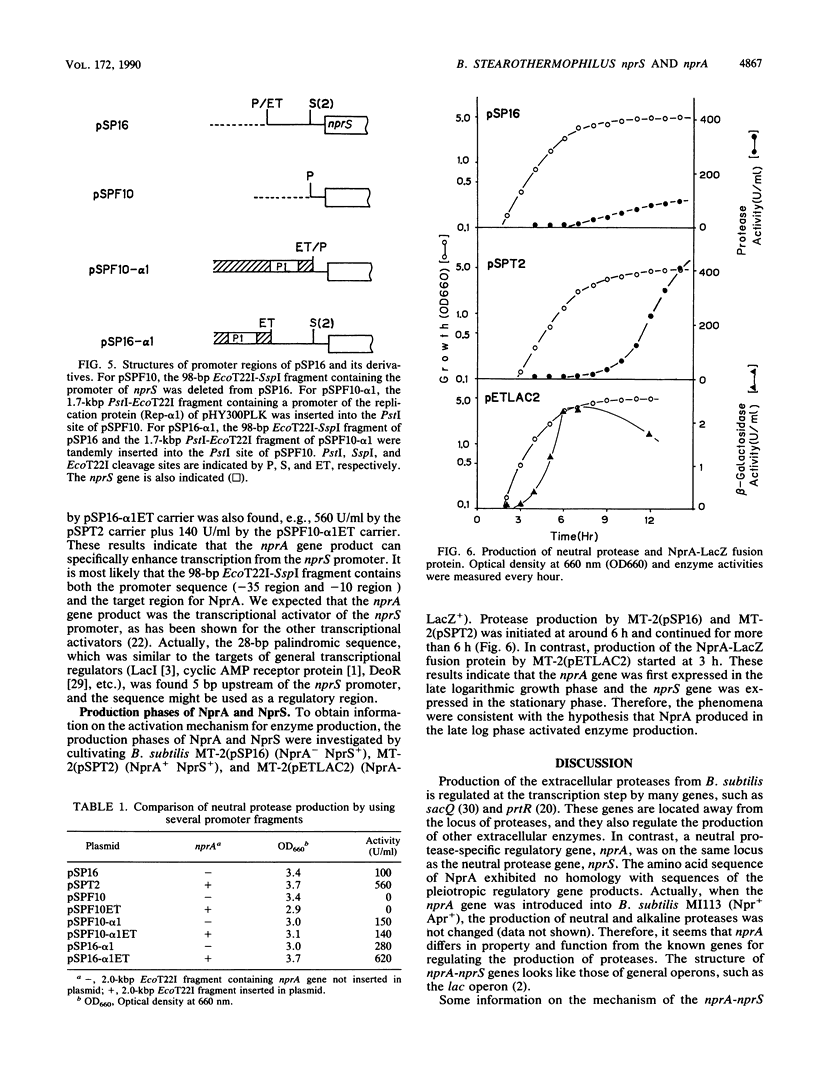
Both the neutral protease gene (nprS) and its transcriptional activator gene (nprA) from Bacillus stearothermophilus TELNE were cloned in Bacillus subtilis by using pTB53 as a vector plasmid. The presence of the nprA gene enhanced protease synthesis by about fivefold. The nucleotide sequences of nprS and its flanking regions were determined. nprS was composed of 1,653 base pairs and 551 amino acid residues. A Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence was found 9 bases upstream from the translation start site (ATG). The deduced amino acid sequence was very similar to that of another thermostable neutral protease gene, nprM (M. Kubo and T. Imanaka, J. Gen. Microbiol. 134:1883-1892, 1988). the amino acid sequence of the extracellular neutral protease NprS was completely identical to that of NprM. By deletion analysis and substitution of the original promoter with a foreign promoter, it was found that the nprA gene existed upstream of nprS. It was also found that a possible target region (palindromic sequence) of the gene product of nprA existed near the promoter sequence of nprS. The nucleotide sequences of nprA and its flanking regions were determined. The DNA sequence revealed only one large open reading frame, composed of 1,218 base pairs (406 amino acids; molecular weight, 49,097). The SD sequence was found 4 bases upstream from the translation start site (GTG). A possible promoter sequence (TTGAAG for the -35 region and AATTTT for the -10 region) was also found about 20 bases upstream of the SD sequence. The nprA gene was separated from nprS by a typical terminator sequence. By constructing an in-frame fusion between the lacZ gene and the 5' region of the nprA gene, it was demonstrated that the coding region of nprA was indeed translated in vivo. Three palindromic sequences, which were highly homologous with a possible target region by NprA, were also found in the 5' region of the nprA gene. This suggests that eh expression of nprA is autoregulated. From the time course of the production of NprA-LacZ fusion protein, it was indicated that nprA was expressed in late log phase, whereas nprS was expressed in the stationary phase. The NprA protein had consensus regions homologous to the DNA recognition domains of DNA-binding proteins but showed no sequence homology with any other regulatory proteins for protease production. It is inferred that NprA protein binds to the upstream region of nprS promoter and activates transcription of nprS. A new regulatory mechanism by the nprA-nprS genes is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M., Manly S. P., Matthews K. S. Model for lactose repressor protein and its interaction with ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7181–7185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Takagi M., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Molecular cloning of a thermostable neutral protease gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus in a vector plasmid and its expression in Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.831-837.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Dubnau E., Smith I. Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):860–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.860-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., McCarthy B. J., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. DNA sequence analysis of the transposon Tn3: three genes and three sites involved in transposition of Tn3. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Ferrari E. Localization of Bacillus subtilis sacU(Hy) mutations to two linked genes with similarities to the conserved procaryotic family of two-component signalling systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5102–5109. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5102-5109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno T., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Nucleotide sequence of the penicillinase repressor gene penI of Bacillus licheniformis and regulation of penP and penI by the repressor. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1128-1132.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Ano T., Fujii M., Aiba S. Two replication determinants of an antibiotic-resistance plasmid, pTB19, from a thermophilic bacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1399–1408. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Fujii M., Aiba S. Isolation and characterization of antibiotic resistance plasmids from thermophilic bacilli and construction of deletion plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1091-1097.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Fujii M., Aramori I., Aiba S. Transformation of Bacillus stearothermophilus with plasmid DNA and characterization of shuttle vector plasmids between Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):824–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.824-830.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Tanaka T., Tsunekawa H., Aiba S. Cloning of the genes for penicillinase, penP and penI, of Bacillus licheniformis in some vector plasmids and their expression in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):776–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.776-786.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo M., Imanaka T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the highly thermostable neutral protease gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1883–1892. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst F., Pascal M., Lepesant-Kejzlarova J., Lepesant J. A., Billault A., Dedonder R. Pleiotropic mutations affecting sporulation conditions and the syntheses of extracellular enzymes in Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1481–1489. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Ramos J. L., Bairoch A., Timmis K. N. The xylS gene positive regulator of TOL plasmid pWWO: identification, sequence analysis and overproduction leading to constitutive expression of meta cleavage operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):349–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00331600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami Y., Tanaka T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a DNA fragment from Bacillus natto that enhances production of extracellular proteases and levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):20–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.20-28.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Hoch J. A. Sequence analysis and regulation of the hpr locus, a regulatory gene for protease production and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2560–2567. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2560-2567.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Nucleotide sequence and promoter region for the neutral protease gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):824–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.824-831.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Takada H., Imanaka T. Nucleotide sequence and cloning in Bacillus subtilis of the Bacillus stearothermophilus pleiotropic regulatory gene degT. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.411-418.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuji A., Maeda M. [Detection methods for immunoassay]. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1987 Sep;(31 Suppl):51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P., Højrup P., Short S. The primary structure of the DeoR repressor from Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5927–5936. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Ferrari E., Chen E., Henner D. J. Identification of the pleiotropic sacQ gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.113-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



