Abstract
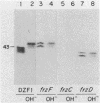
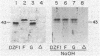
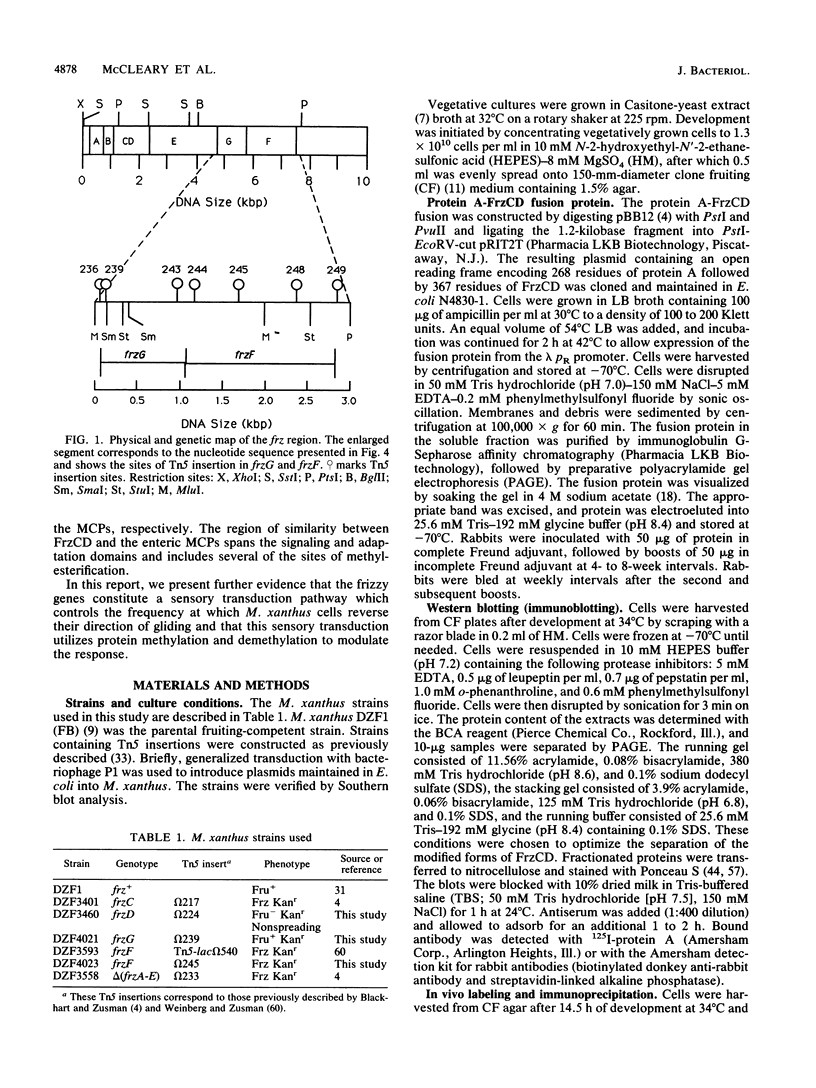
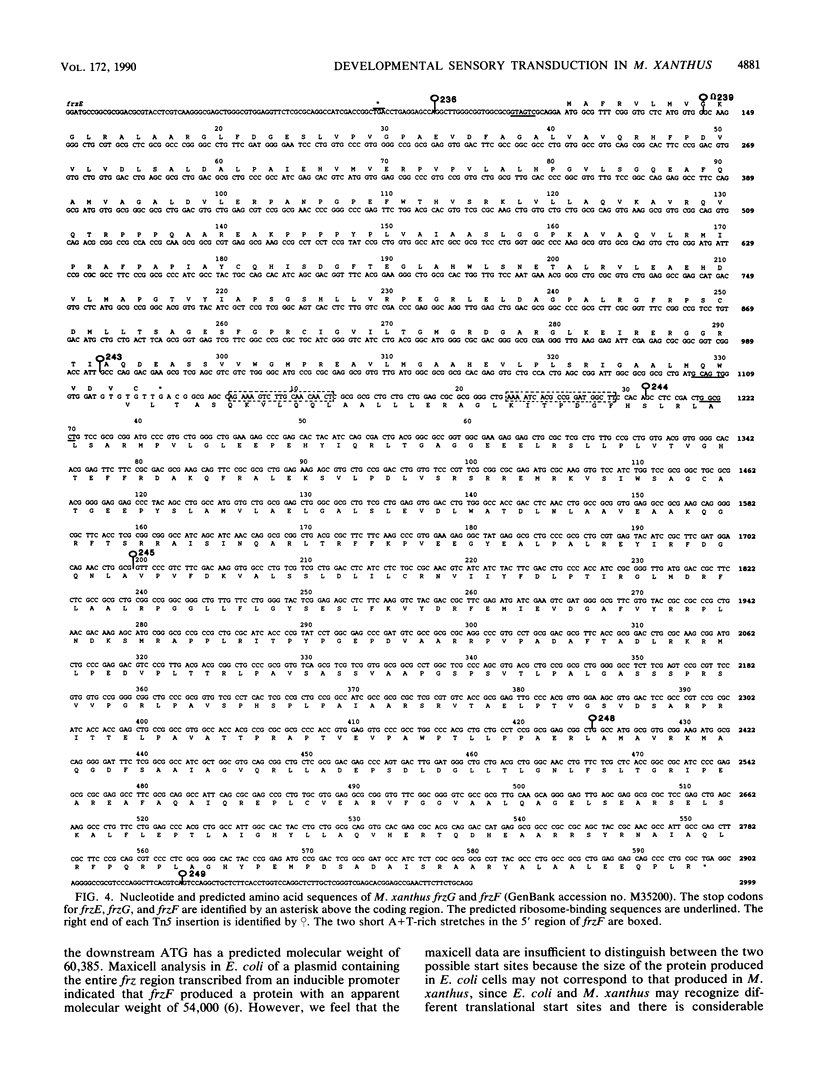
Myxococcus xanthus is a bacterium that moves by gliding motility and exhibits multicellular development (fruiting body formation). The frizzy (frz) mutants aggregate aberrantly and therefore fail to form fruiting bodies. Individual frz cells cannot control the frequency at which they reverse direction while gliding. Previously, FrzCD was shown to exhibit significant sequence similarity to the enteric methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins. In this report, we show that FrzCD is modified by methylation and that frzF encodes the methyltransferase. We also identify a new gene, frzG, whose predicted product is homologous to that of the cheB (methylesterase) gene from Escherichia coli. Thus, although M. xanthus is unflagellated, it appears to have a sensory transduction system which is similar in many of its components to those found in flagellated bacteria.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames P., Parkinson J. S. Transmembrane signaling by bacterial chemoreceptors: E. coli transducers with locked signal output. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):817–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackhart B. D., Zusman D. R. "Frizzy" genes of Myxococcus xanthus are involved in control of frequency of reversal of gliding motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8767–8770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackhart B. D., Zusman D. R. Analysis of the products of the Myxococcus xanthus frz genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):673–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.673-678.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackhart B. D., Zusman D. R. Cloning and complementation analysis of the "Frizzy" genes of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(2):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00383002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Multiple methylation in processing of sensory signals during bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Eide D. Myxococcus xanthus does not respond chemotactically to moderate concentration gradients. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.437-442.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen T. J., Shimkets L. J. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional products of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.15-23.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Kaplan N., Simon M. I. Phosphorylation of three proteins in the signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Matsumura P., Simon M. I. Protein phosphorylation is involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R. C., Dahmus M. E. Rapid visualization of protein bands in preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Franceschini T., Inouye M. Structural similarities between the development-specific protein S from a gram-negative bacterium, Myxococcus xanthus, and calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6829–6833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller K. H., Grady M., Dworkin M. Surface tension gradients: feasible model for gliding motility of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1358–1366. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1358-1366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr Biochemistry of sensing and adaptation in a simple bacterial system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:765–782. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Sanders D. A., Weis R. M. Roles of methylation and phosphorylation in the bacterial sensing system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Conley M. P., Boyd A., Berg H. C., Simon M. I. Chimeric chemosensory transducers of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1326–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Genes required for developmental signalling in Myxococcus xanthus: three asg loci. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2762-2772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus I. R., Berg H. C. Gliding motility of Cytophaga sp. strain U67. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):384–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.384-398.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. D., Parkinson J. S. Role of CheW protein in coupling membrane receptors to the intracellular signaling system of bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8703–8707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Stock J. Phosphorylation of an N-terminal regulatory domain activates the CheB methylesterase in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17337–17342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride M. J., Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. "Frizzy" aggregation genes of the gliding bacterium Myxococcus xanthus show sequence similarities to the chemotaxis genes of enteric bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):424–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh N., Simon M. I. Nucleotide sequence corresponding to five chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):161–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.161-166.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Coliphage P1-mediated transduction of cloned DNA from Escherichia coli to Myxococcus xanthus: use for complementation and recombinational analyses. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):317–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.317-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Yanofsky C. Translational coupling during expression of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1980 Aug;95(4):785–795. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panasenko S. M. Methylation of macromolecules during development in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):495–500. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.495-500.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Protein phosphorylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90478-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Esmon B., Zusman D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the myxobacterial hemagglutinin gene contains four homologous domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A. F., Koshland D. E., Jr Separation of signal transduction and adaptation functions of the aspartate receptor in bacterial sensing. Science. 1983 Jun 3;220(4601):1016–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.6302843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Montelaro R. C. Reversible staining and peptide mapping of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose after separation by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Stock A. M., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the site of phosphorylation of the chemotaxis response regulator protein, CheY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21770–21778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Mendez B., Koshland D. E., Jr Role of the CheW protein in bacterial chemotaxis: overexpression is equivalent to absence. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6271–6278. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6271-6278.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simms S. A., Cornman E. W., Mottonen J., Stock J. Active site of the enzyme which demethylates receptors during bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):29–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Hartzell P., Kaiser D. Gliding motility in Myxococcus xanthus: mgl locus, RNA, and predicted protein products. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):819–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.819-830.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M., Stock J. B., Schutt C. E. Three-dimensional structure of CheY, the response regulator of bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):745–749. doi: 10.1038/337745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein methylesterase involved in bacterial sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Kersulis G., Koshland D. E., Jr Neither methylating nor demethylating enzymes are required for bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):683–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Werf P., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a gamma-glutamyl methyl ester in bacterial membrane protein involved in chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2793–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. Evidence that the Myxococcus xanthus frz genes are developmentally regulated. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6174–6186. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6174-6186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wylie D., Stock A., Wong C. Y., Stock J. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis involves phosphotransfer between Che proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):891–896. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R. "Frizzy" mutants: a new class of aggregation-defective developmental mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1430–1437. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1430-1437.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]