Abstract
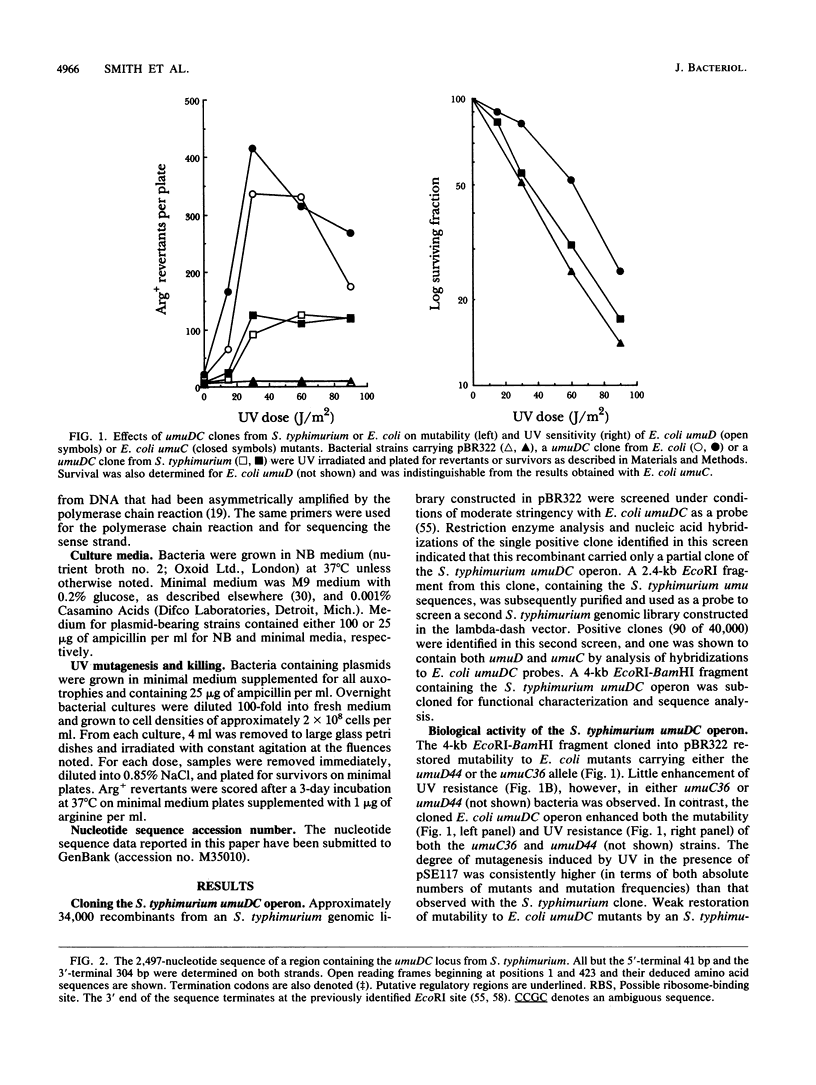
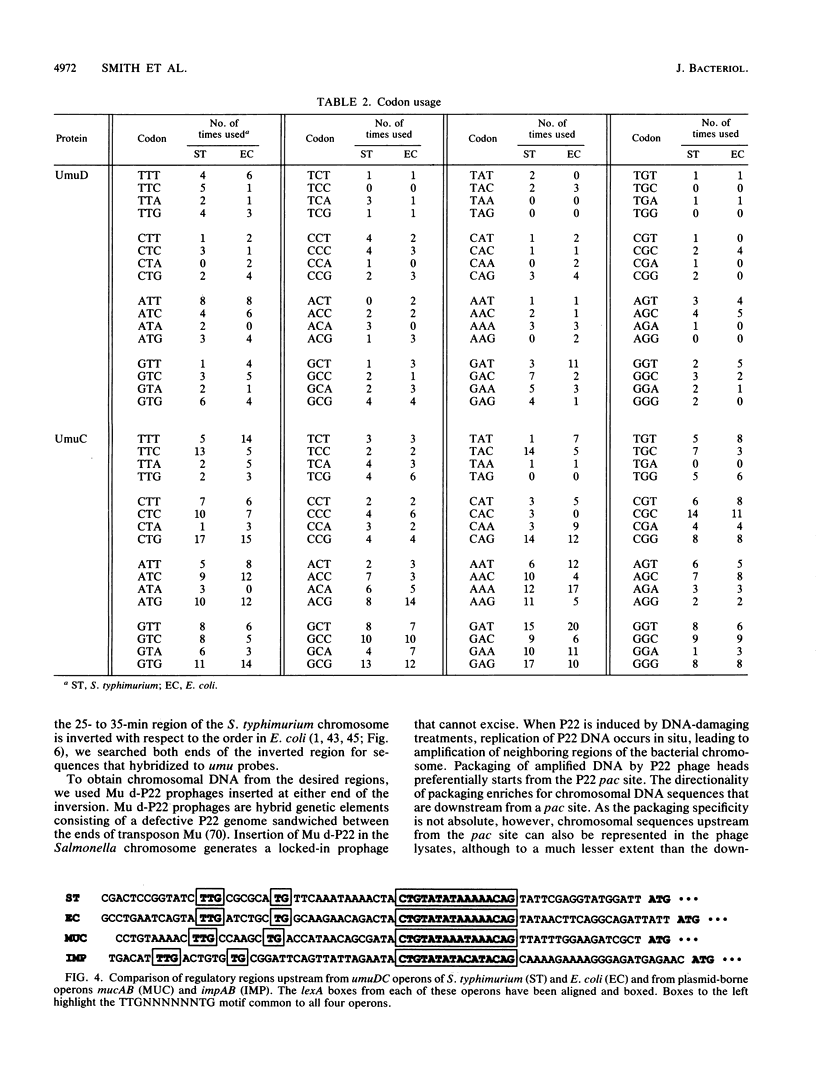
In Escherichia coli, efficient mutagenesis by UV requires the umuDC operon. A deficiency in umuDC activity is believed to be responsible for the relatively weak UV mutability of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 compared with that of E. coli. To begin evaluating this hypothesis and the evolutionary relationships among umuDC-related sequences, we cloned and sequenced the S. typhimurium umuDC operon. S. typhimurium umuDC restored mutability to umuD and umuC mutants of E. coli. DNA sequence analysis of 2,497 base pairs (bp) identified two nonoverlapping open reading frames spanning 1,691 bp that were were 67 and 72% identical at the nucleotide sequence level to the umuD and umuC sequences, respectively, from E. coli. The sequences encoded proteins whose deduced primary structures were 73 and 84% identical to the E. coli umuD and umuC gene products, respectively. The two bacterial umuDC sequences were more similar to each other than to mucAB, a plasmid-borne umuDC homolog. The umuD product retained the Cys-24--Gly-25, Ser-60, and Lys-97 amino acid residues believed to be critical for RecA-mediated proteolytic activation of UmuD. The presence of a LexA box 17 bp upstream from the UmuD initiation codon suggests that this operon is a member of an SOS regulon. Mu d-P22 inserts were used to locate the S. typhimurium umuDC operon to a region between 35.9 and 40 min on the S. typhimurium chromosome. In E. coli, umuDC is located at 26 min. The umuDC locus in S. typhimurium thus appears to be near one end of a chromosomal inversion that distinguishes gene order in the 25- to 35-min regions of the E. coli and S. typhimurium chromosomes. It is likely, therefore, that the umuDC operon was present in a common ancestor before S. typhimurium and E. coli diverged approximately 150 million years ago. These results provide new information for investigating the structure, function, and evolutionary origins of umuDC and for exploring the genetic basis for the mutability differences between S. typhimurium and E. coli.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balganesh M., Setlow J. K. Genes from plasmid pKM101 in Haemophilus influenzae: separation of functions of mucA and mucB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7753–7756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges B. A., Mottershead R. P. Mutagenic DNA repair in Escherichia coli. III. Requirement for a function of DNA polymerase III in ultraviolet-light mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Feb 27;144(1):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00277304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt S. E., Woodgate R., Scheuermann R. H., Echols H. UmuD mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: overproduction, purification, and cleavage by RecA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Kushner S. R., Grossman L. Involvement of helicase II (uvrD gene product) and DNA polymerase I in excision mediated by the uvrABC protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4925–4929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P. Gene rearrangements in the evolution of the tryptophan synthetic pathway. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):87–120. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.87-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J. Inducible repair of oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):466–468. doi: 10.1038/304466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. E., Walker G. C. groE mutants of Escherichia coli are defective in umuDC-dependent UV mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6117–6125. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6117-6125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. L., Sullivan A. D. Interactions between epsilon, the proofreading subunit of DNA polymerase III, and proteins involved in the SOS response of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):467–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00330482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Panda D. K., Das J. Lack of umuDC gene functions in Vibrio cholerae cells. Mutat Res. 1989 Jan;210(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Sauer R. T. Lambda repressor inactivation: properties of purified ind- proteins in the autodigestion and RecA-mediated cleavage reactions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera G., Urios A., Aleixandre V., Blanco M. UV-light-induced mutability in Salmonella strains containing the umuDC or the mucAB operon: evidence for a umuC function. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;198(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Gray J. A., Brody H. Use of the isocitrate dehydrogenase structural gene for attachment of e14 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4083–4084. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4083-4084.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Myambo K. B., Gelfand D. H., Brow M. A. DNA sequencing with Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Shinoura Y. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Escherichia coli deficient in induction of mutations by ultraviolet light. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 14;156(2):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00283484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Akaboshi E., Shinagawa H., Horii T., Ogawa H., Kato T. Structural analysis of the umu operon required for inducible mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4336–4340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Little J. W. Autodigestion and RecA-dependent cleavage of Ind- mutant LexA proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):439–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. Autodigestion of lexA and phage lambda repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1375–1379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Edmiston S. H., Pacelli L. Z., Mount D. W. Cleavage of the Escherichia coli lexA protein by the recA protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. The SOS regulatory system: control of its state by the level of RecA protease. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):791–808. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Walker G. C. Cold sensitivity induced by overproduction of UmuDC in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.155-161.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Kukral A. M., Mekalanos J. J. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5054–5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe R. S., Kredich N. M. Isolation of Salmonella typhimurium cys genes by transduction with a library of recombinant plasmids packaged in bacteriophage P22HT capsids. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.42-47.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortelmans K. E., Stocker B. A. Ultraviolet light protection, enhancement of ultraviolet light mutagenesis, and mutator effect of plasmid R46 in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):271–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.271-282.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi T., Battista J. R., Dodson L. A., Walker G. C. RecA-mediated cleavage activates UmuD for mutagenesis: mechanistic relationship between transcriptional derepression and posttranslational activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego C., Eisenstadt E. An inducible pathway is required for mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2885–2888. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2885-2888.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbye K. M., Margolin P. Role of the supX gene in ultraviolet light-induced mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):170–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.170-178.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Elledge S. J., Mitchell B. B., Marsh L., Walker G. C. umuDC and mucAB operons whose products are required for UV light- and chemical-induced mutagenesis: UmuD, MucA, and LexA proteins share homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4331–4335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. R., Ossanna N., Thliveris A. T., Ennis D. G., Mount D. W. Derepression of specific genes promotes DNA repair and mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.1-4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney R. J. Distribution among incompatibility groups of plasmids that confer UV mutability and UV resistance. Mutat Res. 1980 Aug;72(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Miller W., Ostell J., Benson D. A. Alignment of Escherichia coli K12 DNA sequences to a genomic restriction map. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):313–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Roberts J. W. Nature of the SOS-inducing signal in Escherichia coli. The involvement of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):79–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B., Roth J. R. Gene location affects expression level in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2872–2875. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2872-2875.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Goodwin P. A. Differences in mutagenic and recombinational DNA repair in enterobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4172–4176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Robson M., Malik F. Polymorphisms in the umuDC region of Escherichia species. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1610–1616. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1610-1616.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Shields D. C., Wolfe K. H., Li W. H. Chromosomal location and evolutionary rate variation in enterobacterial genes. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):808–810. doi: 10.1126/science.2683084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa H., Iwasaki H., Kato T., Nakata A. RecA protein-dependent cleavage of UmuD protein and SOS mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa H., Kato T., Ise T., Makino K., Nakata A. Cloning and characterization of the umu operon responsible for inducible mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skavronskaya A. G., Stepanova N. F., Andreeva I. V. UV-mutable hybrids of Salmonella incorporating Escherichia coli region adjacent to tryptophan operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(2):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00330804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slilaty S. N., Little J. W. Lysine-156 and serine-119 are required for LexA repressor cleavage: a possible mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. M., Eisenstadt E. Identification of a umuDC locus in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3860–3865. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3860-3865.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strike P., Lodwick D. Plasmid genes affecting DNA repair and mutation. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;6:303–321. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1984.supplement_6.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Crowne H. M., Pidsley S. C., Sedgwick S. G. Structural characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 umu operon. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4979–4987. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4979-4987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Sedgwick S. G. Cloning of Salmonella typhimurium DNA encoding mutagenic DNA repair. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5776–5782. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5776-5782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsness P. E., Koshland D. E., Jr Inactivation of isocitrate dehydrogenase by phosphorylation is mediated by the negative charge of the phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10422–10425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton C., Pinney R. J. Expression of eight unrelated Muc+ plasmids in eleven DNA repair-deficient E. coli strains. Mutat Res. 1983 Oct;112(5):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Inducible reactivation and mutagenesis of UV-irradiated bacteriophage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium LT2 containing the plasmid pKM101. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):415–421. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.415-421.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C., Kenyon C. J., Bagg A., Elledge S. J., Perry K. L., Shanabruch W. G. Regulation and functions of Escherichia coli genes induced by DNA damage. Basic Life Sci. 1982;20:43–63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-3476-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Miyada C. G. Oligonucleotide probes for the screening of recombinant DNA libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:432–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A., Daub E., Grisafi P., Botstein D., Walsh C. T. Catabolic alanine racemase from Salmonella typhimurium: DNA sequence, enzyme purification, and characterization. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5182–5187. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence binding specificity of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.376-384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate R., Rajagopalan M., Lu C., Echols H. UmuC mutagenesis protein of Escherichia coli: purification and interaction with UmuD and UmuD'. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7301–7305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Sugiono P., Brewer K. L., Higgins N. P., Elliott T. Packaging specific segments of the Salmonella chromosome with locked-in Mud-P22 prophages. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):581–592. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]