Abstract
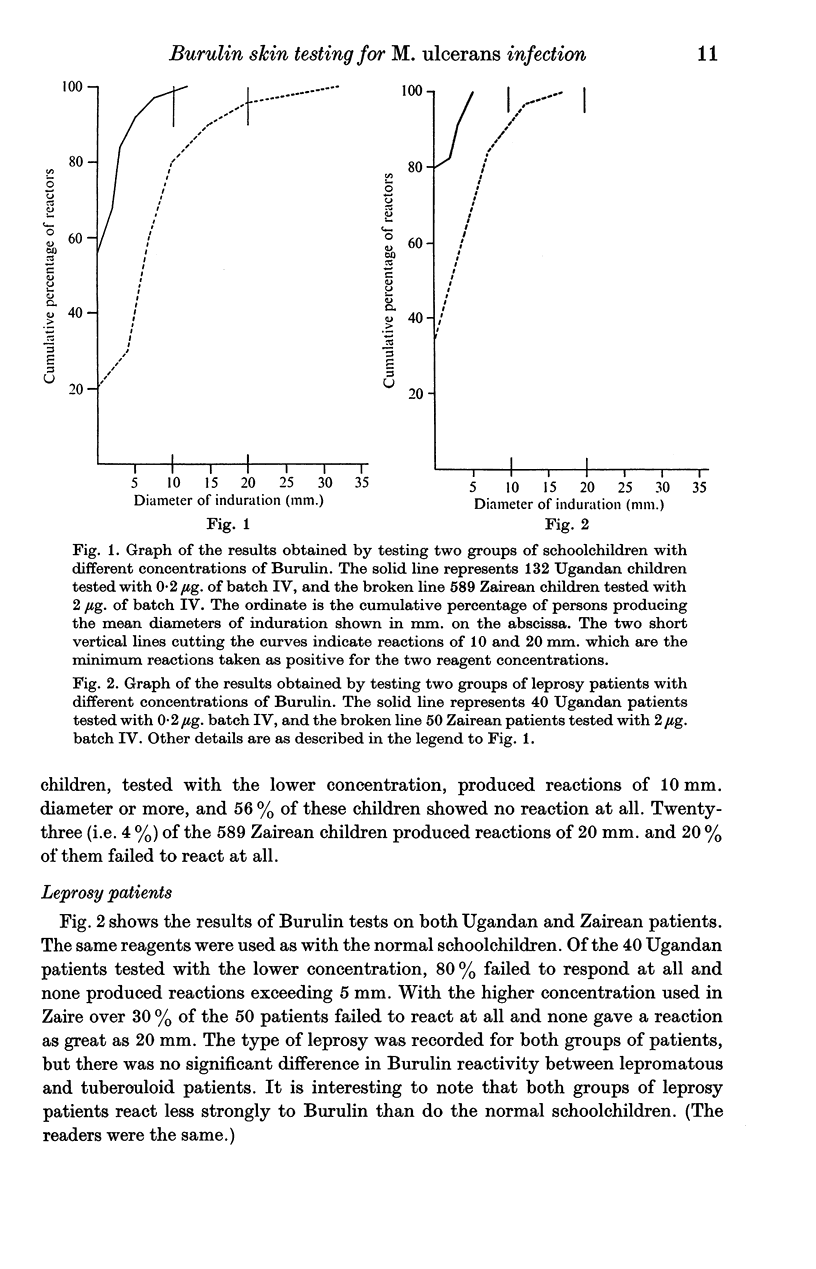
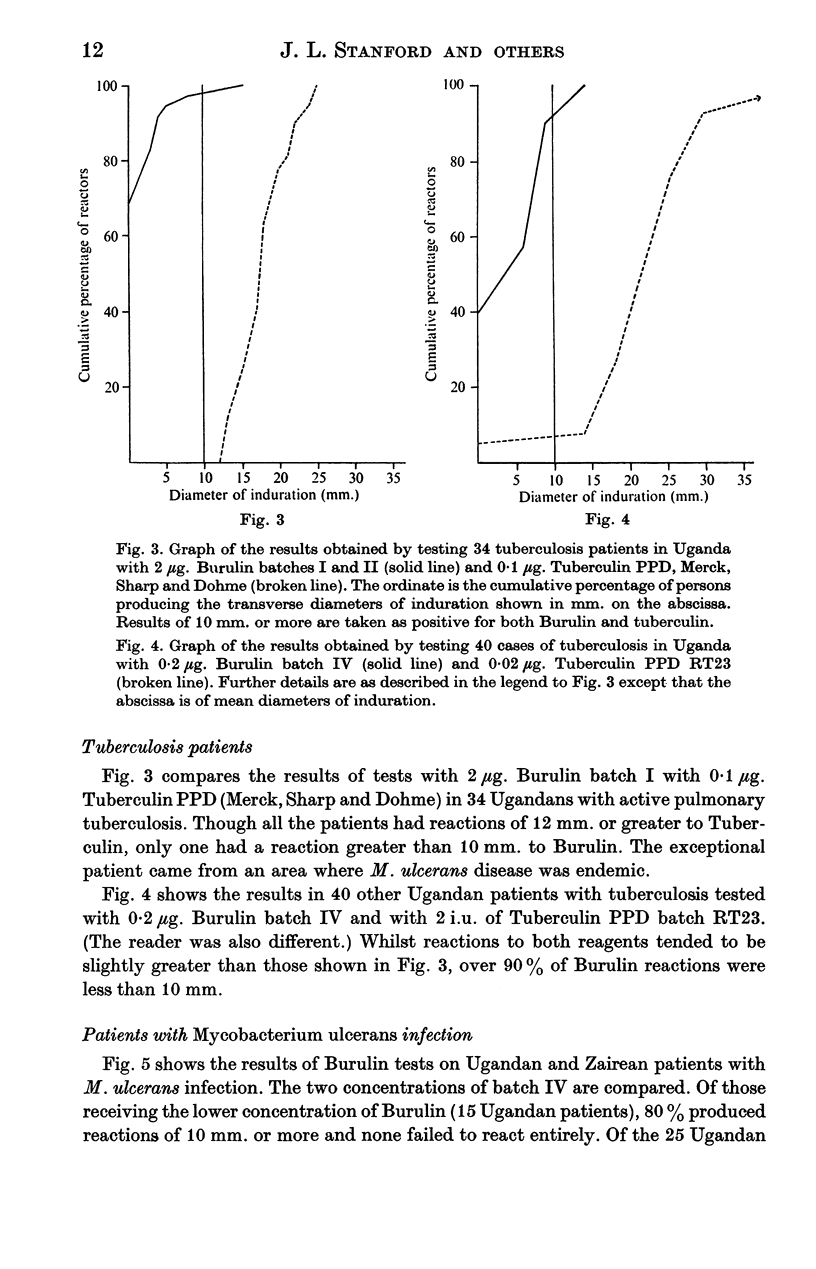
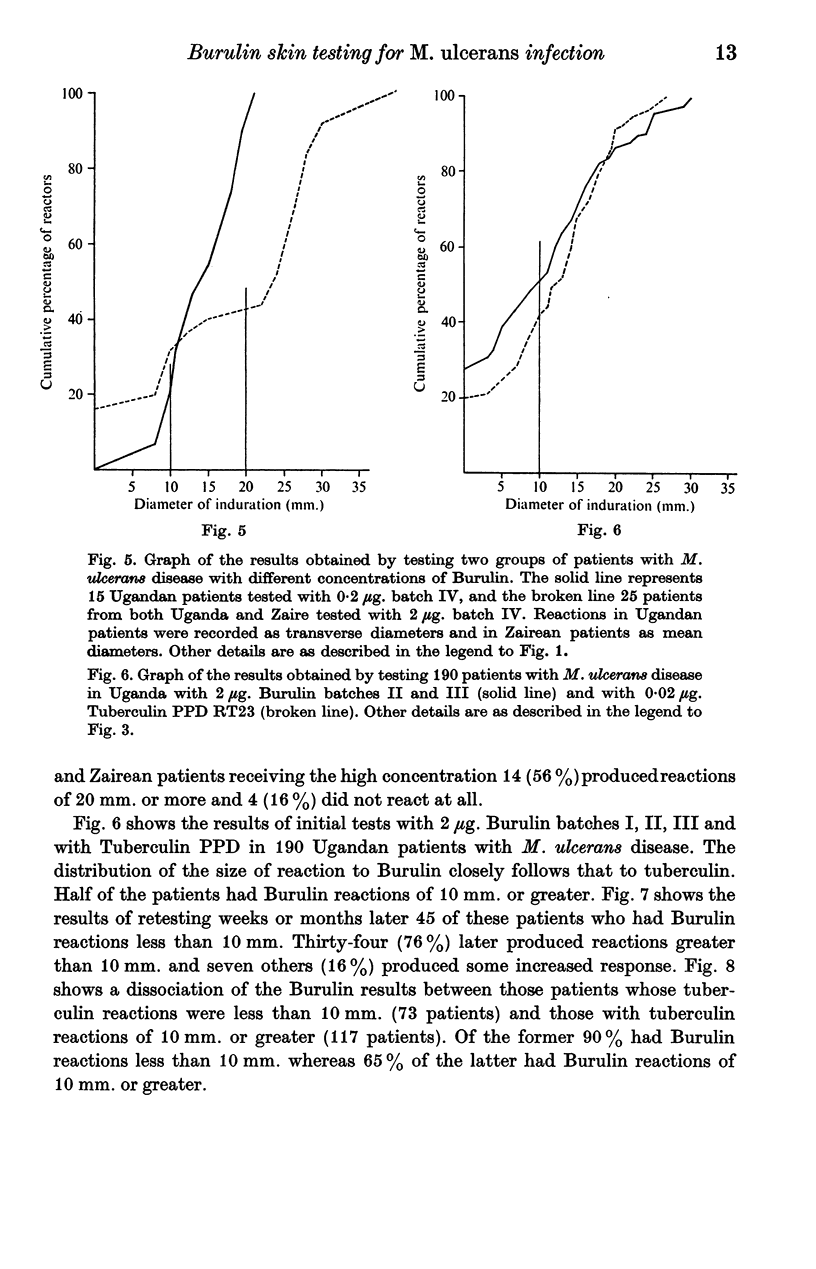
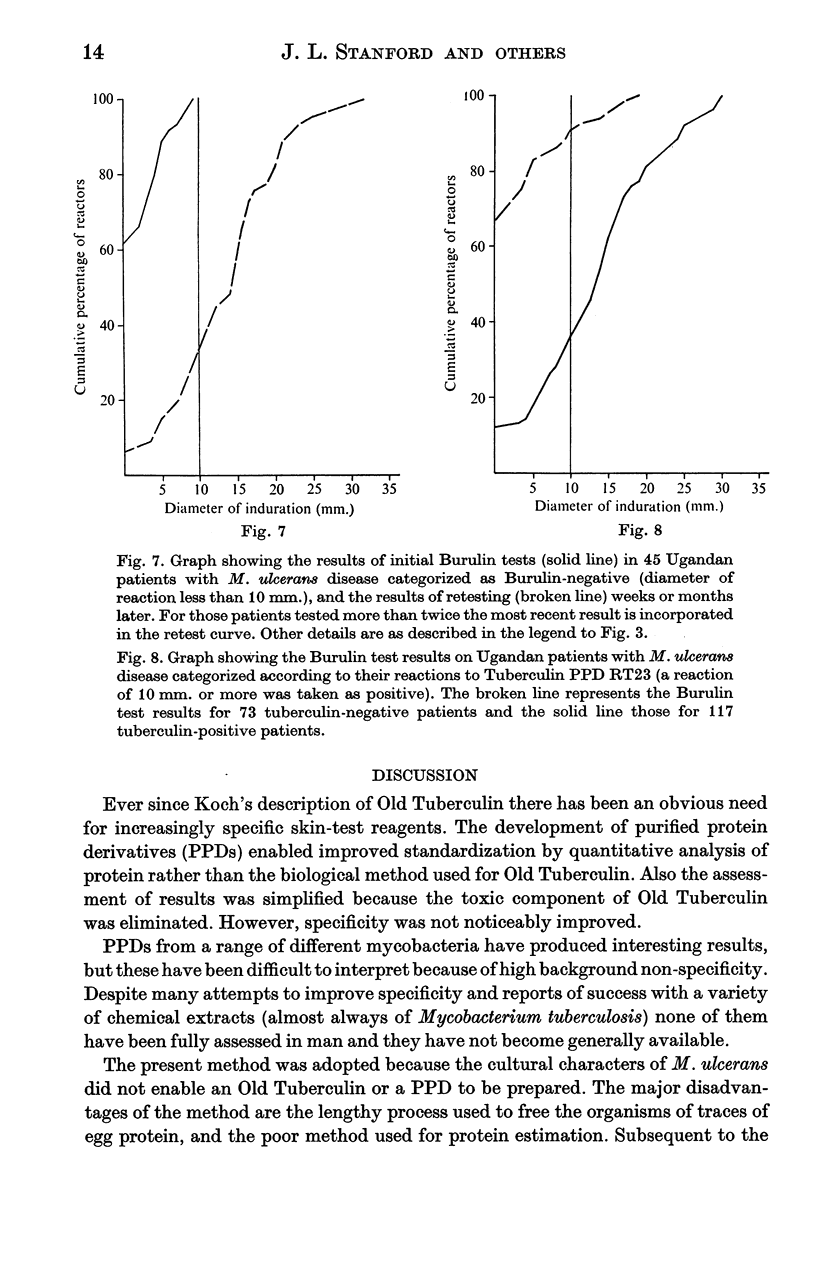
The preparation of a skin test antigen from Mycobacterium ulcerans by ultrasonic disintegration and filtration is described. The reagent, called Burulin, was tested in Africa in normal school children, and in patients with leprosy, tuberculosis or M. ulcerans disease. Those with tuberculosis or M. ulcerans disease were simultaneously tested with Tuberculin PPD. Burulin was found to be highly specific for patients in the reactive stage of M. ulcerans disease, and there was no cross-reaction in patients with other mycobacterioses. On the other hand, the majority of patients with M. ulcerans disease reacting to Burulin also produce positive reactions to Tuberculin PPD.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Stanford J. L. An immunodiffusion analysis of strains of Mycobacterium ulcerans isolated in Australia, Malaya, Mexico, Uganda and Zaire. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Aug;6(3):405–408. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandepitte J., Desmyter J., Gatti F. Mycobacteria, skins, and needles. Lancet. 1969 Sep 27;2(7622):691–691. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


