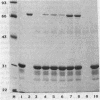
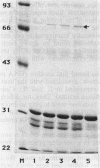
Abstract
When a protein derived from the immunoglobulin G (IgG)-binding domains of staphylococcal protein A was expressed in Escherichia coli and recovered from cell extract by IgG affinity chromatography, the 69-kilodalton heat shock protein DnaK was found to be copurified. DnaK could be selectively eluted from the IgG column by ATP or by lowering the pH to 4.7. Protein A could subsequently be eluted by lowering the pH to 3.2. Thus, this procedure allows a one-step purification of both DnaK and protein A from cell extract. In vitro experiments with pure DnaK and protein A revealed that DnaK did not interfere with the IgG-binding properties of protein A but associated with its unfolded C-terminal in a salt-resistant manner. In addition, a specific interaction between DnaK and denaturated casein was found.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkareva E. S., Lissin N. M., Girshovich A. S. Transient association of newly synthesized unfolded proteins with the heat-shock GroEL protein. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):254–257. doi: 10.1038/336254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Cellular defects caused by deletion of the Escherichia coli dnaK gene indicate roles for heat shock protein in normal metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2337-2346.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Drahos D., Hendrix R. The B66.0 protein of Escherichia coli is the product of the dnaK+ gene. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1175–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1175-1177.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Goldberg A. L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Swamy K. H., Chung C. H., Larimore F. S. Proteases in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):680–702. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goloubinoff P., Gatenby A. A., Lorimer G. H. GroE heat-shock proteins promote assembly of foreign prokaryotic ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oligomers in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):44–47. doi: 10.1038/337044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen S. L., VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Levels of major proteins of Escherichia coli during growth at different temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):185–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.185-194.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang B. J., Park W. J., Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. Escherichia coli contains a soluble ATP-dependent protease (Ti) distinct from protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5550–5554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C., Chandrasekhar G. N., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli DnaK and GrpE heat shock proteins interact both in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1590–1596. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1590-1596.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. Antibodies to two major chicken heat shock proteins cross-react with similar proteins in widely divergent species. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):267–274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren P. A., Eliasson M., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M., Palmcrantz E. Analysis and use of the serum albumin binding domains of streptococcal protein G. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Apr;1(2):69–74. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. pUR 250 allows rapid chemical sequencing of both DNA strands of its inserts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5765–5772. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Escherichia coli heat shock gene mutants are defective in proteolysis. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1851–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Ang D., Georgopoulos C. The grpE protein of Escherichia coli. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17437–17442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein of Escherichia coli possesses an ATPase and autophosphorylating activity and is essential in an in vitro DNA replication system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6431–6435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]