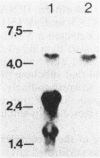
Abstract
We have cloned the operon coding for the Bacillus subtilis S complex, which has been proposed to be a component in protein secretion machinery. A lambda gt10 library of B. subtilis was screened with antiserum directed against the Staphylococcus aureus membrane-bound ribosome protein complex, which is homologous to the B. subtilis S complex. Two positive overlapping lambda clones were sequenced. The S-complex operon, 5 kilobases in size, was shown to contain four open reading frames and three putative promoters, which are located upstream of the first, the third, and the last gene. The four proteins encoded by the operon are 42, 36, 48, and 50 kilodaltons in size. All of these proteins were recognized by antisera separately raised against each protein of the S. aureus membrane-bound ribosome protein and B. subtilis S complexes, thus verifying the S-complex identity of the lambda clones. Sequence analysis revealed that all four proteins of the B. subtilis S complex are homologous to the four subunits of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). Also, the N terminus of the 48-kilodalton protein was found to have 70% amino acid identity with the N-terminal 211 amino acids, determined so far, from the E2 subunit of B. stearothermophilus PDH. Furthermore, chromosomal mapping of the S-complex operon gave a linkage to a marker gene located close to the previously mapped B. subtilis PDH genes. Thus, the S complex is evidently identical to the B. subtilis PDH, which has been shown to contain four subunits with molecular weights very similar to those of the S complex. Therefore, we propose that the S complex is not a primary component of protein secretion.
Full text
PDF


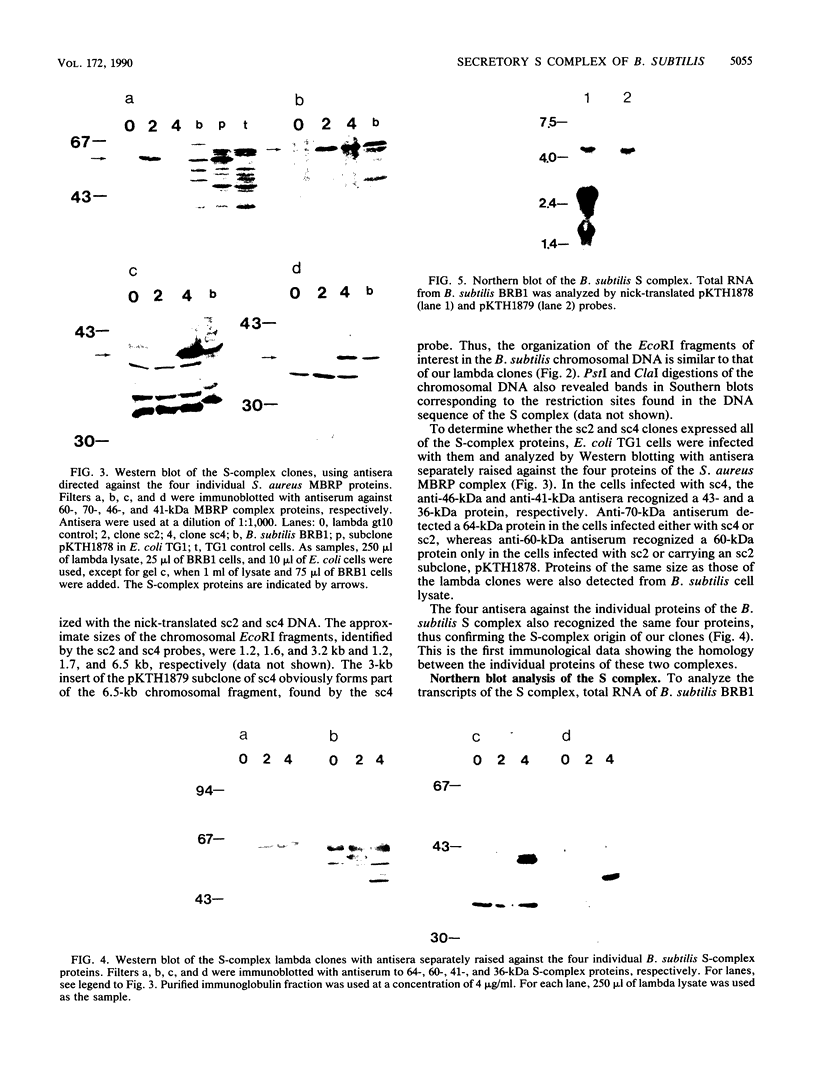



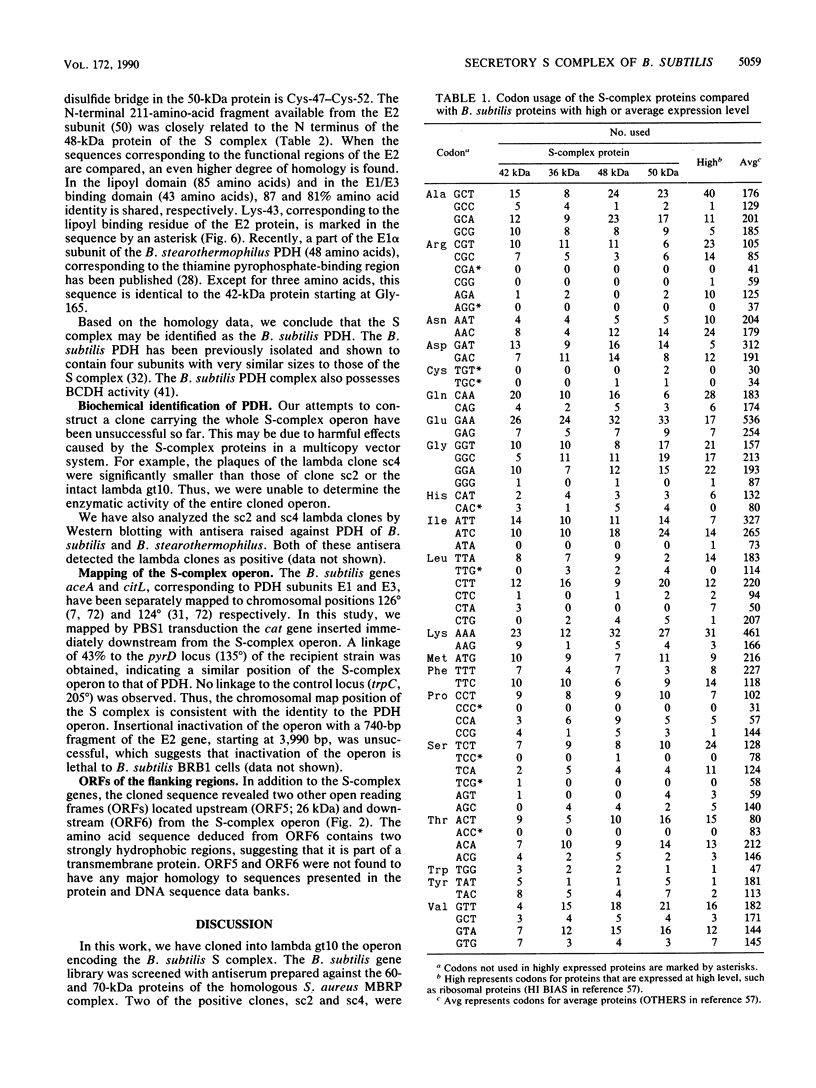




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler L. A., Arvidson S. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of genes encoding a multiprotein complex involved in secretion of proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5337–5343. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5337-5343.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler L. A., Arvidson S. Correlation between the rate of exoprotein synthesis and the amount of the multiprotein complex on membrane-bound ribosomes (MBRP-complex) in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):803–813. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler L. A., Arvidson S. Detection of a membrane-associated protein on detached membrane ribosomes in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1673–1682. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudreaux D. P., Eisenstadt E., Iijima T., Freese E. Biochemical and genetic characterization of an auxotroph of Bacillus subtilis altered in the Acyl-CoA:acyl-carrier-protein transacylase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):175–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning K. S., Uhlinger D. J., Reed L. J. Nucleotide sequence for yeast dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1831–1834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Idriss J. M., Sokatch J. R. Similarity of the E1 subunits of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida to the corresponding subunits of mammalian branched-chain-oxoacid and pyruvate dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 15;176(2):311–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the transacylase components of branched chain oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida, and the pyruvate and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):165–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Sequence analysis of the lpdV gene for lipoamide dehydrogenase of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):61–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Sykes P. J., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Isolation of a third lipoamide dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):665–668. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.665-668.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Hederstedt L. Genetic characterization of Bacillus subtilis odhA and odhB, encoding 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase and dihydrolipoamide transsuccinylase, respectively. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3667–3672. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3667-3672.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P., Furlong D., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Secretory S complex of Bacillus subtilis forms a large, organized structure when released from ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4031–4035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P., Horiuchi S., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. The 64-kilodalton membrane protein of Bacillus subtilis is also present as a multiprotein complex on membrane-free ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7772–7776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meirleir L., MacKay N., Lam Hon Wah A. M., Robinson B. H. Isolation of a full-length complementary DNA coding for human E1 alpha subunit of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1991–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedonder R. A., Lepesant J. A., Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Billault A., Steinmetz M., Kunst F. Construction of a kit of reference strains for rapid genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis 168. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):989–993. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.989-993.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Wang L. F. Multiple procaryotic ribonucleic acid polymerase sigma factors. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Sep;50(3):227–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.227-243.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Nguyen A., Lang D., Hoch J. A. Construction and properties of an integrable plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1513-1515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. W., Chuang J. L., Griffin T. A., Lau K. S., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Molecular phenotypes in cultured maple syrup urine disease cells. Complete E1 alpha cDNA sequence and mRNA and subunit contents of the human branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3448–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Fortnagel U. Growth and sporulation of Bacillus subtilis mutants blocked in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):745–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.745-756.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T. A., Lau K. S., Chuang D. T. Characterization and conservation of the inner E2 core domain structure of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex from bovine liver. Construction of a cDNA encoding the entire transacylase (E2b) precursor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14008–14014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanemaaijer R., Janssen A., de Kok A., Veeger C. The dihydrolipoyltransacetylase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. F., Borges A., Perham R. N. A common structural motif in thiamin pyrophosphate-binding enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Perham R. N., Finch J. T. Structure and symmetry of B. stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex and implications for eucaryote evolution. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Perham R. N. Purificaton of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus and resolution of its four component polypeptides. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):161–172. doi: 10.1042/bj1890161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Coukoulis H. J. Genetics of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):265–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.265-269.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson J. A., Lowe P. N., Perham R. N. Wild-type and mutant forms of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):463–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2110463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Marty-Mazars D., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Localization and quantitation of proteins characteristic of the complexed membrane of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1215–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1215-1221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. A 64-kilodalton membrane protein of Bacillus subtilis covered by secreting ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu C. W., Lau K. S., Griffin T. A., Chuang J. L., Fisher C. W., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Isolation and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the decarboxylase (E1)alpha precursor of bovine branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Expression of E1 alpha mRNA and subunit in maple-syrup-urine-disease and 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9007–9014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. S., Griffin T. A., Hu C. W., Chuang D. T. Conservation of primary structure in the lipoyl-bearing and dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase binding domains of mammalian branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex: molecular cloning of human and bovine transacylase (E2) cDNAs. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1972–1981. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. N., Hodgson J. A., Perham R. N. Dual role of a single multienzyme complex in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate and branched-chain 2-oxo acids in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 1;215(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj2150133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty-Mazars D., Horiuchi S., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Proteins of ribosome-bearing and free-membrane domains in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1381-1388.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers E. W., Miller W. Optimal alignments in linear space. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):11–17. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu X. D., Browning K. S., Behal R. H., Reed L. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene for dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7546–7550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohné M. Regulation of the dicarboxylic acid part of the citric acid cycle in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):224–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.224-234.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otulakowski G., Robinson B. H. Isolation and sequence determination of cDNA clones for porcine and human lipoamide dehydrogenase. Homology to other disulfide oxidoreductases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17313–17318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Borges A., Perham R. N. Amino acid sequence analysis of the lipoyl and peripheral subunit-binding domains in the lipoate acetyltransferase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):79–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2520079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N. An amino acid sequence in the active site of lipoamide dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80839-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva A., Nyberg K., Palva I. Quantification of alpha-amylase mRNA in Bacillus subtilis by nucleic acid sandwich hybridization. DNA. 1988 Mar;7(2):135–142. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C., Radford S. E. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complexes: in the beginning and halfway there. Biochem Soc Symp. 1987;54:67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons G., Raefsky-Estrin C., Carothers D. J., Pepin R. A., Javed A. A., Jesse B. W., Ganapathi M. K., Samols D., Patel M. S. Cloning and cDNA sequence of the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase component human alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1422–1426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J., Thom J. R. Export of protein: a biochemical view. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:507–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D. C., Sharp P. M. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):8023–8040. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.8023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. P., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Extracellular labeling of growing secreted polypeptide chains in Bacillus subtilis with diazoiodosulfanilic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):198–202. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. E., Darlison M. G., Stephens P. E., Duckenfield I. K., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the sucB gene encoding the dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase of Escherichia coli K12 and homology with the corresponding acetyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):361–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srere P. A. Complexes of sequential metabolic enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:89–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Darlison M. G., Lewis H. M., Guest J. R. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleotide sequence encoding the pyruvate dehydrogenase component. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Lewis H. M., Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumegi B., Srere P. A. Complex I binds several mitochondrial NAD-coupled dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15040–15045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sümegi B., Alkonyi I. A study on the physical interaction between the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and citrate synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 12;749(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Kuntz M. J., Goodwin G. W., Harris R. A., Crabb D. W. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for the E1 alpha subunit of rat liver branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15220–15224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]