Abstract
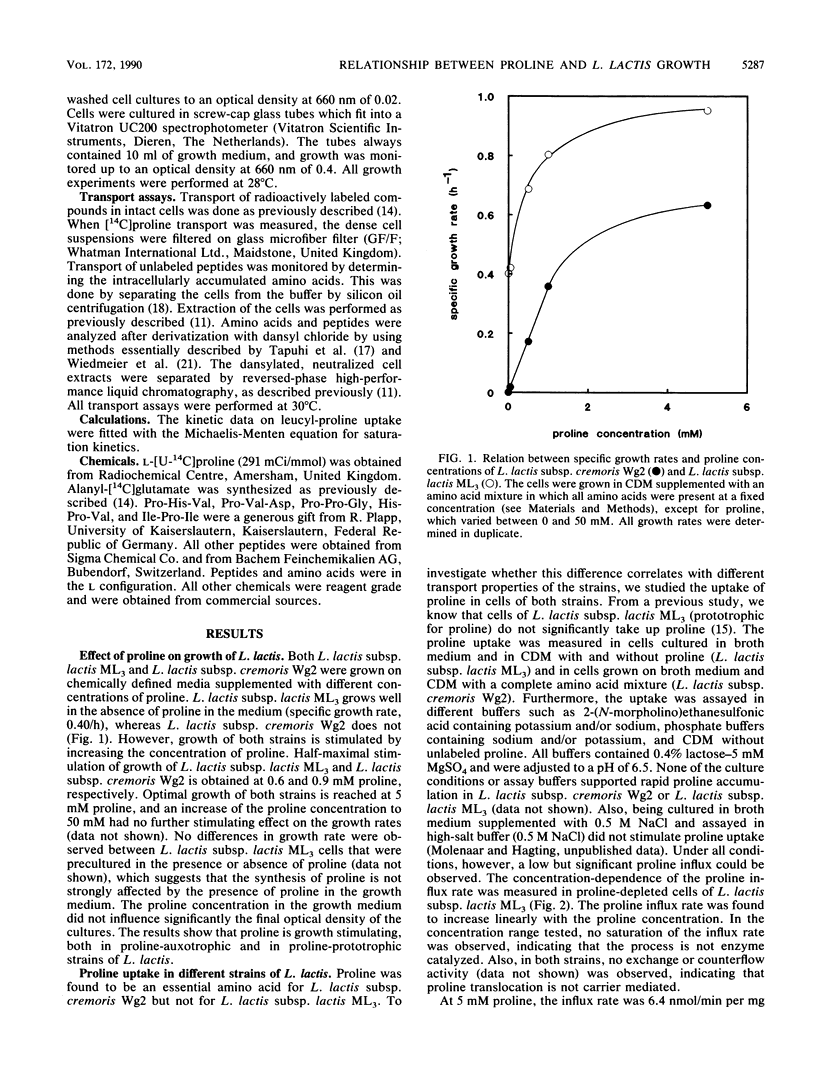
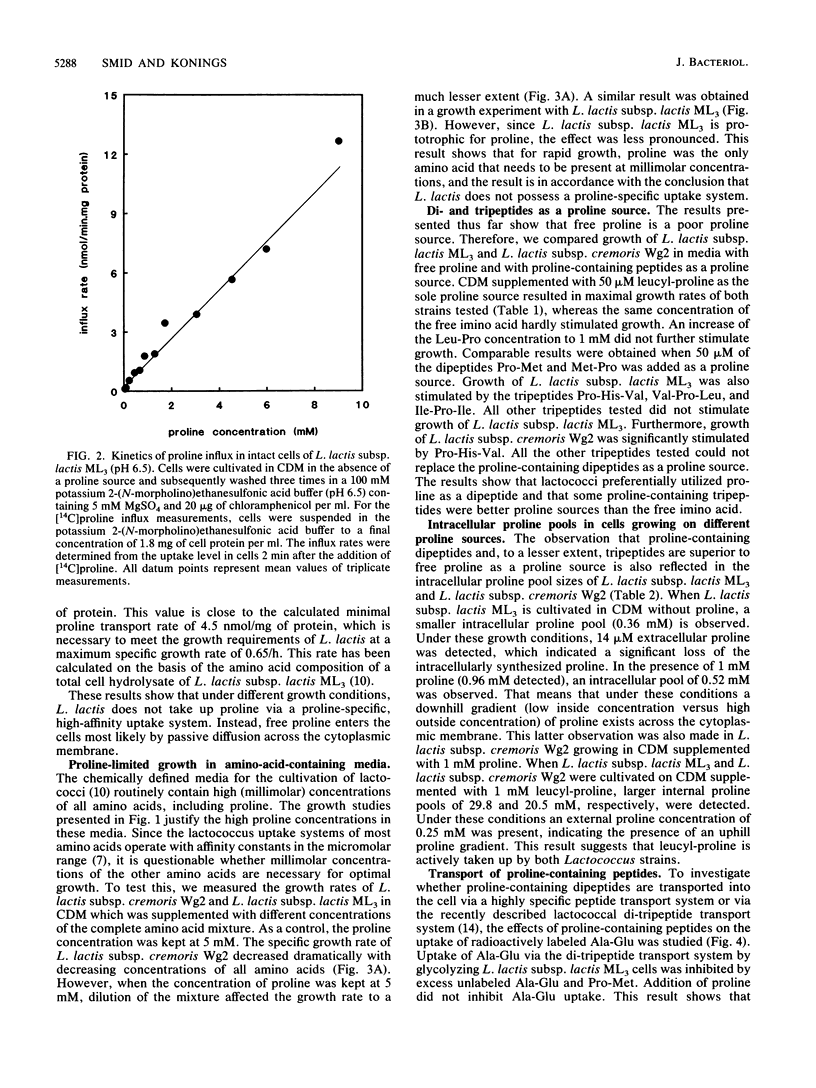
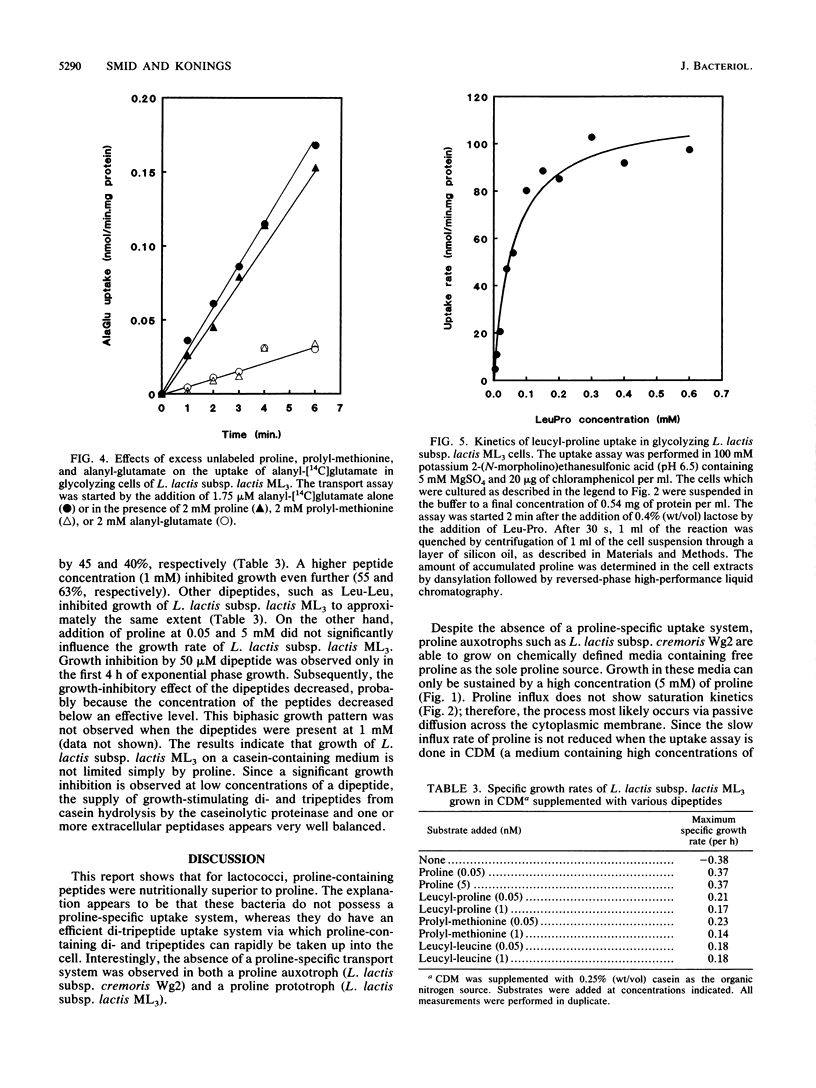
Proline, which is the most abundant residue in beta-casein, stimulates growth of Lactococcus lactis in a proline-requiring strain (Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2) and in a proline-prototrophic strain (Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis ML3). Both strains lack a proline-specific uptake system, and free proline can enter the cell only by passive diffusion across the cytoplasmic membrane. On the other hand, lactococci can actively take up proline-containing peptides via the lactococcal di- and tripeptide transport system, and these peptides are the major source of proline. Consequently, lactococcal growth on amino acid-based media is highly stimulated by the addition of proline-containing di- and tripeptides. Growth of L. lactis subsp. lactis ML3 on chemically defined media supplemented with casein does not appear proline limited. Addition of dipeptides (including proline-containing peptides) severely inhibits growth on a casein-containing medium, which indicates that the specific growth rate is determined by the balanced supply of different di- or tripeptides which compete for the same di- and tripeptide transport system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosman B. W., Tan P. S., Konings W. N. Purification and Characterization of a Tripeptidase from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1839–1843. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1839-1843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Poolman B., Driessen A. J. Bioenergetics and solute transport in lactococci. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;16(6):419–476. doi: 10.3109/10408418909104474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Konings W. N. Relation of growth of Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris to amino acid transport. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.700-707.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Smid E. J., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Bioenergetic consequences of lactose starvation for continuously cultured Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1460-1468.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smid E. J., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Mechanism and energetics of dipeptide transport in membrane vesicles of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):292–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.292-298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smid E. J., Plapp R., Konings W. N. Peptide uptake is essential for growth of Lactococcus lactis on the milk protein casein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6135–6140. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6135-6140.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan P. S., Konings W. N. Purification and Characterization of an Aminopeptidase from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):526–532. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.526-532.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapuhi Y., Schmidt D. E., Lindner W., Karger B. L. Dansylation of amino acids for high-performance liquid chromatography analysis. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90534-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmeier V. T., Porterfield S. P., Hendrich C. E. Quantitation of Dns-amino acids from body tissues and fluids using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Sep 10;231(2):410–417. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81865-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Brink B., Otto R., Hansen U. P., Konings W. N. Energy recycling by lactate efflux in growing and nongrowing cells of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.383-390.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boven A., Tan P. S. T., Konings W. N. Purification and Characterization of a Dipeptidase from Streptococcus cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.43-49.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



