Abstract
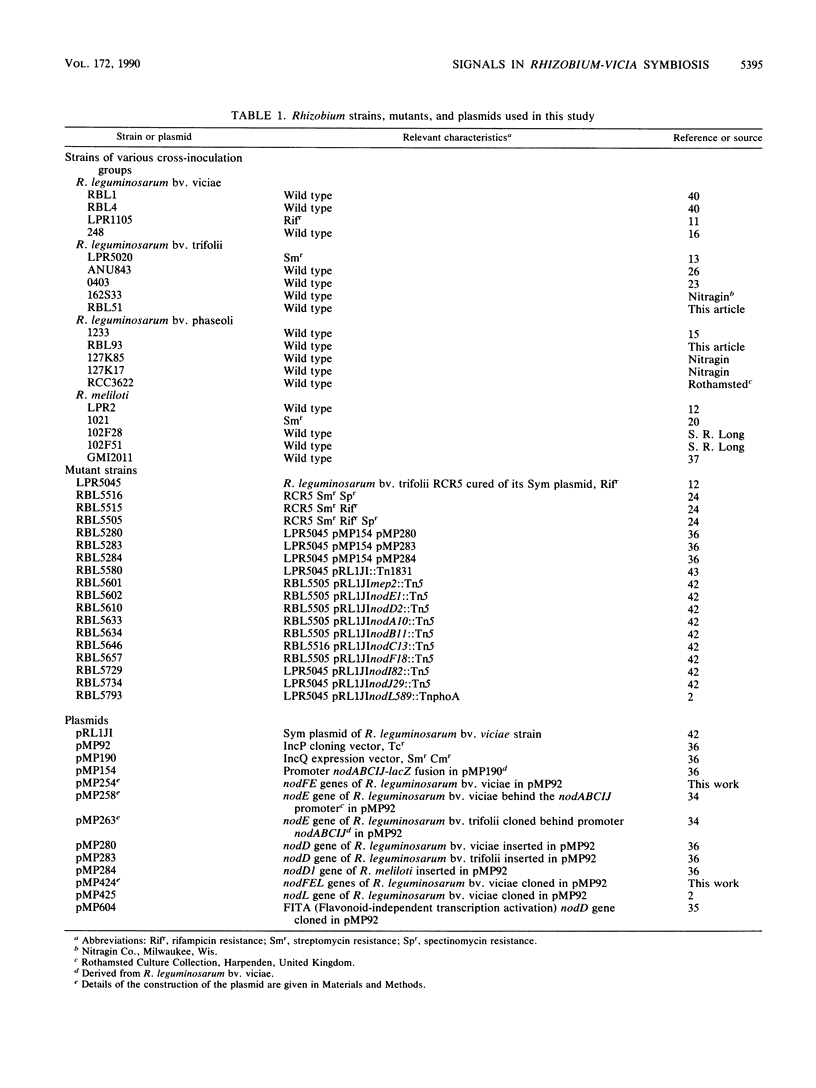
Flavonoids in root exudate of leguminous plants activate the transcription of Rhizobium genes involved in the formation of root nodules (nod genes). We report that inoculation with the homologous symbiont R. leguminosarum bv. viciae results in an increased nod gene-inducing activity (Ini) in root exudate of V. sativa subsp. nigra, whereas inoculation with heterologous Rhizobium strains results in exudates with nod gene-inducing activity comparable to that of uninfected plants. Ini can be demonstrated by using either of the isogenic indicator strains containing an inducible nod promoter fused to the Escherichia coli lacZ reporter gene and the regulatory nodD gene of R. leguminosarum bv. viciae, R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii, or R. meliloti. The presence of genes nodDABCEL of R. leguminosarum bv. viciae appeared to be essential for induction of Ini. Mutation of the genes nodI and nodJ causes a delay of Ini, whereas gene nodF appears to be required for both the timely appearance and the maximum level of Ini activity. The nodE gene is responsible for the biovar specificity of induction of Ini by Rhizobium spp. Ini is caused by a soluble heat-stable factor of rhizobial origin. This Rhizobium-produced Ini factor has an apparent molecular weight between 1,000 and 10,000 and does not originate from flavonoid precursors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Production of root hair deformation factors by Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes in Escherichia coli: HsnD (NodH) is involved in the plant host-specific modification of the NodABC factor. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00027330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canter Cremers H., Spaink H. P., Wijfjes A. H., Pees E., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Additional nodulation genes on the Sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Aug;13(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00016135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou A., Hamilton W. D., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium nodulation gene nodO encodes a Ca2(+)-binding protein that is exported without N-terminal cleavage and is homologous to haemolysin and related proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):349–354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. J., Downie J. A. The nodI gene product of Rhizobium leguminosarum is closely related to ATP-binding bacterial transport proteins; nucleotide sequence analysis of the nodI and nodJ genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher C., Maillet F., Vasse J., Rosenberg C., van Brussel A. A., Truchet G., Dénarié J. Rhizobium meliloti host range nodH gene determines production of an alfalfa-specific extracellular signal. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5489–5499. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5489-5499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Swanson J. A., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. II. Nucleotide Sequence, Transcription Start Sites and Protein Products. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):191–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., Snijdewint F. G., Schilperoort R. A. Identification of the Sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum strain 1001 and its transfer to and expression in other rhizobia and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bookland R., Barkei J., Paaren H. E., Appelbaum E. R. Induction of Bradyrhizobium japonicum common nod genes by isoflavones isolated from Glycine max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip-Hollingsworth S., Hollingsworth R. I., Dazzo F. B. Host-range related structural features of the acidic extracellular polysaccharides of Rhizobium trifolii and Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1461–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Shearman C. A., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The nodD gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum is autoregulatory and in the presence of plant exudate induces the nodA,B,C genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3369–3373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheres B., Van De Wiel C., Zalensky A., Horvath B., Spaink H., Van Eck H., Zwartkruis F., Wolters A. M., Gloudemans T., Van Kammen A. The ENOD12 gene product is involved in the infection process during the pea-Rhizobium interaction. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90743-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Wingender R., John M., Wieneke U., Schell J. Rhizobium meliloti nodA and nodB genes are involved in generating compounds that stimulate mitosis of plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8578–8582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Watson J. M. DNA sequence of Rhizobium trifolii nodulation genes reveals a reiterated and potentially regulatory sequence preceding nodABC and nodFE. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2891–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman C. A., Rossen L., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation gene nodF encodes a polypeptide similar to acyl-carrier protein and is regulated by nodD plus a factor in pea root exudate. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):647–652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Weinman J., Djordjevic M. A., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Genetic analysis and cellular localization of the Rhizobium host specificity-determining NodE protein. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2811–2818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truchet G., Debellé F., Vasse J., Terzaghi B., Garnerone A. M., Rosenberg C., Batut J., Maillet F., Dénarié J. Identification of a Rhizobium meliloti pSym2011 region controlling the host specificity of root hair curling and nodulation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1200-1210.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Brussel A. A., Zaat S. A., Cremers H. C., Wijffelman C. A., Pees E., Tak T., Lugtenberg B. J. Role of plant root exudate and Sym plasmid-localized nodulation genes in the synthesis by Rhizobium leguminosarum of Tsr factor, which causes thick and short roots on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.517-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., Wijffelman C. A., Mulders I. H., van Brussel A. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Root Exudates of Various Host Plants of Rhizobium leguminosarum Contain Different Sets of Inducers of Rhizobium Nodulation Genes. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1298–1303. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., van Brussel A. A., Tak T., Pees E., Lugtenberg B. J. Flavonoids induce Rhizobium leguminosarum to produce nodDABC gene-related factors that cause thick, short roots and root hair responses on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3388–3391. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3388-3391.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R. A., Spaink H. P., Pees E., Mulders I. H., Wijfjes A., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Localization and symbiotic function of a region on the Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI responsible for a secreted, flavonoid-inducible 50-kilodalton protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1151–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1151-1157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


