Abstract
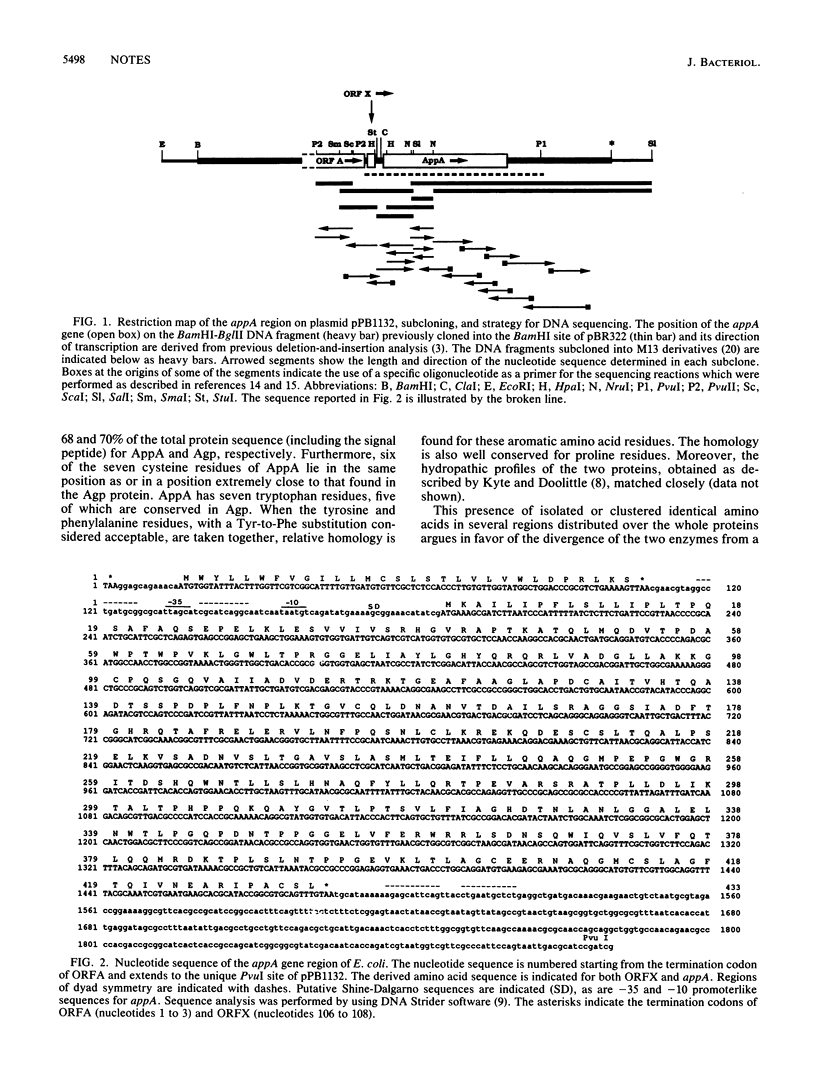
The whole nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli gene appA, which encodes periplasmic phosphoanhydride phosphohydrolase (optimum pH, 2.5), and its flanking regions was determined. The AppA protein is significantly homologous to the product of the nearby gene agp, acid glucose-1-phosphatase. Because identical amino acids are distributed over the whole lengths of the proteins, it is likely that appA and agp originate from the same ancestor gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., Pilkis S. J. Evolution of a bifunctional enzyme: 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9642–9646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. L., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Use of TnphoA to detect genes for exported proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of the plasmid-encoded gene for a periplasmic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1663–1669. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1663-1669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Cancedda F., Ericsson L. H., Neumann P. A., Piccoli S. P., Schlesinger M. J., Shriefer K., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3473–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Identification of the gene appA for the acid phosphatase (pH optimum 2.5) of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):68–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00383314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Is the acid phosphatase of Escherichia coli with pH optimum of 2.5 A polyphosphate depolymerase? FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Cahu M., Desjoyaux-Cherel B., Boquet P. L. The acid phosphatase with optimum pH of 2.5 of Escherichia coli. Physiological and Biochemical study. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6669–6676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel E., Boquet P. L. Acid phosphatases of Escherichia coli: molecular cloning and analysis of agp, the structural gene for a periplasmic acid glucose phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4916–4923. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4916-4923.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel E., Boquet P. L. Mapping of the Escherichia coli acid glucose-1-phosphatase gene agp and analysis of its expression in vivo by use of an agp-phoA protein fusion. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3511–3517. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3511-3517.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel E., Marck C., Boquet P. L. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of the Escherichia coli agp gene encoding periplasmic acid glucose-1-phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):802–807. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.802-807.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati E., Danchin A. The structure of the promoter and amino terminal region of the pH 2.5 acid phosphatase structural gene (appA) of E. coli: a negative control of transcription mediated by cyclic AMP. Biochimie. 1987 Mar;69(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati E., Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Pleiotropic mutations in appR reduce pH 2.5 acid phosphatase expression and restore succinate utilisation in CRP-deficient strains of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00331647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



