Abstract
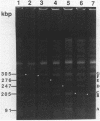
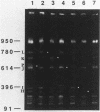
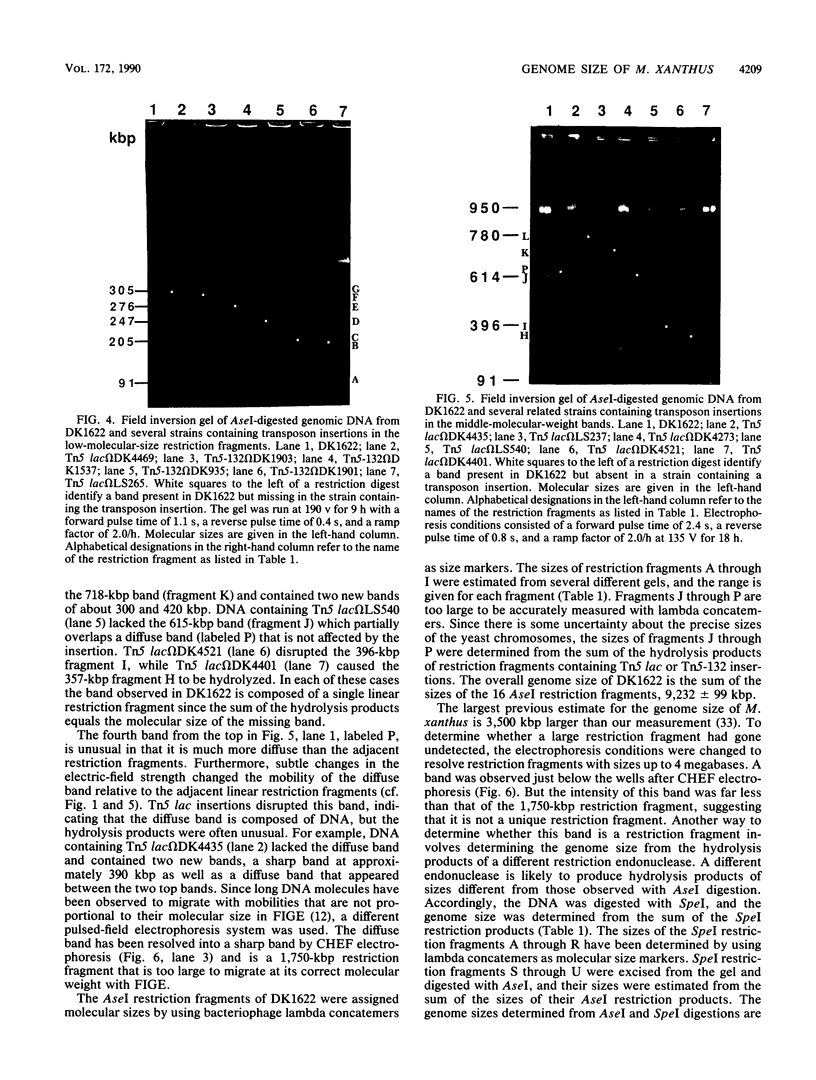
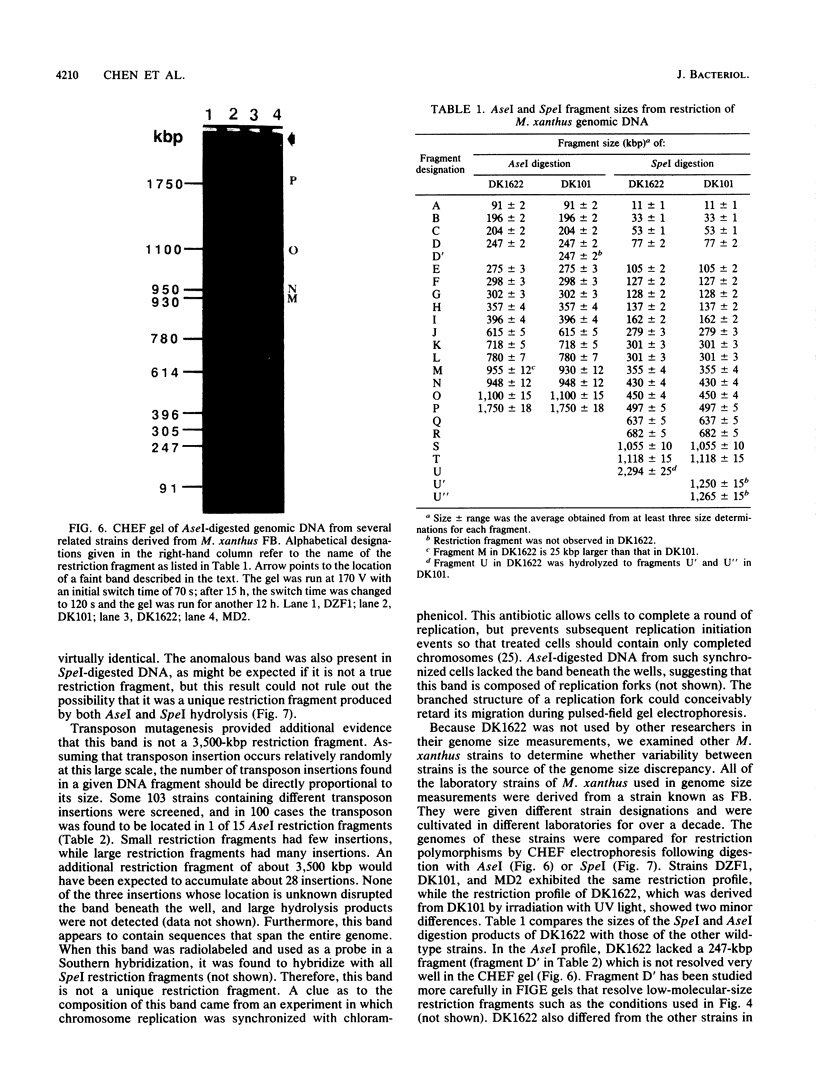
Genomic DNA of the myxobacterium Myxococcus xanthus was digested with the rare cutting restriction endonuclease AseI or SpeI, and the restriction products were separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Transposons Tn5-132 and Tn5 lac, which contain AseI restriction sites, were used to determine the number of restriction fragments in each band. The size of the genome was determined by adding the molecular sizes of the restriction products. The genomes of strains DK101, MD2, and DZF1 have identical restriction patterns and were estimated to be 9,454 +/- 101 kilobase pairs from the AseI digestions and 9,453 +/- 106 kilobase pairs from the SpeI digestions. DK1622, which was derived from DK101 by treatment with UV light, has suffered a 220- to 222-kilobase-pair deletion that removed an AseI and an SpeI restriction site. The deleted DNA may consist exclusively of Mx alpha-associated sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boncinelli E., Simeone A., de Falco A., Fidanza V., La Volpe A. An agarose gel resolving a wide range of DNA fragment lengths. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):40–43. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchel D. E., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lactose permease gene. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):541–545. doi: 10.1038/283541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillen W., Schollmeier K. Nucleotide sequence of the Tn10 encoded tetracycline resistance gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):525–539. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. A global analysis of developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):252–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalande M., Noolandi J., Turmel C., Rousseau J., Slater G. W. Pulsed-field electrophoresis: application of a computer model to the separation of large DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8011–8015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pecq J. B., Paoletti C. A new fluorometric method for RNA and DNA determination. Anal Biochem. 1966 Oct;17(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Barile M. F., Harasawa R., Amikam D., Glaser G. Characterization of the mycoplasma genome. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):357–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Control of morphogenesis in myxobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(3):195–227. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. The role of the cell surface in social and adventurous behaviour of myxobacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1295–1299. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starich T., Cordes P., Zissler J. Transposon tagging to detect a latent virus in Myxococcus xanthus. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):541–543. doi: 10.1126/science.2996138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starich T., Zissler J. Movement of multiple DNA units between Myxococcus xanthus cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2323–2336. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2323-2336.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin S. S., Rosenberg E. Induction of morphogenesis by methionine starvation in Myxococcus xanthus: polyamine control. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):641–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.641-649.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Platt T., Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Christie G. E., Horowitz H., VanCleemput M., Wu A. M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6647–6668. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee T., Inouye M. Reexamination of the genome size of myxobacteria, including the use of a new method for genome size analysis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1257–1265. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1257-1265.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee T., Inouye M. Two-dimensional DNA electrophoresis applied to the study of DNA methylation and the analysis of genome size in Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):181–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R., Krotoski D. M., Cumsky M. Chromosome replication in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):122–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.122-129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D., Rosenberg E. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis during microcyst germination in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):981–986. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.981-986.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]