Abstract
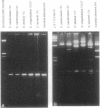
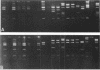
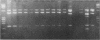
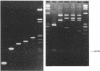
Detailed restriction analyses of many samples often require substantial amounts of time and effort for DNA extraction, restriction digests, Southern blotting, and hybridization. We describe a novel approach that uses the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for rapid simplified restriction typing and mapping of DNA from many different isolates. DNA fragments up to 2 kilobase pairs in length were efficiently amplified from crude DNA samples of several pathogenic Cryptococcus species, including C. neoformans, C. albidus, C. laurentii, and C. uniguttulatus. Digestion and electrophoresis of the PCR products by using frequent-cutting restriction enzymes produced complex restriction phenotypes (fingerprints) that were often unique for each strain or species. We used the PCR to amplify and analyze restriction pattern variation within three major portions of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) repeats from these fungi. Detailed mapping of many restriction sites within the rDNA locus was determined by fingerprint analysis of progressively larger PCR fragments sharing a common primer site at one end. As judged by PCR fingerprints, the rDNA of 19 C. neoformans isolates showed no variation for four restriction enzymes that we surveyed. Other Cryptococcus spp. showed varying levels of restriction pattern variation within their rDNAs and were shown to be genetically distinct from C. neoformans. The PCR primers used in this study have also been successfully applied for amplification of rDNAs from other pathogenic and nonpathogenic fungi, including Candida spp., and ought to have wide applicability for clinical detection and other studies.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new genus, filobasidiella, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1975 Nov-Dec;67(6):1197–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Bennett J. E., Rhodes J. C. Taxonomic studies on Filobasidiella species and their anamorphs. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982;48(1):25–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00399484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. H., Gyllensten U. B., Cui X. F., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):414–417. doi: 10.1038/335414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R., Magee B. B., Magee P. T. Separation of chromosomes of Cryptococcus neoformans by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2624–2627. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2624-2627.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo B. I., Barbour A. G. Cloning of 18S and 25S rDNAs from the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5596–5600. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5596-5600.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent R. D., Goewert R., Goldman W. E., Kobayashi G. S., Lambowitz A. M., Medoff G. Classification of Histoplasma capsulatum isolates by restriction fragment polymorphisms. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):813–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.813-818.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. J., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. The polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]