Abstract
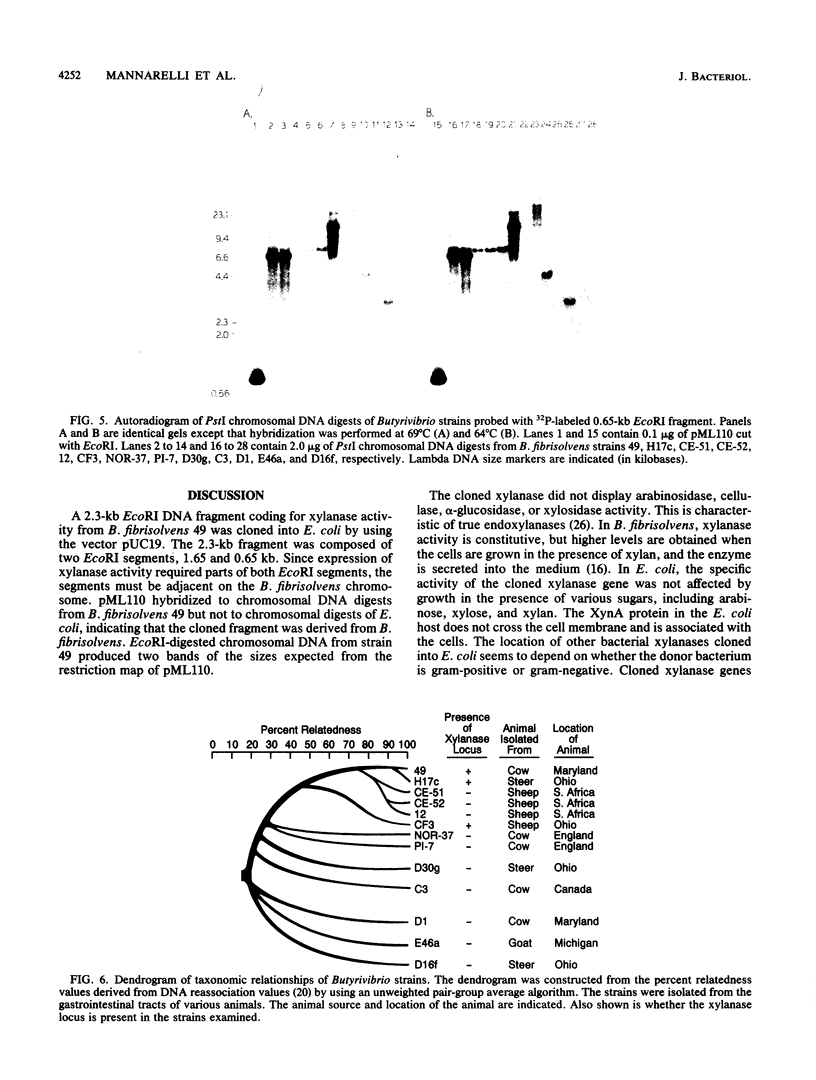
A gene coding for xylanase activity, xynA, from the anaerobic ruminal bacterium Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens 49 was cloned into Escherichia coli JM83 by using plasmid pUC19. The gene was located on a 2.3-kilobase (kb) DNA insert composed of two adjacent EcoRI fragments of 1.65 and 0.65 kb. Expression of xylanase activity required parts of both EcoRI segments. In E. coli, the cloned xylanase enzyme was not secreted and remained cell associated. The enzyme exhibited no arabinosidase, cellulase, alpha-glucosidase, or xylosidase activity. The isoelectric point of the cloned protein was approximately 9.8, and optimal xylanase activity was obtained at pH 5.4. The nucleotide sequence of the 1,535-base-pair EcoRV-EcoRI segment from the B. fibrisolvens chromosome that included the xynA gene was determined. An open reading frame was found that encoded a 411-amino-acid-residue polypeptide of 46,664 daltons. A putative ribosome-binding site, promoter, and leader sequence were identified. Comparison of the XynA protein sequence with that of the XynA protein from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain C-125 revealed considerable homology, with 37% identical residues or conservative changes. The presence of the cloned xylanase gene in other strains of Butyrivibrio was examined by Southern hybridization. The cloned xylanase gene hybridized strongly to chromosomal sequences in only two of five closely related strains.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.16-21.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier R., Jr, Driguez H., Desrochers M. Molecular cloning of a Bacillus subtilis xylanase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biely P., Markovic O., Mislovicová D. Sensitive detection of endo-1,4-beta-glucanases and endo-1,4-beta-xylanases in gels. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Bedouelle H., Winter G. Improved oligonucleotide site-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis P., Digneffe C., Willemot K. Cloning and expression of a Bacillus coagulans amylase gene in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(4):507–511. doi: 10.1007/BF00337957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Hemicellulose degradation by rumen bacteria. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1819–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierasch L. M. Signal sequences. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):923–930. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Ohkoshi A., Horikoshi K. Molecular cloning and expression of a xylanase gene of alkalophilic Aeromonas sp. no. 212 in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2825–2830. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panbangred W., Kondo T., Negoro S., Shinmyo A., Okada H. Molecular cloning of the genes for xylan degradation of Bacillus pumilus and their expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(3):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00392172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly P. J. Xylanases: structure and function. Basic Life Sci. 1981;18:111–129. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3980-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell G. W., Utt E. A., Hespell R. B., Mackenzie K. F., Ingram L. O. Identification of the Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens xylosidase gene (xylB) coding region and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):306–311. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.306-311.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillero A., Ribeiro J. M. Isoelectric points of proteins: theoretical determination. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jun;179(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipat A., Taylor K. A., Lo R. Y., Forsberg C. W., Krell P. J. Molecular cloning of a xylanase gene from Bacteroides succinogenes and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):477–481. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.477-481.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Relationship between the limited and wide host range octopine-type Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.484-493.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R. C., MacKenzie C. R., Narang S. A. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus circulans xylanase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7187–7187. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]