Abstract
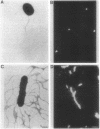
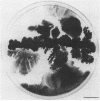
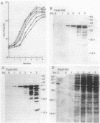
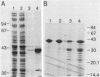
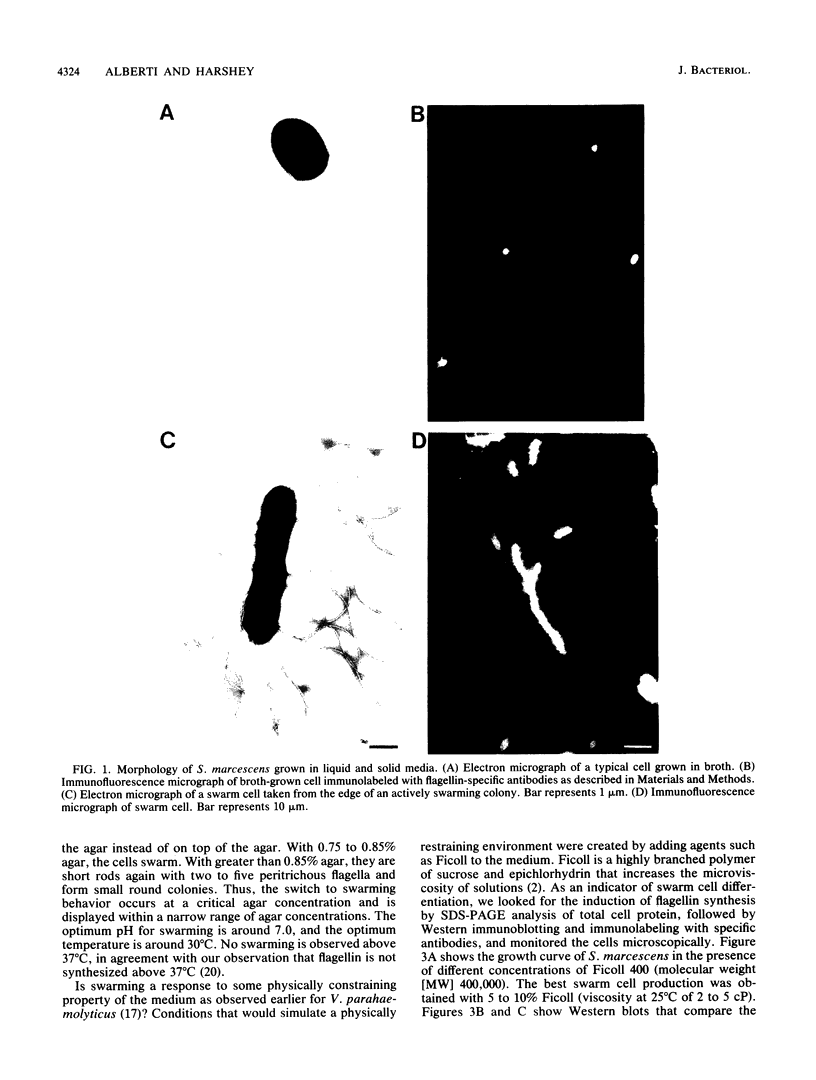
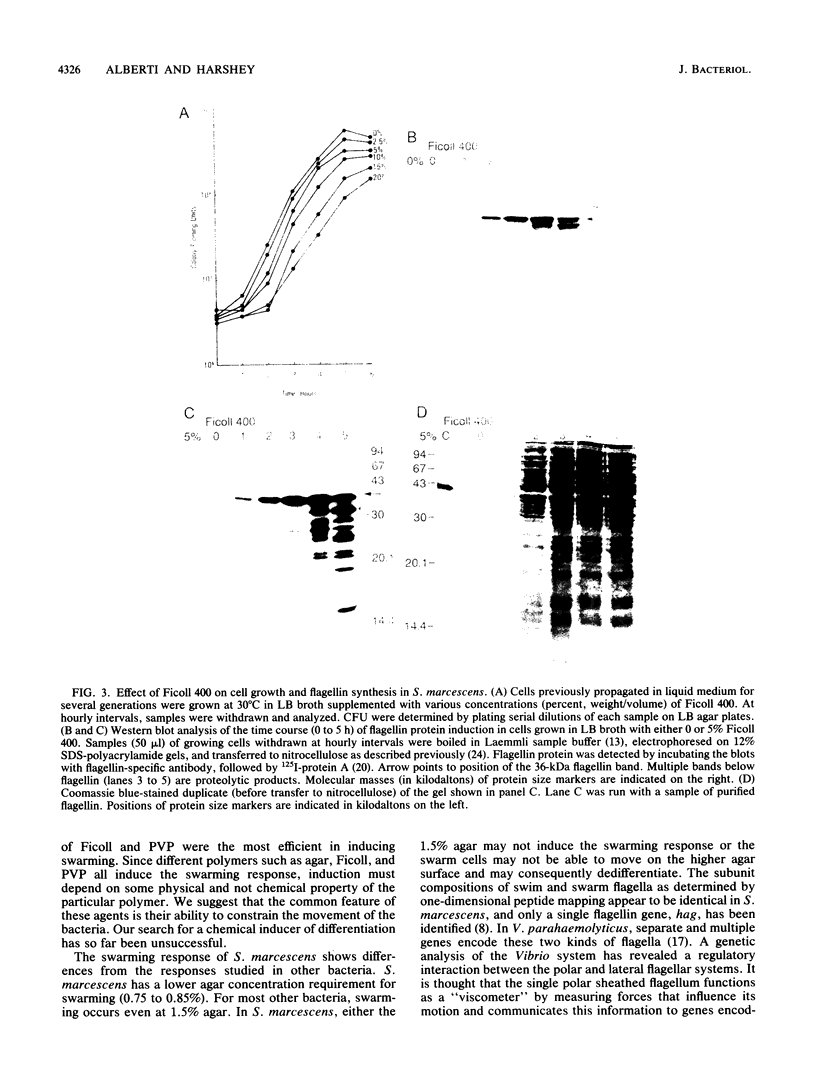
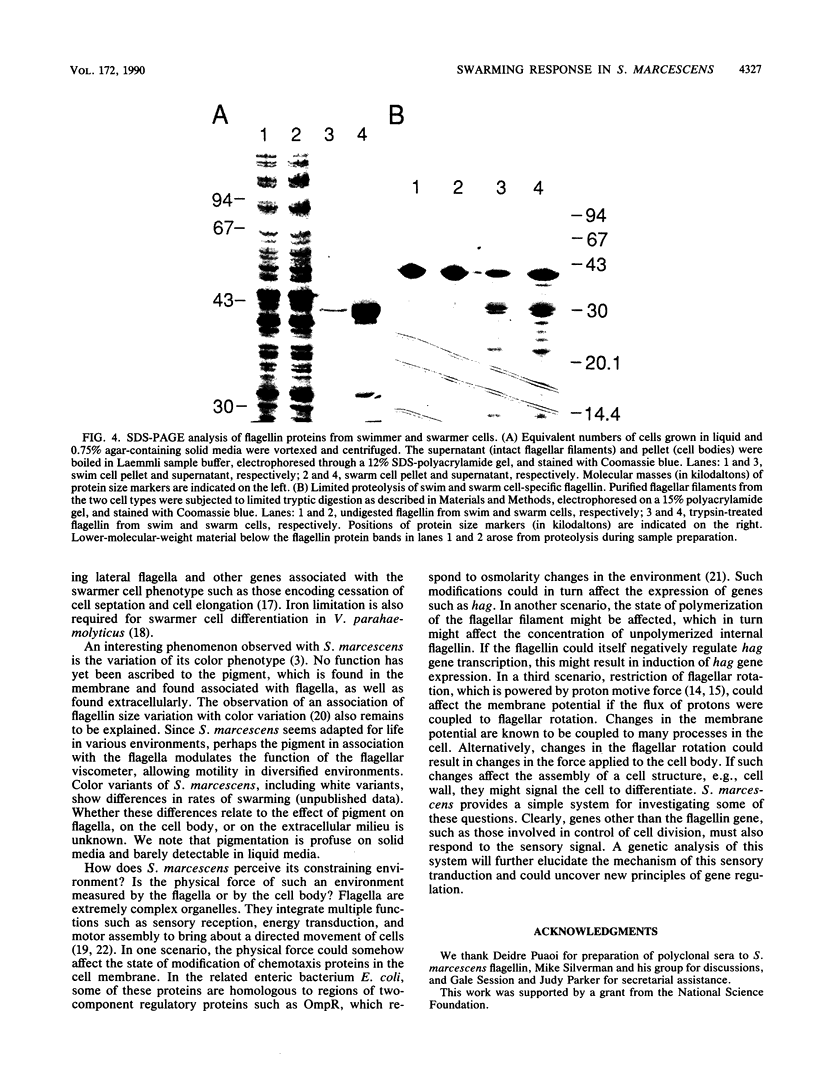
We describe a new sensory response in the enteric bacterium Serratia marcescens. When grown in liquid media, the bacteria were short rods with one to two flagella and displayed classical swimming behavior. Upon transfer to a solid surface (0.7 to 0.8T% agar medium), the bacteria underwent a dramatic change of form. They ceased septation, elongated, and expressed numerous (10 to 100) flagella that covered the lateral sides of the cells. The bacteria now displayed a different form of locomotion--swarming--which allowed them to rapidly move over the top of the solid surface. The differentiation to either swimmer or swarmer cells could be reversed by growth on solid or liquid medium, respectively. To identify conditions that influence this differentiation, the growth environment of S. marcescens was manipulated extensively. The swarming response was monitored by visual and microscopic observation of cell movement on solid surfaces, by immunofluorescent labeling followed by microscopic observation for the presence of elongated, profusely flagellated cells, as well as by estimation of induction of flagellin protein, using Western immunoblot analysis. Conditions that imposed a physical constraint on bacterial movement, such as solid or viscous media, were the most efficient at inducing the swarming response. No chemical constituent of the medium that might contribute to the response could be identified, although the existence of such a component cannot be ruled out. Both swimmer and swarmer cells had flagellin proteins of identical molecular weight, which produced similar proteolysis patterns upon digestion with trypsin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belas R., Simon M., Silverman M. Regulation of lateral flagella gene transcription in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):210–218. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.210-218.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Turner L. Movement of microorganisms in viscous environments. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):349–351. doi: 10.1038/278349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont P. A., Grimont F. The genus Serratia. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:221–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES W. H. A reconsideration of the swarming of Proteus vulgaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):49–58. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshey R. M., Estepa G., Yanagi H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a flagellin-coding gene (hag) from Serratia marcescens 274. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Bacterial surface translocation: a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):478–503. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.478-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines D. A., Saurugger P. N., Ihler G. M., Benedik M. J. Genetic analysis of extracellular proteins of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4141–4146. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4141-4146.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Hilmen M., Silverman M. Flagellar dynamometer controls swarmer cell differentiation of V. parahaemolyticus. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Silverman M. Iron regulation of swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):731–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.731-736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Behavioral genetics in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:397–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paruchuri D. K., Harshey R. M. Flagellar variation in Serratia marcescens is associated with color variation. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):61–65. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.61-65.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Conserved domains in bacterial regulatory proteins that respond to environmental stimuli. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):579–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Stewart K. R., Williams F. D. Extracellular slime associated with Proteus mirabilis during swarming. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.930-937.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzer S. The mechanism of swarming of Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 20;104(1):67–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00447301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S. Induction of swarming in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(4):357–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00455952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]