Abstract
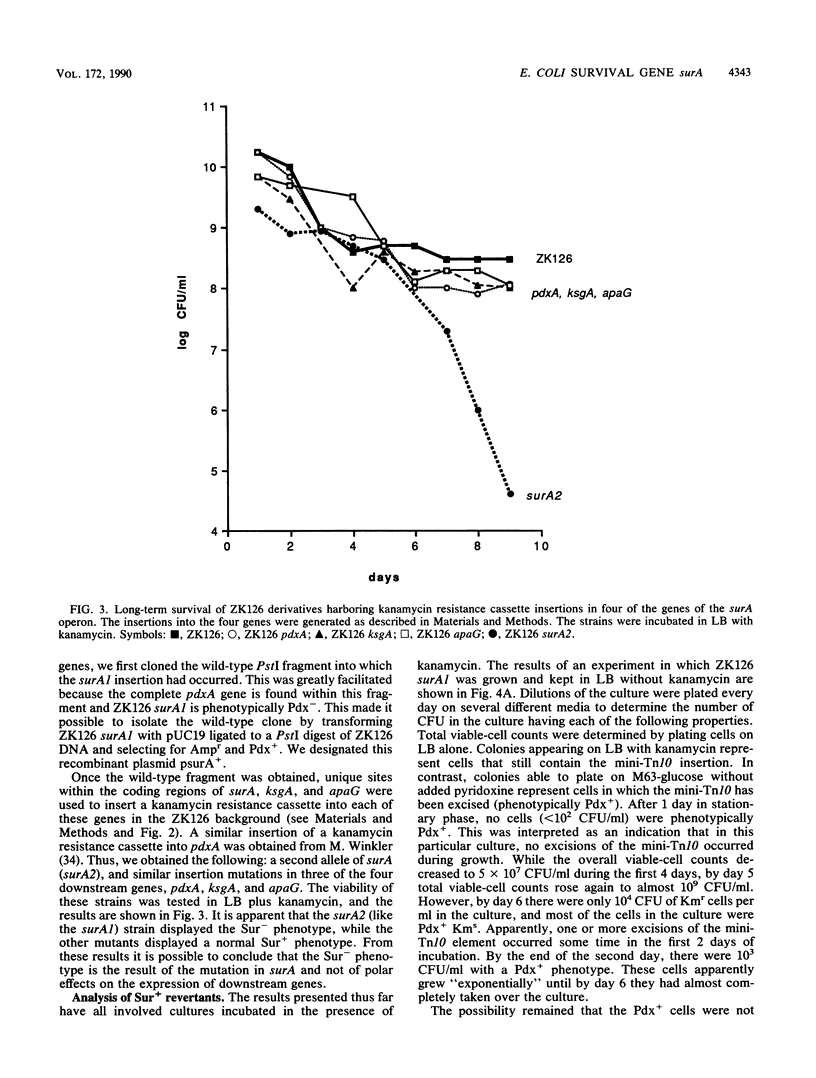
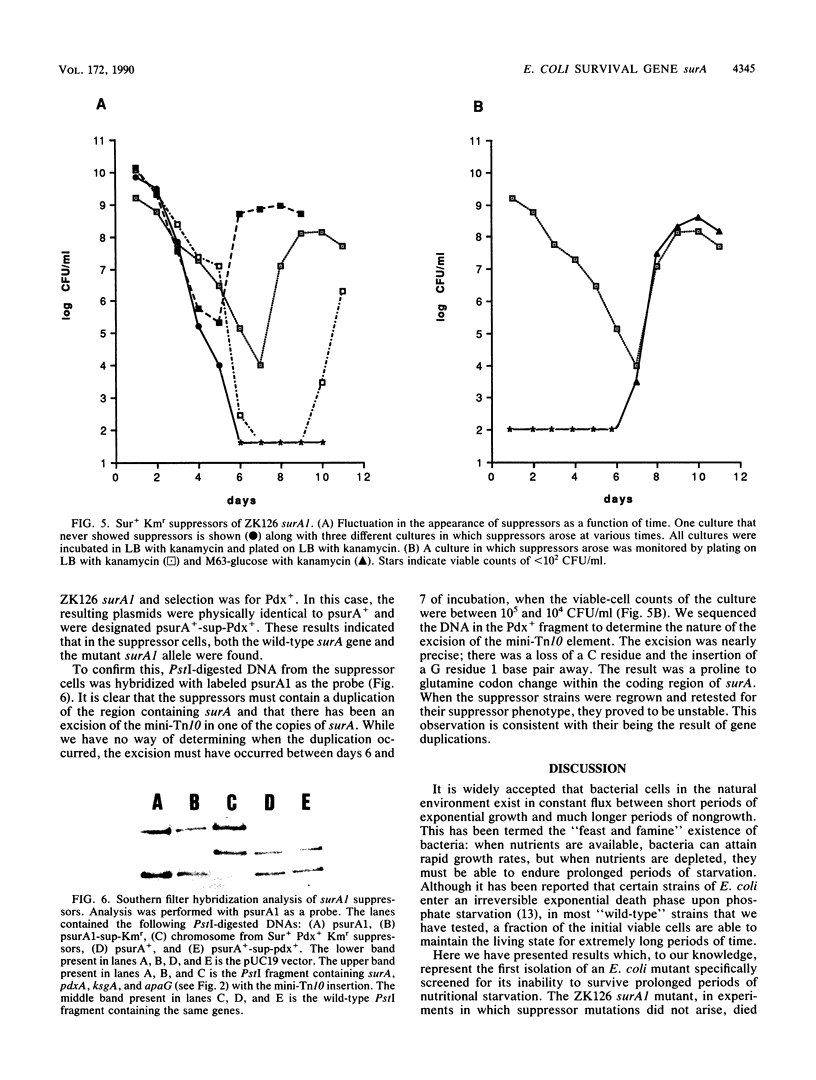
Mutations in genes not required for exponential growth but essential for survival in stationary phase were isolated in an effort to understand the ability of wild-type Escherichia coli cells to remain viable during prolonged periods of nutritional deprivation. The phenotype of these mutations is referred to as Sur- (survival) and the genes are designated sur. The detailed analysis of one of these mutations is presented here. The mutation (surA1) caused by insertion of a mini-Tn10 element defined a new gene located near 1 min on the E. coli chromosome. It was located directly upstream of pdxA and formed part of a complex operon. Evidence is presented supporting the interpretation that cells harboring the surA1 mutation die during stationary phase while similar insertion mutations in other genes of the operon do not lead to a Sur- phenotype. Strains harboring surA1 had a normal doubling time in both rich and minimal medium, but cultures lost viability after several days in stationary phase. Analysis of revertants and suppressors of surA1, which arose after prolonged incubation in stationary phase, indicates that DNA rearrangements (excisions and duplications) occurred in cultures of this strain even when the viable-cell counts were below 10(2) cells per ml. Cells containing suppressing mutations then grew in the same culture to 10(8) cells per ml, taking over the population. The implications of these observations to our understanding of stationary-phase mutagenesis are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldea M., Garrido T., Hernández-Chico C., Vicente M., Kushner S. R. Induction of a growth-phase-dependent promoter triggers transcription of bolA, an Escherichia coli morphogene. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3923–3931. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrésson O. S., Davies J. E. Genetic organization and restriction enzyme cleavage map of the ksgA-pdxA region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):211–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00268465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrésson O. S., Davies J. E. Isolation and characterization of lambda transducing phages for the E. coli genes ksgA and pdxA. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00268464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrésson O. S., Davies J. E. Some properties of the ribosomal RNA methyltransferase encoded by ksgA and the polarity of ksgA transcription. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00268466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlung T., Nielsen A., Hansen F. G. Isolation, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of appY, a regulatory gene for growth-phase-dependent gene expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1683–1691. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1683-1691.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchin-Roland S., Blanquet S., Schmitter J. M., Fayat G. The gene for Escherichia coli diadenosine tetraphosphatase is located immediately clockwise to folA and forms an operon with ksgA. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):515–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00338091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F. H., Fox M. S. Fractionation of transformable bacteria from ocompetent cultures of Bacillus subtilis on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.867-875.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J., Overbaugh J., Miller S. The origin of mutants. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):142–145. doi: 10.1038/335142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N., Han Z., Moreno F., Kolter R. An E. coli promoter induced by the cessation of growth. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Cahu M., Desjoyaux-Cherel B., Boquet P. L. The acid phosphatase with optimum pH of 2.5 of Escherichia coli. Physiological and Biochemical study. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6669–6676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Luger S. M., Tai P. C. Role of ribosome degradation in the death of starved Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.439-445.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D. Transcriptional bias: a non-Lamarckian mechanism for substrate-induced mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5005–5009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. J., Fraenkel D. G. alpha-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase mutant of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):415–419. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.415-419.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Guerra L., Moreno F., San Millán J. L. appR gene product activates transcription of microcin C7 plasmid genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2906–2908. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2906-2908.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr S. B., Arnosti D. N., Chamberlin M. J., Ames B. N. An apaH mutation causes AppppA to accumulate and affects motility and catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schultz J. E., Zychlinsky E., Bockman A., Matin A. Starvation proteins in Escherichia coli: kinetics of synthesis and role in starvation survival. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.486-493.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G. Adaptive evolution that requires multiple spontaneous mutations. I. Mutations involving an insertion sequence. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):887–897. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Chico C., San Millán J. L., Kolter R., Moreno F. Growth phase and ompR regulation of transcription of microcin B17 genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1058–1065. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1058-1065.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P. New versatile cloning and sequencing vectors based on bacteriophage M13. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korgaonkar K. S., Ranade S. S. Evaluation of acridine orange fluorescence test in viability studies on Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):185–190. doi: 10.1139/m66-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Switala J., Triggs-Raine B. L. Catalases HPI and HPII in Escherichia coli are induced independently. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):144–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90782-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Auger E. A., Blum P. H., Schultz J. E. Genetic basis of starvation survival in nondifferentiating bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:293–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittler J. E., Lenski R. E. New data on excisions of Mu from E. coli MCS2 cast doubt on directed mutation hypothesis. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):173–175. doi: 10.1038/344173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M. R., Loewen P. C. Nucleotide sequence of katF of Escherichia coli suggests KatF protein is a novel sigma transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9979–9991. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Rodriguez R. L., Preiss J. Biosynthesis of bacterial glycogen. Cloning of the glycogen biosynthetic enzyme structural genes of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6944–6952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN F. J., OKADA T., NAGATA T. Spontaneous mutation in spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Feb;30:193–199. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. N., Roberts M. F., Torriani A. Amount and chain length of polyphosphates in Escherichia coli depend on cell growth conditions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):242–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.242-247.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve C. A., Amy P. S., Matin A. Role of protein synthesis in the survival of carbon-starved Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1041–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1041-1046.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roa B. B., Connolly D. M., Winkler M. E. Overlap between pdxA and ksgA in the complex pdxA-ksgA-apaG-apaH operon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4767–4777. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4767-4777.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Observations on the formation of clones containing araB-lacZ cistron fusions. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):79–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00383501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Park Y. K., Tirgari S., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Identification and characterization of starvation-regulated genetic loci in Salmonella typhimurium by using Mu d-directed lacZ operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.345-351.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati E., Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Pleiotropic mutations in appR reduce pH 2.5 acid phosphatase expression and restore succinate utilisation in CRP-deficient strains of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00331647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Elledge S. J., Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. Site-directed insertion and deletion mutagenesis with cloned fragments in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1219–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1219-1221.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




