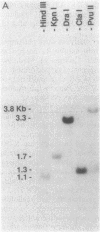
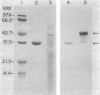
Abstract
The streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin (SPE) type B-encoding structural gene, speB, was subcloned from a 4.5-kilobase streptococcal DNA insert onto a 2.4-kilobase insert, which was then sequenced. Studies indicated that a 1,194-base-pair open reading frame encoded a 398-amino-acid protein. Removal of the putative signal peptide resulted in a mature protein with 371 residues (molecular weight, 40,314), which was subsequently proteolyzed to yield a 253-residue breakdown product (molecular weight, 27,588). This processing was confirmed by amino-terminal sequencing of both the 40,314-molecular-weight protein and the breakdown product. Monte Carlo analysis indicated that SPE B was relatively dissimilar to other members of the pyrogenic toxin family that also includes SPEs A and C, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, and the staphylococcal enterotoxins. Comparison with the published amino acid sequence of streptococcal proteinase precursor as well as DNA hybridization experiments indicated that SPE B is a variant of this protein even though the particular gene sequenced did not encode a proteolytically active molecule.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Erickson B. W. Optimal sequence alignment using affine gap costs. Bull Math Biol. 1986;48(5-6):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF02462326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsumian E. L., Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Nonspecific and specific immunological mitogenicity by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):681–688. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.681-688.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayles K. W., Iandolo J. J. Genetic and molecular analyses of the gene encoding staphylococcal enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4799–4806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4799-4806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Kornblum J. S., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequence of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15783–15786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Hauser A. R., Schlievert P. M. Cloning of the gene, speB, for streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type B in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1665–1667. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1665-1667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Schlievert P. M. Conservation of the biologically active portions of staphylococcal enterotoxins C1 and C2. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2249–2252. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2249-2252.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 gene and relatedness to other pyrogenic toxins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00329830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Hunsaker W. R. Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: a direct comparison with 5'-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Soltis M. T., Betley M. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type E staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2954–2960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2954-2960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. M., Barsumian E. L., Watson D. W. Further purification of group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin and characterization of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):767–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.767-775.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach D., Knöll H., Köhler W., Ozegowski J. H., Hríbalova V. Isolation and characterization of erythrogenic toxins. V. Communication: identity of erythrogenic toxin type B and streptococcal proteinase precursor. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshorn S. C., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequence of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2518–2520. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2518-2520.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Khan S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., ELLIOTT S. D. STREPTOCOCCAL PROTEINASE: THE ZYMOGEN TO ENZYME TRANSFROMATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1138–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., NEUMANN N. P., ELLIOTT S. D., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Chemical properties of streptococcal proteinase and its zymogen. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., STEIN W. H., MOORE S., ELLIOTT S. D. THE SEQUENCE OF AMINO ACID RESIDUES AROUND THE SULFHYDRYL GROUP AT THE ACTIVE SITE OF STREPTOCOCCAL PROTEINASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1143–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB J. H., WATSON D. W., CROMARTIE W. J. Further studies of group A streptococcal factors with lethal and cardiotoxic properties. J Infect Dis. 1955 Jan-Feb;96(1):14–18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shany S., Grushoff P. S., Bernheimer A. W. Physical separation of streptococcal nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase from streptolysin O. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):731–734. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.731-734.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Jones K. W. The use of heparin as a simple cost-effective means of controlling background in nucleic acid hybridization procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5627–5638. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O. Recovery of DNA from gels. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):371–380. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanier J. G., Cleary P. P. A DNA substitution in the group A streptococcal bacteriophage SP24. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):514–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai J. Y., Kortt A. A., Liu T. Y., Elliott S. D. Primary structure of streptococcal proteinase. III. Isolation of cyanogen bromide peptides: complete covalent structure of the polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1955–1959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled casein assay for proteolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;143(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90553-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. R., Ferretti J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.144-150.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]