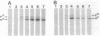Abstract
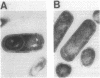
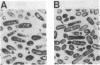
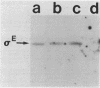
A potential regulatory link between the activation of a sporulation-specific sigma factor (sigma E) and forespore septum formation was investigated by treating Bacillus subtilis with inhibitors of protein or peptidoglycan synthesis and monitoring the consequences of these treatments on sigma E activation and septation. Western blot (immunoblot) and electron microscopic analyses revealed that both the formation of sigma E and septation were inhibited to a similar degree when either rifampin or chloramphenicol was added at different times before the second hour into sporulation but that penicillin preferentially blocked septation. We interpret these results as indicating that the syntheses of the gene products for both septation and sigma E activation occur at approximately the same time in development but that synthesis of an intact septum is unlikely to be a prerequisite for the formation of sigma E. We observed that penicillin could not only block septation but, depending on the time of its addition, could also inhibit both the activation of sigma E and the synthesis of its precursor. The basis of this effect is unknown, but it is not due to an overall disruption of protein synthesis. The incorporation of [35S] methionine by the sporulating cultures was unaffected by penicillin treatment. A time course study of the effects of rifampin and chloramphenicol treatments on sigma E levels revealed that both the synthesis of sigma E and its disappearance from sporulating cultures is inhibited by these antibiotics. This suggests that ongoing macromolecular synthesis is required for the turnover of sigma E.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dancer B. N. Requirement for peptidoglycan synthesis during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):786–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.786-797.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes I. W., Kay D., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Establishment of a time scale for the morphological events. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 May;56(2):171–179. doi: 10.1099/00221287-56-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Weir J., Nair G., Carter L., 3rd, Moran C., Jr, Smith I. Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for sigma 30 (sigma H). J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1054-1062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Piggot P. J. Nucleotide sequence of sporulation locus spoIIA in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2147–2153. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Lang N., Losick R. A sporulation-induced sigma-like regulatory protein from B. subtilis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Haldenwang W. G. Influence of spo mutations on sigma E synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5226–5228. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5226-5228.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Peters H. K., 3rd, Haldenwang W. G. Phenotypes of Bacillus subtilis mutants altered in the precursor-specific region of sigma E. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4178–4186. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4178-4186.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Weaver E. A., Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr, Haldenwang W. G. The Bacillus subtilis spoIIG operon encodes both sigma E and a gene necessary for sigma E activation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):507–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.507-511.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmazyn-Campelli C., Bonamy C., Savelli B., Stragier P. Tandem genes encoding sigma-factors for consecutive steps of development in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):150–157. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Kirchman P. A., Moran C. P., Jr Gene encoding sigma E is transcribed from a sigma A-like promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3058–3064. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3058-3064.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Organization and regulation of an operon that encodes a sporulation-essential sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3329–3339. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3329-3339.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBell T. L., Trempy J. E., Haldenwang W. G. Sporulation-specific sigma factor sigma 29 of Bacillus subtilis is synthesized from a precursor protein, P31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1784–1788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J. Penicillin: reversible inhibition of forespore septum development in Bacillus megaterium cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):815–820. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda E. S., Anaguchi H., Yamada K., Kobayashi Y. Two developmental genes encoding sigma factor homologs are arranged in tandem in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7637–7641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell T. D., McCurdy W., Reed K. E. Talk-back regulation: a regulatory response to the inhibitions of cell surface growth. Microbios. 1989;57(232-233):187–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong S., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional control of the Bacillus subtilis spoIID gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):771–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.771-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bonamy C., Karmazyn-Campelli C. Processing of a sporulation sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis: how morphological structure could control gene expression. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P. Comment on 'Duplicated sporulation genes in bacteria' by J. Errington, P. Fort and J. Mandelstam. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Kunkel B., Kroos L., Losick R. Chromosomal rearrangement generating a composite gene for a developmental transcription factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):507–512. doi: 10.1126/science.2536191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Stragier P., Setlow P. Identification of a new sigma-factor involved in compartmentalized gene expression during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):141–149. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma factor sigma 29 is the product of the sporulation-essential gene spoIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4189–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Morrison-Plummer J., Haldenwang W. G. Synthesis of sigma 29, an RNA polymerase specificity determinant, is a developmentally regulated event in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):340–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.340-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin M. D. Structure and function in a Bacillus subtilis sporulation-specific sigma factor: molecular nature of mutations in spoIIAC. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):475–481. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]